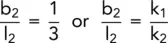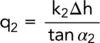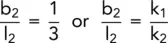
The effect on a flow net is illustrated in Fig. 2.31.
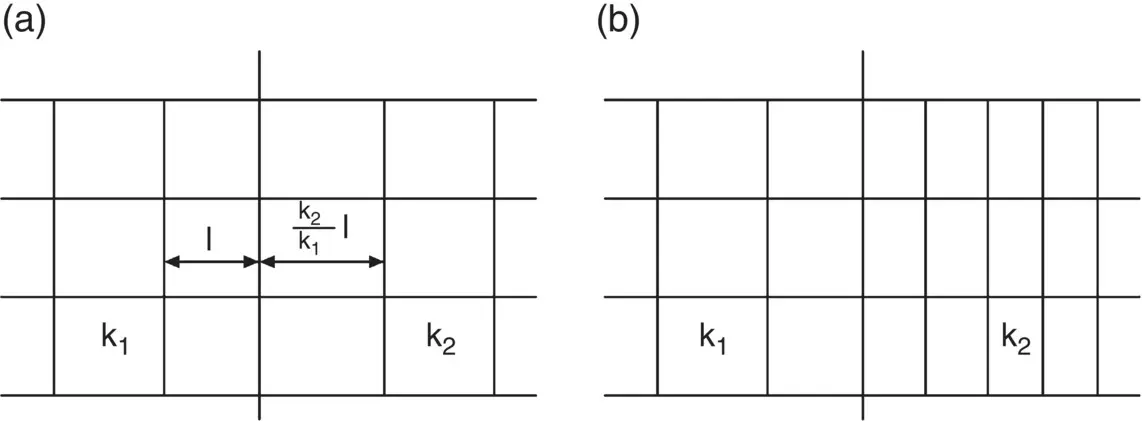
Fig. 2.31 Effect of variation of permeability on a flow net. (a) k 2> k 1. (b) k 2< k 1.
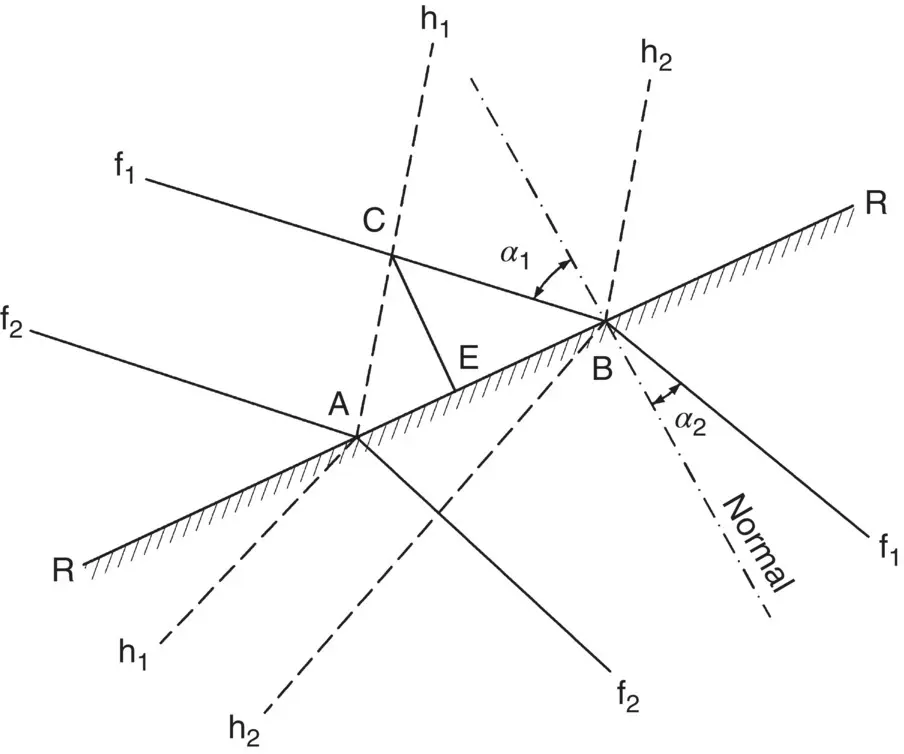
Fig. 2.32 Flow across an interface when the flow lines are at an angle to it.
2.15.5 Refraction of flow lines at interfaces
An interface is the surface or boundary between two soils. If the flow lines across an interface are normal to it, then there will be no refraction and the flow net appears as shown in Fig. 2.31. When the flow lines meet the interface at some acute angle to the normal, then the lines are bent as they pass into the second soil.
In Fig. 2.32, let RR be the interface of two soils of permeabilities, k 1and k 2. Consider two flow lines, f 1and f 2, making angles to the normal of α 1and α 2in soils 1 and 2, respectively.
Let f 1cut RR in B and f 2cut RR in A.
Let h 1and h 2be the equipotentials passing through A and B, respectively, and let the head drop between them be Δh.
With uniform flow conditions, the flow into the interface will equal the flow out. Consider flow normal to the interface.
In soil (1):


Fig. 2.33 Flow net for seepage through two soils of different permeabilities.
Similarly, it can be shown that, in soil (2):
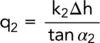
Now q 1= q 2,
(2.38) 
A flow net which illustrates the effect is shown in Fig. 2.33.
In a falling head permeameter test on a fine sand, the sample had a diameter of 76 mm and a length of 152 mm with a standpipe of 12.7 mm diameter. A stopwatch was started when h was 508 mm and read 19.6 s when h was 254 mm. The test was repeated for a drop from 254 to 127 mm and the time was 19.4 s.
Determine an average value for k in m/s.
Answer 1.5 × 10 −4m/s
A sample of coarse sand 150 mm high and 55 mm in diameter was tested in a constant head permeameter. Water percolated through the soil under a head of 400 mm for 6.0 s and the discharge water had a mass of 400 g.
Determine k in m/s.
Answer 1.05 × 10 −2m/s
To determine the average permeability of a bed of sand 12.5 m thick overlying an impermeable stratum, a well was sunk through the sand and a pumping test carried out. After some time, the discharge was 850 kg/min and the drawdowns in observation wells 15.2 and 30.4 m from the pump were 1.625 and 1.360 m, respectively. If the original water table was at a depth of 1.95 m below ground level, find the permeability of the sand (in m/s) and an approximate value for the effective grain size.
Answer k = 6.7 × 10 −4m/s, D 10≈ 0.26 mm
A cylinder of cross‐sectional area 2500 mm 2is filled with sand of permeability 5.0 mm/s. Water is caused to flow through sand under a constant head using the arrangement shown in Fig. 2.34.
Determine the quantity of water discharged in 10 minutes.
Answer 9 × 10 6mm 3
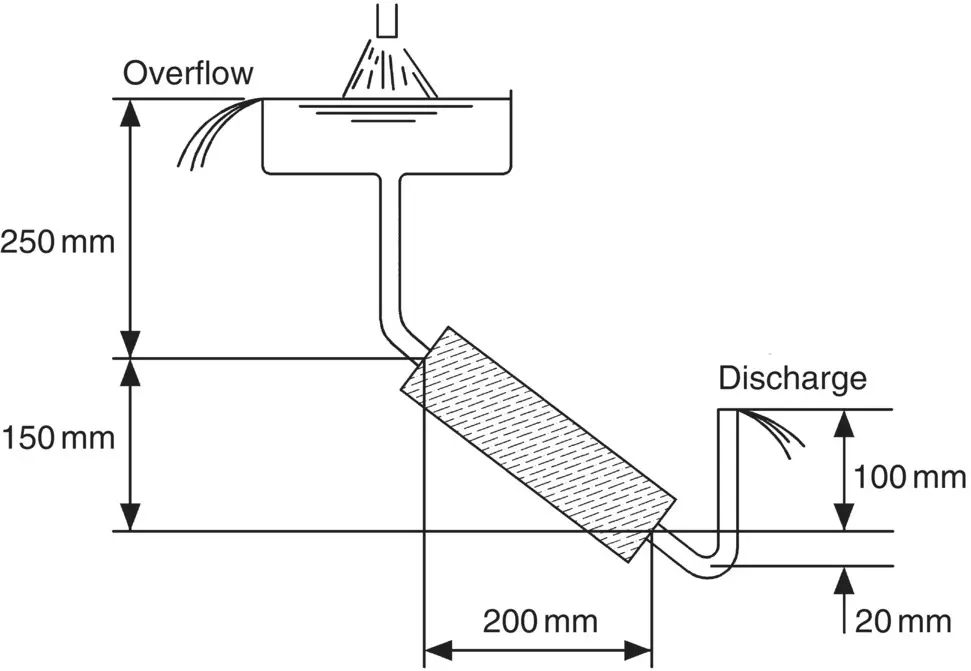
Fig. 2.34 Exercise 2.4.
The specific gravity of particles of a sand is 2.54 and their porosity is 45% in the loose state and 37% in the dense state. What are the critical hydraulic gradients for these two states?
Answer 0.85, 0.97
A large open excavation was made into a stratum of clay with a saturated unit weight of 17.6 kN/m 3. When the depth of the excavation reached 7.63 m the bottom rose, gradually cracked, and was flooded from below with a mixture of sand and water. Subsequent borings showed that the clay was underlain by a bed of sand with its surface at a depth of 11.3 m.
Determine the elevation to which water would have risen from the sand into a drill hole before excavation was started.
Answer 6.45 m above top of sand
A soil deposit consists of three horizontal layers of soil: an upper stratum A (1 m thick), a middle stratum B (2 m thick), and a lower stratum C (3 m thick). Permeability tests gave the following values:
Soil A 3 × 10−1 mm/s
Soil B 2 × 10−1 mm/s
Soil C 1 × 10−1 mm/s
Determine the ratio of the average permeabilities in the horizontal and vertical directions.
Answer 1.22
Beneath the deposit there is a gravel layer subjected to artesian pressure, the surface of the deposit coinciding with the groundwater level. Standpipes show that the fall in head across soil A is 150 mm. Determine the value of the water pressure in the gravel.
Answer 80 kPa
Конец ознакомительного фрагмента.
Текст предоставлен ООО «ЛитРес».
Прочитайте эту книгу целиком, купив полную легальную версию на ЛитРес.
Безопасно оплатить книгу можно банковской картой Visa, MasterCard, Maestro, со счета мобильного телефона, с платежного терминала, в салоне МТС или Связной, через PayPal, WebMoney, Яндекс.Деньги, QIWI Кошелек, бонусными картами или другим удобным Вам способом.