i. Active Solar Techniques
A. Solar Photovoltaic System
It works with the phenomenon of the PV effect, which is a combination of the physical and chemical process that generates voltage and current when light falls on a semiconducting device. In a semiconductor, conduction takes place when the electrons move from valence band to conduction band. There is some energy required for this operation. In a solar cell, the energy is produced from photons that are emitted from the sun. These photons help in moving the electrons from valence band to conduction band, thereby overcoming the gap between the bands. A photon incident on the surface could be reflected or transmitted. If it is reflected, then the electron cannot be dislodged. So, the photon must be absorbed to move the electrons from the valence band to the conduction band. Thus, the electron movement across the metallic junction takes place, creating a negative charge on one side with respect to the other. It is similar to a battery with a negative terminal on one side and positive on the other side. The voltage and current are generated as long as light radiation is incident on the material. This effect only exists in the solar cells used in solar panels.
A solar panel is constructed by arranging PV cells or solar cells in series and parallel. A solar cell is a typical PN junction layer sandwiched as shown in Figure 1.2. Sunlight consists of photons or radiant solar energy. When the photons are incident on a PV cell, some get reflected and some get absorbed [3]. The absorbed photons aids in dislodging the electrons from the atoms of the solar cell material. These electrons move to the front surface of the solar cell and create an imbalance with respect to the back surface due to more flow of negative charge on one side. This imbalance results in a developed potential which creates electricity and a flow of current through an external load as shown in Figure 1.2. In general, a solar panel may have 60 cells connected together, yet, some solar panels are having even 72 cells also.
Monocrystalline and polycrystalline are the two major types of the solar cell. A monocrystalline solar cell is made from a single crystal of silicon, whereas polycrystalline cells are made by melting together many shards of silicon crystals. Monocrystalline solar cells are efficient when compared to polycrystalline type. It is due to the usage of monolithic crystal of silicon which aids in the easy flow of electrons that constitute the electric current. The electricity flow in polycrystalline silicon is very difficult due to the many layers of silicon structure. The process of making solar panel using polycrystalline is very simple when compared to monocrystalline.
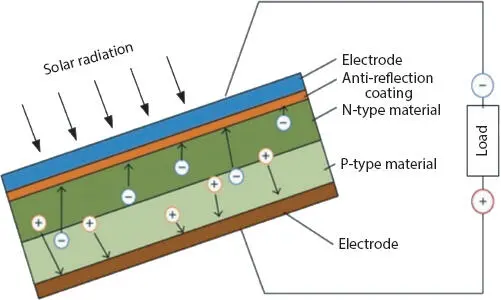
Figure 1.2 Structure of a solar cell.
B. Concentrated Solar Power The main objective of CSP is to focus the entire solar beam into a specific area. The heat energy thus produced in that area is converted into electricity. Other techniques developed based on the concept are parabolic trough system, dish system, and linear Fresnel collector. The concentrated solar beam produces heat energy which is used to drive the steam turbine and generate electricity.
Figure 1.3shows the diagram of a CSP system. It uses lenses or mirrors to concentrate the major beam of light to concentrate on an area that is a receiver here. The light energy is converted into heat energy and it drives the steam turbine coupled with a generator and generates electricity. The following are the types of CPS system.
B1.1 Parabolic Trough Collector
Figure 1.4shows the parabolic trough collector system which consists of a parabolic reflector that focuses the light onto a receiver aligned on the focal line of a reflector. The receiver is a tube which is filled with a working fluid and located above the reflector mirror arrangement. The working fluid is heated with the obtained light energy from the sun through the concentrator system [4].
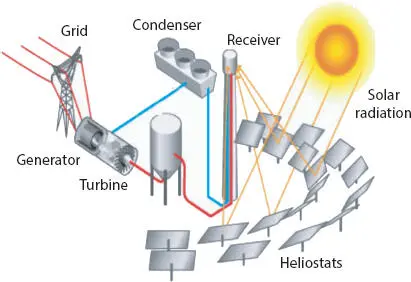
Figure 1.3 Concentrated solar power system.
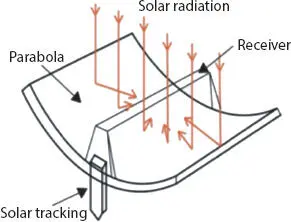
Figure 1.4 Parabolic trough collector.
B1.2 Parabolic Dish System
Figure 1.5shows the parabolic dish system which consists of a parabolic dish concentrator to focus the solar beam. An axis tracking system to follow the sun’s radiation is incorporated. The heat energy [5] from the concentrator is collected at the receiver side and used for generating electricity. The temperature at the dish can reach the maximum and can be used in solar reactors which are need for high temperature.
B1.3 Linear Fresnel System
Figure 1.6shows the Fresnel reflector system. It uses flat mirrors to focus sunlight onto the receiver tubes which contains fluid in it. The diagram shows a primary and a secondary reflector system to make light energy completely fall on the receiving tubes [6]. As a result of it, the fluid is heated and steam produced drives the steam turbine. The generator coupled with the turbine generates electricity and fed to the loads. They are cheaper than the parabolic system and also captures more light energy from the sun. It can also be designed in various sizes.
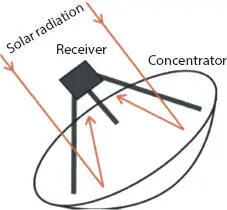
Figure 1.5 Parabolic dish system.
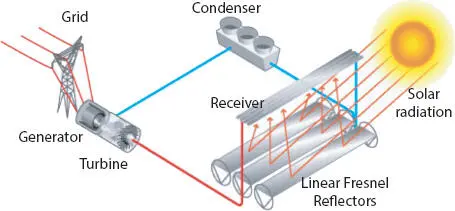
Figure 1.6 Linear Fresnel system.
Sometimes, the output yield is very low in this Fresnel system and so Fresnel reflectors with ray tracing was introduced to yield maximum output.
In the current scenario, the wind energy system is one of the fastest-growing renewable energy. Wind turbine capacity has increased over time. In 1985, typical turbines had a rated capacity of 0.05 megawatts (MW) and a rotor diameter of 15 meters. Today’s new wind power projects have turbine capacities of about 2-MW onshore and 3- to 5-MW offshore. Commercially available wind turbines have reached 10-MW capacity, with rotor diameters of up to 164 meters. The average capacity of wind turbines increased from 1.6 MW in 2009 to 2 MW in 2014 [7].
Wind energy conversion system (WECS) comprises of a wind turbine, gearbox, generator, converter, and transformers as shown in Figure 1.7. The wind energy or the kinetic energy is converted to mechanical energy using a wind turbine. The mechanical energy input is given to the generator and converted into electrical energy. Permanent magnet synchronous generator, Squirrel cage induction generator or doubly fed induction generator can be used in the WECS. The AC output from the generator is converted to a required form using power electronic converter. It is then connected to grid through to a step-up transformer.
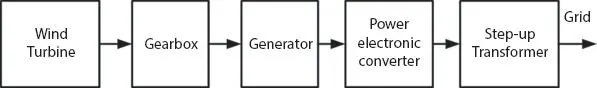
Figure 1.7 Wind energy conversion system (WECS).
Читать дальше


















