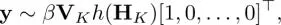The approximated version of h ( L) xby the K th order shifted Chebyshev polynomial, h Cheb( L) x, is given by Shuman et al . (2013); Hammond et al. (2011)
[1.60] 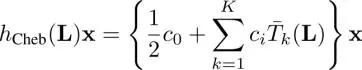
and it has the recurrence property:
[1.61] 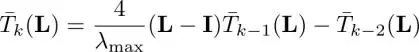
with  . The k th Chebyshev coefficient c kis defined as
. The k th Chebyshev coefficient c kis defined as
[1.62] 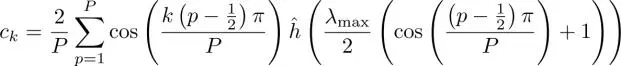
for k = 0 ,...,K , where P is the number of sampling points used to compute the Chebyshev coefficients and is usually set to P = K + 1. The approximated filter in equation [1.60]is clearly a K th order polynomial of λ . As a result, it is K- hop localized in the vertex domain, as previously mentioned (Shuman et al. 2011; Hammond et al. 2011).
The approximation error for the Chebyshev polynomial has been well studied in the context of numerical computation (Vetterli et al. 2014; Phillips 2003):
THEOREM 1.1.– Let K be the polynomial degree of the Chebyshev polynomial and assume that 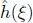 has ( K + 1) continuous derivatives on [−1, 1]. In this case, the upper bound of the error is given as follows:
has ( K + 1) continuous derivatives on [−1, 1]. In this case, the upper bound of the error is given as follows:
[1.63] 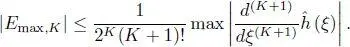
1.6.6. Krylov subspace method
The Krylov subspace 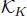 of an arbitrary square matrix
of an arbitrary square matrix 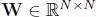 and a vector xis defined as follows:
and a vector xis defined as follows:
[1.64] 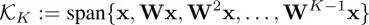
The Krylov subspace method, in terms of GSP, refers to filtering, i.e. evaluating an arbitrary filtered response h ( W) x, realized in a Krylov subspace  . Many methods to evaluate h ( W) xin a Krylov subspace have been proposed, mainly in computational linear algebra and numerical computation (Golub and Van Loan 1996). A famous approximation method is the Arnoldi approximation, which is given by
. Many methods to evaluate h ( W) xin a Krylov subspace have been proposed, mainly in computational linear algebra and numerical computation (Golub and Van Loan 1996). A famous approximation method is the Arnoldi approximation, which is given by
[1.65] 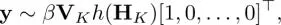
where h ( H K) is evaluating h (·) for the upper Heisenberg matrix H K, which is obtained by using the Arnoldi process. Furthermore, H Kis expected to be much smaller than the original matrix; therefore, evaluating h ( H K) using full eigendecomposition will be feasible and light-weighted.
This chapter introduces the filtering of graph signals performed in the graph frequency domain. This is a key ingredient of graph spectral image processing presented in the following chapters. The design methods of efficient and fast graph filters and filter banks, along with fast GFT (such attempts can be found in Girault et al . (2018); Lu and Ortega (2019)), are still a vibrant area of GSP: the chosen graph filters directly affect the quality of processed images. This chapter only provided a brief overview of graph spectral filtering. Please refer to the references for more details.
Anderson Jr. W.N. and Morley, T.D. (1985). Eigenvalues of the Laplacian of a graph. Linear and Multilinear Algebra , 18(2), 141–145.
Barash, D. (2002). Fundamental relationship between bilateral filtering, adaptive smoothing, and the nonlinear diffusion equation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. , 24(6), 844–847.
Chang, C.-L. and Girod, B. (2007). Direction-adaptive discrete wavelet transform for image compression. IEEE Trans. Image Process. , 16(5), 1289–1302.
Choudhury, P. and Tumblin, J. (2003). The trilateral filter for high contrast images and meshes. Eurographics Rendering Symposium , 186–196.
Desbrun, M., Meyer, M., Schröder, P., Barr, A.H. (1999). Implicit fairing of irregular meshes using diffusion and curvature flow. Proceedings of the 26th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques , 317–324.
Ding, W., Wu, F., Wu, X., Li, S., Li, H. (2007). Adaptive directional lifting-based wavelet transform for image coding. IEEE Trans. Image Process , 16(2), 416–427.
Durand, F. and Dorsey, J. (2002). Fast bilateral filtering for the display of high-dynamic-range images. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) , 21, 257–266.
Farbman, Z., Fattal, R., Lischinski, D., Szeliski, R. (2008). Edge-preserving decompositions for multi-scale tone and detail manipulation. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) , 27, 67.
Fleishman, S., Drori, I., Cohen-Or, D. (2003). Bilateral mesh denoising. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG) , 22, 950–953.
Gadde, A., Narang, S.K., Ortega, A. (2013). Bilateral filter: Graph spectral interpretation and extensions. IEEE International Conference on Image Processing , 1222–1226.
Girault, B., Ortega, A., Narayanan, S. (2018). Irregularity-aware graph Fourier transforms. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing , 66(21), 5746–5761.
Golub, G.H. and Van Loan, C.F. (1996). Matrix Computations , Johns Hopkins University Press, Maryland.
Hammond, D.K., Vandergheynst, P., Gribonval, R. (2011). Wavelets on graphs via spectral graph theory. Applied and Computational Harmonic Analysis , 30(2), 129–150.
Harel, J., Koch, C., Perona, P. (2006). Graph-based visual saliency. Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems , 545–552.
He, K., Sun, J., Tang, X. (2013). Guided image filtering. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence , 35(6), 1397–1409.
Hu, W., Cheung, G., Ortega, A., Au, O.C. (2015). Multiresolution graph Fourier transform for compression of piecewise smooth images. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing , 24(1), 419–433.
Itti, L., Koch, C., Niebur, E. (1998). A model of saliency-based visual attention for rapid scene analysis. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. , 20(11), 1254–1259.
Читать дальше

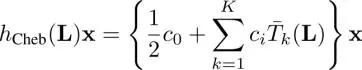
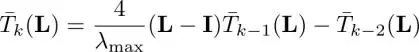
 . The k th Chebyshev coefficient c kis defined as
. The k th Chebyshev coefficient c kis defined as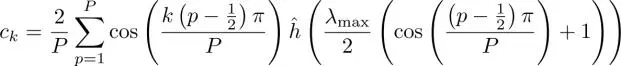
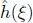 has ( K + 1) continuous derivatives on [−1, 1]. In this case, the upper bound of the error is given as follows:
has ( K + 1) continuous derivatives on [−1, 1]. In this case, the upper bound of the error is given as follows: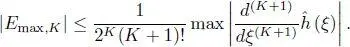
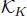 of an arbitrary square matrix
of an arbitrary square matrix 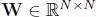 and a vector xis defined as follows:
and a vector xis defined as follows: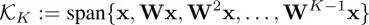
 . Many methods to evaluate h ( W) xin a Krylov subspace have been proposed, mainly in computational linear algebra and numerical computation (Golub and Van Loan 1996). A famous approximation method is the Arnoldi approximation, which is given by
. Many methods to evaluate h ( W) xin a Krylov subspace have been proposed, mainly in computational linear algebra and numerical computation (Golub and Van Loan 1996). A famous approximation method is the Arnoldi approximation, which is given by