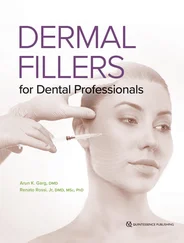
Measurements are normally made using a microscope since the indentations are often too small to be seen with the naked eye. The hardness is a function of the diameter of the circle for Brinell hardness and the distance across the diagonal axes for Vickers and Knoop hardness. Allowance is naturally made for the magnitude of the applied loads. In the case of Rockwell hardness, a direct measurement of the depth of penetration of a conical diamond indenter is made. The Rockwell hardness test method consists of indenting the test material with a diamond cone or hardened steel ball indenter. This method is useful to evaluate surface hardness of plastic materials used in dentistry [4] (as shown in Figure 1.16).
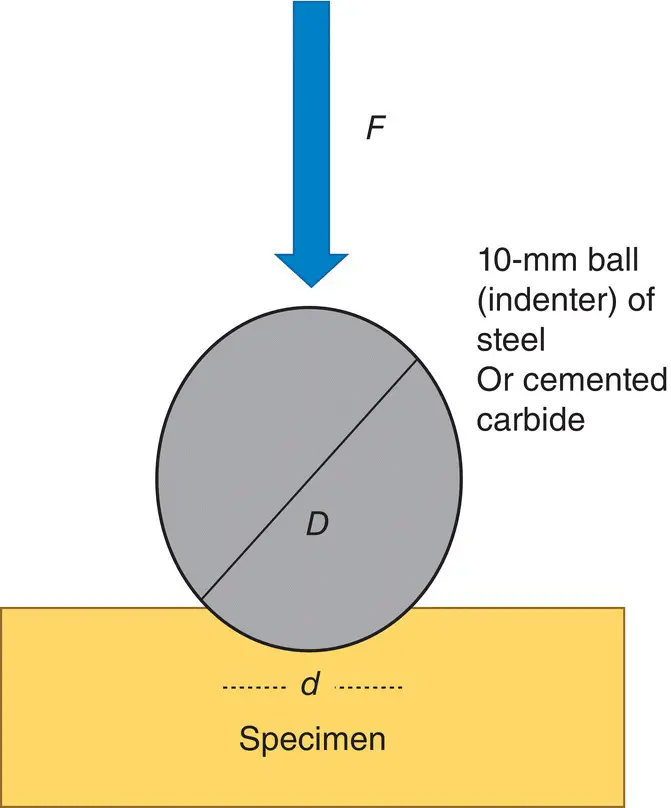
Figure 1.15 Brinell hardness testing.
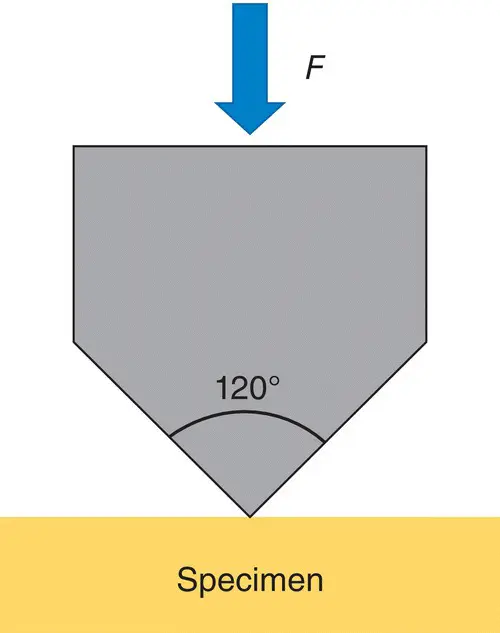
Figure 1.16 Rockwell hardness testing.
Source: Vieira [4]. Licensed under CC BY 4.0.
All materials require different hardness testing. The specificity of a hardness tester is dependent on the following factors:
1 Material of the indenter
2 Shape and size of the indenter and the sample to be tested.
3 Loading parameter (amount of force it can apply)
Hardness tests are extremely used and have important applicability on Dentistry. Hardness test can evaluate the degree of mineralization of a dental substrate for example. A specific force applied for a specific time and distance provides important data in studies assessing the ability of enamel and dentin remineralization after different treatments as happens in unbalanced situations of des‐remineralization. Another important use of this test is to evaluate the degree of polymerization of resin composite and resin cements.
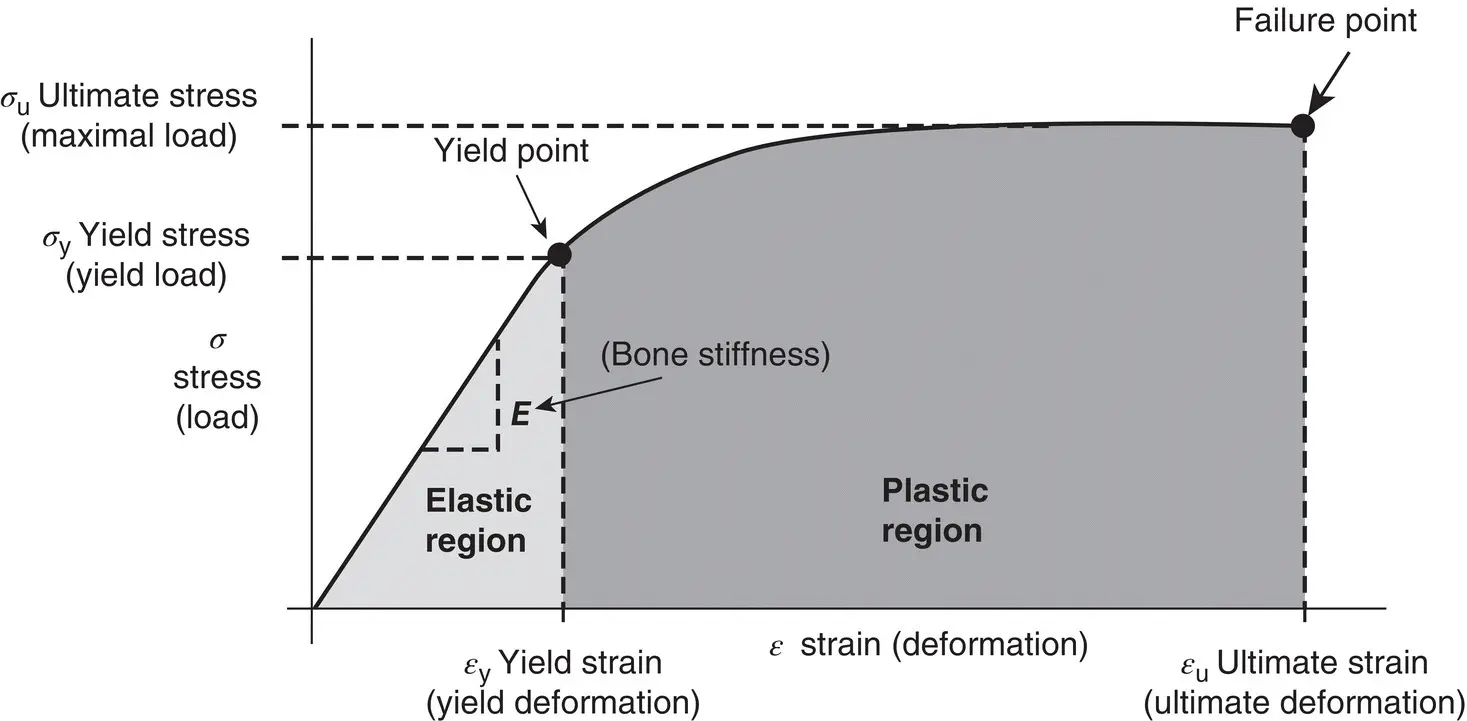
Figure 1.17 Stress–strain curve for assessment of Young's modulus.
The modulus of elasticity, or measure of a material's stiffness, is also important in relation to anticipated longevity of a restoration. An elastic material (one with a low elastic modulus) will deform when a load is placed on it but will return to its original shape once the load falls below the elastic limit of the material. As a general rule, restorative materials need to be very stiff (high elastic modulus), so that under load the elastic deformation will be very small. An exception to this is in the Class V situation. Micro‐filled composite materials have a lower modulus of elasticity than hybrid composite materials; this may be why micro‐filled materials show higher retention rates in Class V cavities, given that they deform more readily as the tooth deforms at the cervical area under occlusal loading.
Models involving the use of springs and dashpots can be used to explain the elastic and viscoelastic behaviour of materials. When a spring, which represents an elastic material, is fixed at one end and a load applied at the other, it becomes instantaneously extended. When the load is removed, it immediately recovers its original length. This behaviour is analogous to that of a perfectly elastic material. The two things that characterize the material are firstly the perfect recovery after removal of the force and secondly the lack of any time dependency of either the deformation under load or the recovery after removal of the applied force. The extent of deformation under load is characterized by the modulus of elasticity of the material (analogous to the spring constant of the spring) (as shown in Figure 1.17).
Fracture toughness determines the resistance of a material to the propagation of a crack. This test has been considered to be efficient given that other parameters can be derived from it. It should be kept in mind, however, that fracture toughness measures the failure of a material after one continuous period of loading, whereas fatigue strength experiments measure crack propagation after repeated applications of a small cyclic load. A UTM (Instron) is used to apply a central load to the specimen in a three‐point bending mode at a cross‐head speed of 0.125 mm/minute. Fracture of the specimen is identified by a sudden drop in load during the test. Visual examination of the fractured parts is performed to ensure that the fracture plane is through the notch, and that it is perpendicular to the vertical and horizontal planes through the center of the specimens.
The fracture toughness was then calculated by:
(1.2) 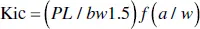
The variables are defined as: Kic is the stress intensity factor, P is the load at fracture, L is the span, distance between the supports, w is the width of the specimen, b is the thickness of the specimen, and a is the crack length.
Cross‐head speed is also known as deformation rate. It is measured in mm/min. Every material has different average cross‐head speeds recommended by ISO 4049. For e.g. resin‐based composites have a speed of (0.75 ± 0.25 mm/min).
With nanoscience gaining popularity, nanoindenters have advantages over traditional mechanical testing by providing both elastic modulus and hardness data of the tested samples. Nanoindentation is conducted with a calibrated Berkovich diamond indenter tip. A Berkovich tip is a three‐sided pyramidal indenter.
During the nanoindentation process, a calibrated indenter tip approaches the surface of the sample. The force–displacement data is used to determine the point of contact. After the sample is contacted, the force is linearly increased and the tip indents into the surface of the sample. A short dwell time occurs at the maximum force and then the sample is unloaded. At the initial point of unloading, the stiffness is measured.
Longevity of a restoration is predicted to some extent by its adhesive ability, and this in turn can be measured by bond strength testing. An ideal bond strength test should be accurate, clinically reliable and less technique‐sensitive. It should involve the use of relatively unsophisticated and inexpensive test protocols. Static tests are categorized into macro‐tests where the bond area is >3 mm 2and micro‐tests with <3 mm 2bond area [15].
1.10.1 Macro‐Test Methods
The macro‐bond strength can be measured in shear, tensile or using a push‐out protocol.
1.10.1.1 Macro‐Shear (SBS) Test
In a shear bond test, two materials are connected via an adhesive agent and loaded in shear until fracture occurs.
1.10.1.2 Macro‐Tensile (TBS) Test
In a tensile bond test, load will be exerted on either sides of the test specimen. The specimen can be held by active or passive gripping methods. Active gripping method involves mechanical fastening of specimen to gripping device, such as glue or clamps, whereas in passive gripping method, specimen is placed in a testing device without the aid of glue or mechanical gripping. It can be used to measure, for instance, the bond strength of cements to hard materials such as ceramics and metal alloys [16].
Читать дальше