Figure 1.5 Inception module.
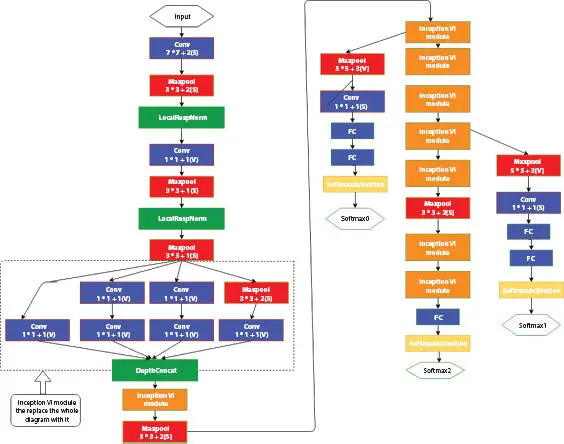
Figure 1.6 Architecture of GoogleNet.
First layer: Here, input image is 224 × 224 × 3, and the output feature is 112 × 112 × 64. Followed by the convolutional layer uses a kernel of size 7 × 7 × 3 and with step 2. Then, followed by ReLU and max pooling by 3 × 3 kernel with step 2, now the output feature map size is 56 × 56 × 64. Then, do the local response normalization.
Second layer: It is a simplified inception model. Here, 1 × 1 convolution using 64 filters generate feature maps from the previous layer’s output before performing the 3 × 3 (with step 2) convolutions using 64 filters. Then, perform ReLU and local response normalization. Finally, perform a 3 × 3 max pooling with stride 2 to obtain 192 numbers of output of 28 feature maps.
Third layer: Is a complete inception module. The previous layer’s output is 28 × 28 with 192 filters and there will be four branches originating from the previous layer. The first branch uses 1 × 1 convolution kernels with 64 filters and ReLU, generates 64, 28 × 28 feature map; the second branch uses 1 × 1 convolution with 96 kernels (ReLU) before 3 × 3 convolution operation (with 128 filters), generating 128 × 28 × 28 feature map; the third branch use 1 × 1 convolutions with 16 filters (using ReLU) of 32 × 5 × 5 convolution operation, generating 32 × 28 × 28 feature map; the fourth branch contains 3 × 3 max pooling layer and a 1 × 1 convolution operation, generating 32 × 28 × 28 feature maps. And it is followed by concatenation of the generated feature maps that provide an output of 28 × 28 feature map with 258 filters.
The fourth layer is inception module. Input image is 28 × 28 × 256. The branches include 1 × 1 × 128 and ReLU, 1 × 1 × 128 as reduce before 3 × 3 × 192 convolutional operation, 1 × 1 × 32 as reduce before 5 × 5 × 96 convolutional operation, 3 × 3 max pooling with padding 1 before 1 × 1 × 64. The output is 28 × 28 × 128, 28 × 28 × 192, 28 × 28 × 96, and 28 × 28 × 64, respectively for each branch. The final output is 28 × 28 × 480. Table 1.6shows the parameters of GoogleNet.
Usually, the input feature map will be fed through a series of convolutional layer, a non-linear activation function (ReLU) and a pooling layer to provide the output for the next layer. The training is done by the back-propagation algorithm. The accuracy of the network can be improved by increasing depth. Once the network gets converged, its accuracy saturates. Further, if we add more layers, then the performance gets degraded rapidly, which, in turn, results in higher training error. To solve the problem of the vanishing/exploding gradient, ResNet with a residual learning framework [6] was proposed by allowing new layers to fit a residual mapping. When a model is converged than to fit the mapping, it is easy to push the residual to zero. The principle of ResNet is residual learning and identity mapping and skip connections. The idea behind the residual learning is that it feeds the input image to the next convolutional layer and adds them together and performs non-linear activation (ReLU) and pooling.
Table 1.6 Various parameters of GoogleNet.
| Layer name |
Input size |
Filter size |
Window size |
# Filters |
Stride |
Depth |
# 1 × 1 |
# 3 × 3 reduce |
# 3 × 3 |
# 5 × 5 reduce |
# 5 × 5 |
Pool proj |
Padding |
Output size |
Params |
Ops |
| Convolution |
224 × 224 |
7 × 7 |
- |
64 |
2 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
112 × 112 × 64 |
2.7M |
34M |
| Max pool |
112 × 112 |
- |
3 × 3 |
- |
2 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
56 × 56 × 64 |
|
|
| Convolution |
56 × 56 |
3 × 3 |
- |
192 |
1 |
2 |
|
64 |
192 |
|
|
|
1 |
56 × 56 × 192 |
112K |
360M |
| Max pool |
56 × 56 |
- |
3 × 3 |
192 |
2 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
28 × 28 × 192 |
|
|
| Inception (3a) |
28 × 28 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
2 |
64 |
96 |
128 |
16 |
32 |
32 |
- |
28 × 28 × 256 |
159K |
128M |
| Inception (3b) |
28 × 28 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
2 |
128 |
128 |
192 |
32 |
96 |
64 |
- |
28 × 28 × 480 |
380K |
304M |
| Max pool |
28 × 28 |
- |
3 × 3 |
480 |
2 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
14 × 14 × 480 |
|
|
| Inception (4a) |
14 × 14 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
2 |
192 |
96 |
208 |
16 |
48 |
64 |
- |
14 × 14 × 512 |
364K |
73M |
| Inception (4b) |
14 × 14 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
2 |
160 |
112 |
224 |
24 |
64 |
64 |
- |
14 × 14 × 512 |
437K |
88M |
| Inception (4c) |
14 × 14 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
2 |
128 |
128 |
256 |
24 |
64 |
64 |
- |
14 × 14 × 512 |
463K |
100M |
| Inception (4d) |
14 × 14 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
2 |
112 |
144 |
288 |
32 |
64 |
64 |
- |
14 × 14 × 528 |
580K |
119M |
| Inception (4e) |
14 × 14 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
2 |
256 |
160 |
320 |
32 |
128 |
128 |
- |
14 × 14 × 832 |
840K |
170M |
| Max pool |
14 × 14 |
- |
3 × 3 |
- |
2 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
7 × 7 × 832 |
|
|
| Inception (5a) |
7 × 7 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
2 |
256 |
160 |
320 |
32 |
128 |
128 |
- |
7 × 7 × 832 |
1,072K |
54M |
| Inception (5b) |
7 × 7 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
2 |
384 |
192 |
384 |
48 |
128 |
128 |
- |
7 × 7 × 1,024 |
1,388K |
71M |
| Avg pool |
7 × 7 |
- |
7 × 7 |
- |
- |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
1 × 1 × 1,024 |
|
|
| Dropout (40 %) |
- |
- |
- |
1,024 |
- |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
1 × 1 × 1,024 |
|
|
| Linear |
- |
- |
- |
1,000 |
- |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
1 × 1 × 1,000 |
1,000K |
1M |
| Softmax |
- |
- |
- |
1,000 |
- |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
1 × 1 × 1,000 |
|
|
The architecture is a shortcut connection of VGGNet (consists of 3 × 3 filters) that is inserted to form a residual network as shown in figure. Figure 1.7(b)shows 34-layer network converted into the residual network and has lesser training error as compared to the 18-layer residual network. As in GoogLeNet, it utilizes a series of a global average pooling layer and the classification layer. ResNets were capable of learning a network with a maximum depth of 152. Compared to the GoogLeNet and VGGNet, accuracy is better and computationally efficient than VGGNet. ResNet-152 achieves 95.51 top-5 accuracies. Figure 1.7(a)shows a residual block, Figure 1.7(b)shows the architecture of ResNet and Table 1.7shows the parameters of ResNet.
Читать дальше













