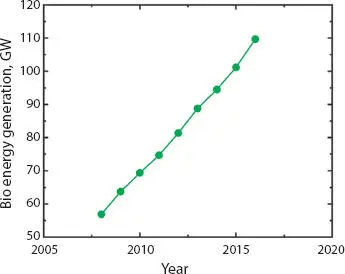
Figure 1.10 Cumulative bioenergy generation.
Initially, direct combustion method was employed with wood as a fuel to produce energy. In the recent times, chemical treatments such as pyrolysis, fermentation, and anaerobic processes are implemented to convert these sources into a usable form such as ethanol. During pyrolysis treatment, coal is obtained as a product that strengthens the matter by burning it in the absence of oxygen.
The sources of biomass energy generation include the following:
1 Wood and its processing waste: Heat energy is generated from the combustion of wood waste.
2 Agricultural waste: It is burned as a fuel and it can be converted into liquid bio-fuels.
3 Food and garbage waste: It is converted to bio-gas by landfill method or burned to generate electricity in power plants.
4 Animal manure and sewage waste: it is converted to bio-gas.
1.1.4.1 Energy Production From Biomass
Solid biomass, such as wood and garbage, can be burned directly to produce heat. Biomass can also be converted into a gas called biogas or into liquid biofuels such as ethanol and biodiesel. These fuels can then be burned for energy production.
Biogas is formed when paper, food scraps, and yard waste are decomposed in landfills; it can also be produced by processing sewage and animal manure in special vessels called digesters. Ethanol is extracted from crops such as corn and sugar-cane by fermentation process. Biodiesel is produced from vegetable oils and animal fats and can be used in vehicles and as heating oil.
The current availability of biomass in India is estimated at about 500 million metric tonnes per year [10]. Studies from the Ministry has estimated surplus biomass availability of about 120–150 million metric tonnes per annum covering agricultural and forestry residues corresponding to a potential of about 18,000 MW. Apart from this, it is predicted that about 7,000-MW additional power could be generated through co-generation process.
1.1.5 Hydro-Electric Energy
As water is a never depleted source and the pressure of water is used to generate energy, hydro-electric power plants gained its significance in renewable energy industry. The energy of flowing water is converted into mechanical energy using a turbine and the coupled generator produced electricity from the mechanical energy.
Figure 1.11shows hydro-electric power plant. The generator generates electricity by converting the input mechanical energy produced from the energy of water flow. Whenever a magnet moves past a conductor, it causes electricity and the flow of current exists. In a large generator, the electromagnets are made by circulating direct current through wire loops which is wound on steel laminations. These are called as poles, which are held on the outer surface of the rotor. The rotor rotates at a fixed speed as it is connected to the turbine shaft. As the rotor rotates, it cuts the flux produced and induces an emf, and thus, a potential is developed across the generator output.
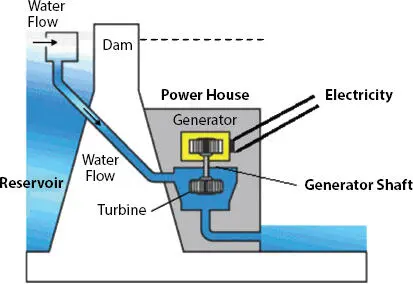
Figure 1.11 Typical hydro-electric power plant.
The reservoir system acts as a storage pump and can be used whenever required to generate electricity based on the demand. The construction of it is also very simple and this is one of the advantageous features of hydro-electric power generation [11].
India is blessed with immense amount of hydro-electric potential and ranks fifth in terms of exploitable hydro-potential on global scenario. As per assessment made by CEA, India is endowed with economically exploitable hydro-power potential to the tune of 148,700 MW of installed capacity.
In 1998, Government of India announced “Policy on Hydro Power Development” under which impetus is given to development of hydropower in the country. This was a welcome step toward effective utilization of our water resources in the direction of hydropower development. During October 2001, Central Electricity Authority (CEA) came out with a ranking study which prioritized and ranked the future executable projects. As per the study, 399 hydro schemes with an aggregate installed capacity of 106,910 MW were ranked in A, B, and C categories depending upon their inter se attractiveness. During May 2003, Government of India launched 50,000-MW hydro initiative in which preparation of Pre-Feasibility Reports of 162 Projects totaling to 50,000 MW was taken up by CEA through various agencies. The PFRs for all these projects have already been prepared and projects with low tariff (first year tariff less than Rs.2.50/kWh) have been identified for preparation of DPR.
As India is a tropical country, heat energy is abundant on our earth’s crust. The energy obtained from the heat of the inner surface of the earth is geothermal energy. It is the unused heat energy stored under the earth’s surface. It is carried to the earth’s surface by steam and water. It can be used for heating and cooling purpose. The temperature gradient on the earth’s surface with respect to the inner area is only used to generate electricity [12].
There are three types of geothermal power plants: dry steam, flash steam, and binary cycle.
1 (i) Dry Steam: Dry steam power plants draw from underground resources of steam. The steam is piped directly from underground wells to the power plant where it is directed into a turbine/generator unit.
2 (ii) Flash Steam: Flash steam power plants are the most common and use geothermal reservoirs of water with temperatures greater than 360°F (182°C). This very hot water flows up through wells in the ground under its own pressure. As it flows upward, the pressure decreases and some of the hot water boils into steam. The steam is then separated from the water and used to power a turbine/generator. Any leftover water and condensed steam are injected back into the reservoir, making this a sustainable resource.
3 (iii) Binary Steam: Binary cycle power plants operate on water at lower temperatures of about 225°F–360°F (107°C–182°C). Binary cycle plants use the heat from the hot water to boil a working fluid, usually an organic compound with a low boiling point. The working fluid is vaporized in a heat exchanger and used to turn a turbine. The water is then injected back into the ground to be reheated. The water and the working fluid are kept separated during the whole process, so there are little or no air emissions.Currently, two types of geothermal resources can be used in binary cycle power plants to generate electricity: enhanced geothermal systems (EGSs) and low-temperature or co-produced resources [13].a) Enhanced Geothermal Systems:EGS provide geothermal power by tapping into the Earth’s deep geothermal resources that are otherwise not economical due to lack of water, location, or rock typeb) Low-Temperature and Co-Produced Resources:Low-temperature and co-produced geothermal resources are typically found at temperatures of 300°F (150°C) or less. Some low-temperature resources can be harnessed to generate electricity using binary cycle technology. Co-produced hot water is a by-product of oil and gas wells in the United States. This hot water is being examined for its potential to produce electricity, helping to lower greenhouse gas emissions and extend the life of oil and gas fields.
Читать дальше














