Fundamentals of Terahertz Devices and Applications
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Fundamentals of Terahertz Devices and Applications» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Fundamentals of Terahertz Devices and Applications
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:4 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 80
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Fundamentals of Terahertz Devices and Applications: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Fundamentals of Terahertz Devices and Applications»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
Fundamentals of Terahertz Devices and Applications
Fundamentals of Terahertz Devices and Applications — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «Fundamentals of Terahertz Devices and Applications», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
3 Chapter 4Figure 4.1 THz generation by photomixing.Figure 4.2 Photomixing in a photoconductor.Figure 4.3 Electrical model of a photoconductor coupled to a load admittance...Figure 4.4 (a) Electrical circuit at ω= ω band (b) ω= 0 .Figure 4.5 Photomixing experiment AC/DC decoupling using a Bias‐T.Figure 4.6 Small signal Equivalent circuit at ω b.Figure 4.7 Schematic band diagram of a p – i – n photodiode.Figure 4.8 Schematic band diagram of a UTC photodiode.Figure 4.9 Electric model of a UTC photodiode.Figure 4.10 Equivalent circuit of an UTC photodiode at ω ( G L= 1/ R L) .Figure 4.11 Heterodyne mixing in a photoconductor illuminated by an optical ...Figure 4.12 SEM picture of an ultrafast photoconductor based on interdigitat...Figure 4.13 LT‐GaAs planar photoconductor.Figure 4.14 Refracting facet UTC photodiode.Figure 4.15 TEM horn UTC photodiode.Figure 4.16 Waveguide UTC photodiode coupled to a planar antenna.Figure 4.17 LT GaAs optical cavity photoconductor.Figure 4.18 Calculated optical quantum efficiency versus active layer thickn...Figure 4.19 Experimental set‐up aimed at photoresponse measurement.Figure 4.20 Theoretical (solid line) and experimental (in squares) photoresp...Figure 4.21 Optical cavity LT‐GaAs photoconductor.Figure 4.22 Experimental set‐up. ECLD, external cavity laser diode; SOA, sem...Figure 4.23 Photocurrent as a function of optical power V b= 3 V.Figure 4.24 Output power at f B= 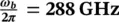 and V b= 3 V.Figure 4.25 Top view of a 6‐μm‐diameter photoconductor coupled to the impeda...Figure 4.26 SEM micrograph of an optical cavity LT‐GaAs photoconductor linke...Figure 4.27 Down conversion experimental‐set‐up.Figure 4.28 Conversion loss and (1/G0) 2as a function of the optical power (Figure 4.29 Design of the nanostructured contact. (a) Geometry of the metall...Figure 4.30 Fabrication of the PD. (a, b) Schematic cross section of the fab...Figure 4.31 (a)SEM image of UTC‐PD integrated with CPW, and (b) SEM image of...Figure 4.32 Experimental comparison of photoresponse of UTC‐PD devices and R...Figure 4.33 RF power generated at 300 GHz by various B‐type photodiodes for ...Figure 4.34 SEM picture of an equiangular spiral antenna.Figure 4.35 Geometry of the TEM‐HA (a). Geometry of the monopole configurati...Figure 4.36 SEM picture of a THz Horn antenna.Figure 4.37 E‐plane radiation patterns of the TEM‐HA: comparison between exp...Figure 4.38 Different probes technologies: GGB probes (Picoprobes for wafer‐...Figure 4.39 (a) Experimental setup for photomixing at wafer‐level. (b) Photo...Figure 4.40 Frequency response example of a UTC‐PD [19].Figure 4.41 Frequency response example of and device linearity.Figure 4.42 Example of free space UTC‐PD measurement using a Schottky quasi‐...
and V b= 3 V.Figure 4.25 Top view of a 6‐μm‐diameter photoconductor coupled to the impeda...Figure 4.26 SEM micrograph of an optical cavity LT‐GaAs photoconductor linke...Figure 4.27 Down conversion experimental‐set‐up.Figure 4.28 Conversion loss and (1/G0) 2as a function of the optical power (Figure 4.29 Design of the nanostructured contact. (a) Geometry of the metall...Figure 4.30 Fabrication of the PD. (a, b) Schematic cross section of the fab...Figure 4.31 (a)SEM image of UTC‐PD integrated with CPW, and (b) SEM image of...Figure 4.32 Experimental comparison of photoresponse of UTC‐PD devices and R...Figure 4.33 RF power generated at 300 GHz by various B‐type photodiodes for ...Figure 4.34 SEM picture of an equiangular spiral antenna.Figure 4.35 Geometry of the TEM‐HA (a). Geometry of the monopole configurati...Figure 4.36 SEM picture of a THz Horn antenna.Figure 4.37 E‐plane radiation patterns of the TEM‐HA: comparison between exp...Figure 4.38 Different probes technologies: GGB probes (Picoprobes for wafer‐...Figure 4.39 (a) Experimental setup for photomixing at wafer‐level. (b) Photo...Figure 4.40 Frequency response example of a UTC‐PD [19].Figure 4.41 Frequency response example of and device linearity.Figure 4.42 Example of free space UTC‐PD measurement using a Schottky quasi‐...
4 Chapter 5Figure 5.1 Band to band absorption of a photon in a semiconductor, creating ...Figure 5.2 (a) Schematic of a PCA in operation. (b) Equivalent circuit model...Figure 5.3 Comparison between a short‐carrier‐lifetime and a long‐carrier‐li...Figure 5.4 Equivalent circuit model of a PCA‐based THz detector.Figure 5.5 Surface plasmon dispersion relation, showing that surface plasmon...Figure 5.6 Illustrations for (a) conventional and (b) plasmonic PCAs based o...Figure 5.7 Finite element simulation of the conventional photoconductor and ...Figure 5.8 (a) SEM images of the conventional (left) and plasmonic (right) P...Figure 5.9 (a) THz waveform measured by a conventional (red) and plasmonic (...Figure 5.10 PCAs with plasmonic light concentrators. (a) Device illustration...Figure 5.11 Pulsed THz generation and detection using PCAs with plasmonic co...Figure 5.12 CW THz generation using PCAs with plasmonic contact electrodes. ...Figure 5.13 (a) Device structure and SEM images of a large‐area plasmonic ph...Figure 5.14 Device structure and SEM images of a large‐area plasmonic photoc...Figure 5.15 Plasmonic PCAs with optical nanocavities. (a) Device schematic o...
5 Chapter 6Figure 6.1 (a) Conduction‐band lineup of a generic semiconductor QW and squa...Figure 6.2 Conduction‐band diagram of a representative bound‐to‐bound QC gai...Figure 6.3 Conduction‐band diagram of a representative superlattice QC gain ...Figure 6.4 Conduction‐band diagram of a representative resonant‐phonon THz Q...Figure 6.5 Real part of the dielectric constant ε and mode intensity pr...Figure 6.6 Metal–metal corrugated ridge DFB THz QC laser.Figure 6.7 Voltage‐tunable cw emission spectra measured at 15 K with the low...Figure 6.8 Temperature‐dependent LIV characteristics measured with the highe...Figure 6.9 (a) Schematic illustration of ISB relaxation between two QW subba...Figure 6.10 Dispersion of light in a polar crystal in the spectral vicinity ...Figure 6.11 Conduction‐band diagram of a resonant‐phonon THz QC gain medium ...Figure 6.12 (a) Photocurrent spectrum of a double‐step III‐nitride ISB photo...Figure 6.13 (a) Valence‐band lineup of the SiGe/Si QC active material of Dem...Figure 6.14 (a) Fabrication process developed in [81, 82] for the formation ...Figure 6.15 Conduction‐band lineup and squared envelope functions of the rel...
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «Fundamentals of Terahertz Devices and Applications»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «Fundamentals of Terahertz Devices and Applications» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «Fundamentals of Terahertz Devices and Applications» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.












