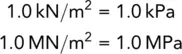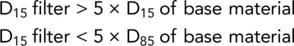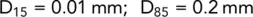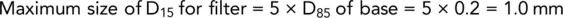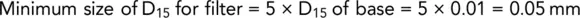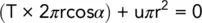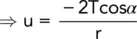
Fig. 2.13 Example 2.6.
The pascal is the stress value of one newton per square metre, 1.0 N/m 2, and is given the symbol Pa. In the example above, pressure has been expressed in kilopascals, kPa. Pressure could have equally been expressed in kN/m 2as the two terms are synonymous.
2.12 Design of soil filters
As seen above, water seeping out of the soil can lead to piping and therefore drainage should be provided in such situations to ensure ground stability. To prevent soil particles being washed into the drainage system, soil filters can be provided as the interface between base material and drain. The design procedure for a filter is largely empirical, but it must comprise granular material fine enough to prevent soil particles being washed through it and yet coarse enough to allow the passage of water.
The following formulae are used in the specification of the filter material, based initially on the work of Terzaghi and developed through the experimental research of Sherard et al . (1984a, b):
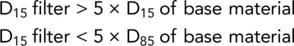
The first equation ensures that the filter layer has a permeability several times higher than that of the soil it is designed to protect. The requirement of the second equation is to prevent piping within the filter. The ratio D 15(filter)/D 85(base) is known as the piping ratio .
The required thickness of a filter layer depends upon the flow conditions and can be estimated with the use of Darcy's law of flow. The filter material should be well graded, with a grading curve more or less parallel to the soil. All material should pass the 75 mm size sieve and not more than 5% should pass the 0.063 mm size sieve (see Example 2.7and Fig. 2.14).
Protective filters are usually constructed in layers, each of which is coarser than the one below it, and for this reason they are often referred to as reversed filters . Even when there is no risk of piping, filters are often used to prevent erosion of foundation materials and they are extremely important in earth dams.
Example 2.7Filter material limits
Determine the approximate limits for a filter material suitable for the material shown in Fig. 2.14.
Solution:
From the particle size distribution curve:
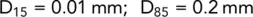
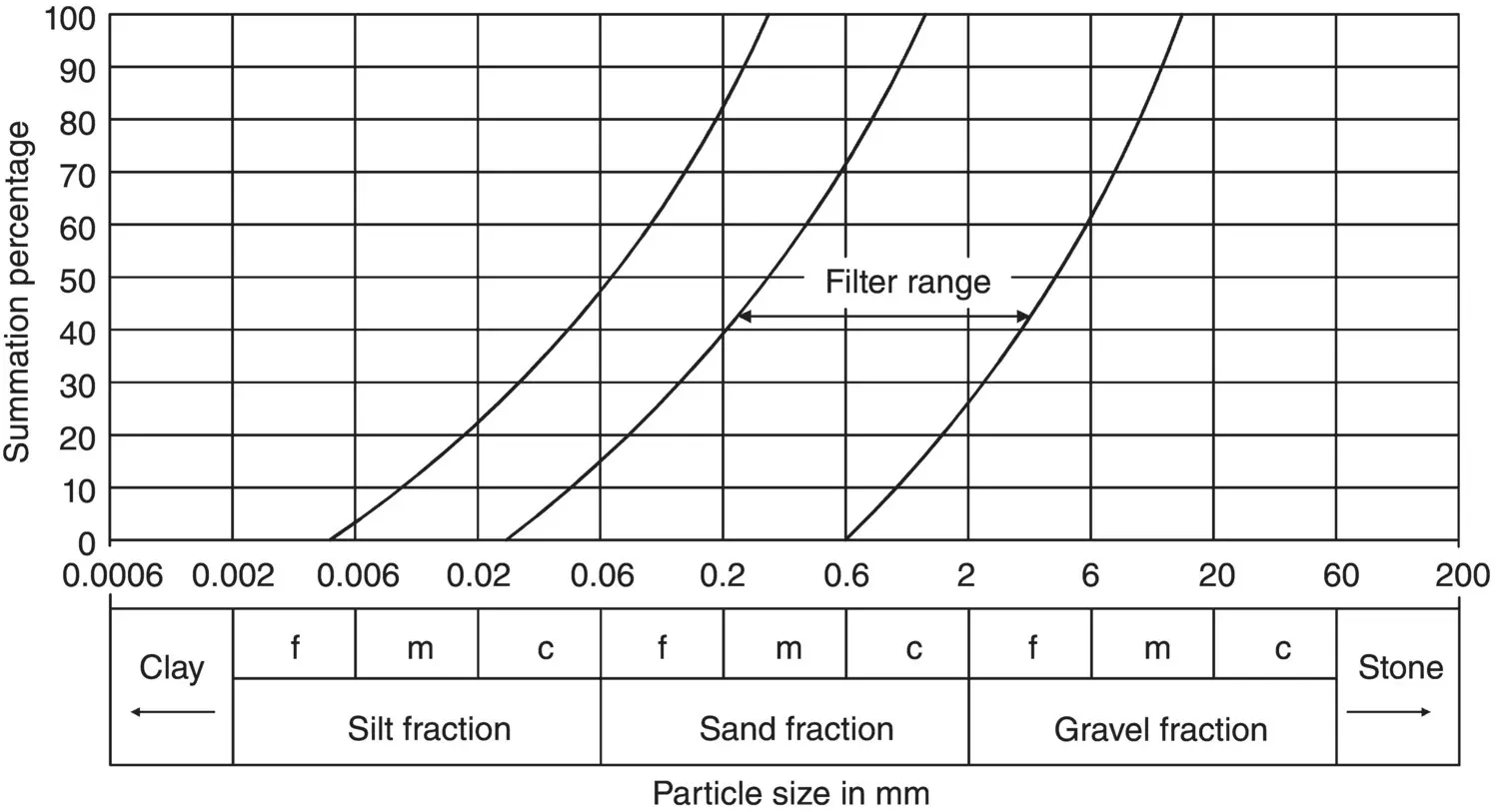
Fig. 2.14 Example 2.7
Using Terzaghi's method:
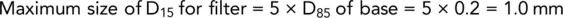
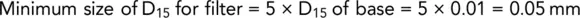
This method gives two points on the 15% summation line. Two lines can be drawn through these points roughly parallel to the grading curve of the soil, and the space between them is the range of material suitable as a filter ( Fig. 2.14).
2.13 Capillarity and unsaturated soils
The behaviour of unsaturated soils is a relatively specialised subject area and readers interested in gaining a good understanding of the topic are referred to the publications by Fredlund et al . (2012) and Ng and Menzies (2007). Simple coverage of some of the key aspects involved are offered in the following sections.
Surface tension is the property of water that permits the surface molecules to carry a tensile force. Water molecules attract each other, and within a mass of water, these forces balance out. At the surface, however, the molecules are only attracted inwards and towards each other, which creates surface tension. Surface tension causes the surface of a body of water to attempt to contract into a minimum area: hence, a drop of water is spherical.
The phenomenon is easily understood if we imagine the surface of water to be covered with a thin molecular skin capable of carrying tension. Such a skin, of course, cannot exist on the surface of a liquid, but the analogy can explain surface tension effects without going into the relevant molecular theories.
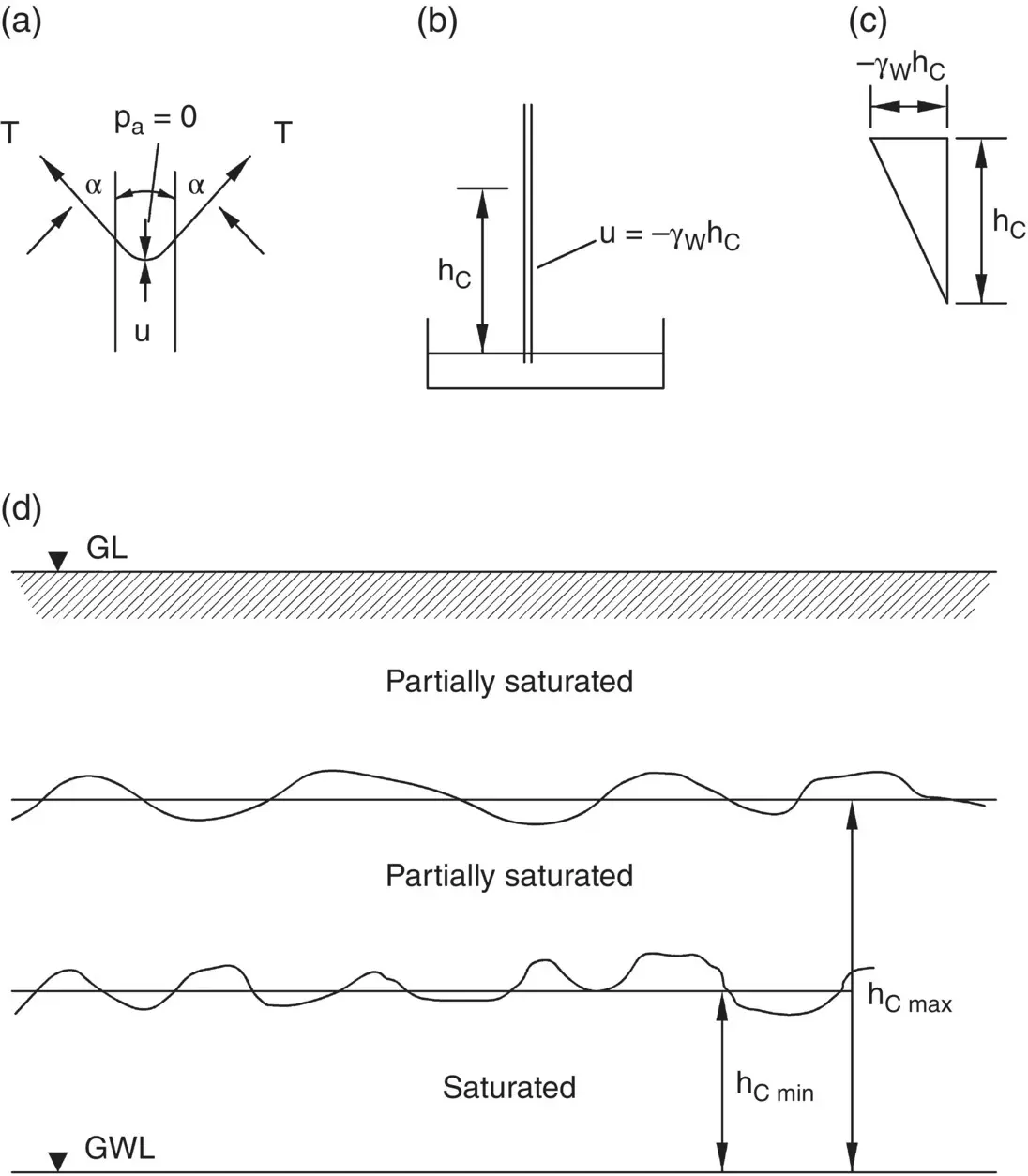
Fig. 2.15 Capillary effects.
Surface tension is given the symbol T and can be defined as the force in Newtons per millimetre length that the water surface can carry. T varies slightly with temperature, but this variation is small, and an average value usually taken for the surface tension of water is 0.000 075 N/mm (0.075 N/m).
The fact that surface tension exists can be shown in a simple laboratory experiment in which an open‐ended glass capillary tube is placed in a basin of water subjected to atmospheric pressure; the rise of water within the tube is then observed. It is seen that the water wets the glass and the column of water within the tube reaches a definite height above the liquid in the basin.
The surface of the column forms a meniscus such that the curved surface of the liquid is at an angle α to the walls of the tube ( Fig. 2.15a). The arrangement of the apparatus is shown in Fig. 2.15b.
The base of the column is at the same level as the water in the basin and, as the system is open, the pressure must be atmospheric. The pressure on the top surface of the column is also atmospheric. There are no externally applied forces that keep the column in position, which shows that there must be a tensile force acting within the surface film of the water.
Let
Height of water column = hc
Radius of tube = r
Unit weight of water = γw
If we take atmospheric pressure as datum, i.e. the air pressure = 0, we can equate the vertical forces acting at the top of the column:
(2.23) 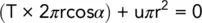
(2.24) 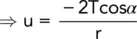
Hence, as expected, we see that u is negative which indicates that the water within the column is in a state of suction. The maximum value of this negative pressure is γ wh cand occurs at the top of the column. The pressure distribution along the length of the tube is shown in Fig. 2.15c. It is seen that the water pressure gradually increases with loss of elevation to a value of 0 at the base of the column.
An expression for the height h ccan be obtained by substituting u = − γ wh cin the above expression to yield:
Читать дальше