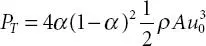The wind energy is captured by the rotor blades and transferred to rotor hub. The rotating shaft provides mechanical energy input to the generator, which is further converted into electricity. The gear box helps in increasing the rotational speed of the shaft for the generator. The power extracted by the rotor blades may be expressed as follows:
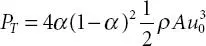
where α is perturbation factor, ρ is density of the air, A is swept area of the blades, and uo is speed of the upstream wind.
The wind turbines are largely classified into Horizontal Axis Wind Turbines (HAWT) and Vertical Axis Wind Turbines (VAWT). As the name implies, the HAWT has their blades rotating on an axis parallel to the ground. If the blades are placed in such a way that their rotational axis is perpendicular to the ground, it is called as VAWT. The HAWT can capable of producing more electricity as compared to VAWT. It is because the HAWT has more swept area than VAWT. Hence, the HAWT is generally preferred for commercial WECS. However, VAWT is used for small power applications.
In search of a clean energy source in the current energy sector, fuel cell has gained its importance. Fuel cell uses hydrogen as a fuel and the energy companies have started concentrating on low carbon hydrogen production. The industries have started using electrolyzer to produce clean hydrogen. In recent years, the electrolyzer installation has increased considerably. The survey says that 350,000 tonnes of low carbon hydrogen production has taken place by the end of year 2019 and 20 other new projects have been targeted by 2020. Fuel cell plays a vital role in generating electricity by using hydrogen as fuel. The more the hydrogen, the more the power. It is similar to a battery in some aspects but can supply energy for a long period of time and it is due to the continuous supply of fuel and oxygen to produce power. Due to these factors, fuel cell finds its application in satellites, manned spacecraft, and other relevant areas. It is also a type of RES that works on the principle of electrochemical reaction that converts chemical energy into an electrical energy. It converts the chemical energy of a fuel, namely, the hydrogen and an oxidizing agent, the oxygen, into electricity.
Figure 1.8shows the diagram of a fuel cell. A fuel cell consists of an anode, cathode, and an electrolyte membrane. Hydrogen fuel is passed through the anode of a fuel cell and oxygen through the cathode. The hydrogen is split into electrons and protons at the anode side. The protons will pass through the membrane to the cathode side and the electrons are made to flow through an external circuit connected to the load After passing through the circuit, the electrons combine with the protons along with oxygen in air and produces water and heat as their by-product. Fuel cells are very clean as they use pure hydrogen as fuel. The efficiency of the fuel cell is high when compared to conventional techniques like steam turbine and internal combustion engine. The efficiency of a fuel cell can further be increased by interfacing it with a combined heat power system. The waste heat generated from the fuel cell can be used for various applications.
The types of fuel cell are as follows:
1 Proton exchange membrane (PEM) fuel cell
2 Direct methanol fuel cell (DMFC)
3 Alkaline fuel cell (AFC)
4 Phosphoric acid fuel cell (PAFC)
5 Molten carbonate fuel cell (MCFC)
6 Solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC)
7 Reversible fuel cell
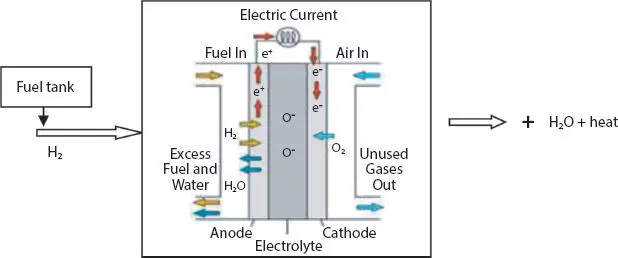
Figure 1.8 Diagram of a fuel cell.
1.1.3.1 Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell
The frequently used fuel cell is PEM fuel cell. Figure 1.9shows the PEM fuel cell. It is a light weight fuel cell and delivers high power density. It is also called as polymer electrolyte membrane (PEM) fuel cell [8]. It consists of carbon porous electrodes with solid polymer as an electrolyte and platinum as a catalyst. It operates with hydrogen, oxygen and water. Hydrogen fuel is given as an input from storage tanks. It operates at low temperatures and so considered as a durable one. A good catalyst is used but platinum is not so economical and it is sensitive to carbon monoxide poisoning. It requires a reactor to eradicate this poisoning effect and hence the cost also increases. Since it operates at low temperatures, its start-up time is very quick, and hence, it is suitable for automotive applications.
1.1.3.2 Direct Methanol Fuel Cell
Most of the fuel cells use hydrogen as the fuel to generate electricity, However, DMFC use methanol as a fuel input along with water. Methanol has higher energy density than hydrogen and it is easy to transport as it is like a liquid and similar to gasoline. It is a dense liquid but considered as a stable one. Its efficiency is around 40% and the operating temperature is between 50°C and 120°C. It is used as a powering circuit for laptops, cell phones, and other portable items.
Figure 1.9 Proton exchange membrane (PEM) fuel cell.
1.1.3.3 Alkaline Fuel Cell
AFCs were the widely used fuel cells in space industry. Alkaline fuel cell is also called as “Bacon fuel cell” as it was invented by Francis Thomas Bacon. It is one of the considered fuel cell design. It is similar to PEM fuel cell except for the use of alkaline membrane instead of acid membrane. It uses a solution of potassium hydroxide in water as the electrolyte and non-precious metal as a catalyst at the anode and cathode. It uses hydrogen as fuel and pure oxygen to produce water and electricity. Because of its efficiency greater than 60%, it is used in space industries.
1.1.3.4 Phosphoric Acid Fuel Cell
It was the first commercial fuel cell in the mid-1960s. PAFC uses phosphoric acid as an electrolyte. The electrolyte is a pure or concentrated liquid phosphoric acid (H 3PO 4) in a silicon carbide matrix. It operates in the temperature range between 150°C and 210°C. Electrodes are made of carbon paper coated with platinum catalyst. It is used in buses and in stationary power generators in the range of 100 to 400 kW.
1.1.3.5 Molten Carbonate Fuel Cell
The conventional source–based power plants use MCFC for industrial and military applications. The electrolyte used in MCFC is a molten carbonate salt mixture immersed in ceramic matrix of beta alumina solid electrolyte. Because of its high operating temperature, metals are used as catalyst at the anode and cathode. It offers better efficiency when compared to PAFC which is around 65%. PAFC’s efficiency is only 30% to 40%.
Solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) and reversible fuel cells are the other types of fuel cell that are generally employed for various applications.
The energy derived from the organic matter of the living organism is the biomass. It is a RES that produces electricity with minimum cost. The organic material produced from plants and animals, crops and algae are used in biomass energy production. The global cumulative biomass energy generation is shown in Figure 1.10. When biomass is burned, heat is generated and the thermal energy is converted into electrical energy. This biomass can either be burned directly or converted into liquid biofuels or biogas. The conversion methods for biomass energy production include chemical, thermal, and bio-chemical [9].
Читать дальше