Marja-Liisa Siikonen - People Flow in Buildings
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Marja-Liisa Siikonen - People Flow in Buildings» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:People Flow in Buildings
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:4 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
People Flow in Buildings: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «People Flow in Buildings»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
People Flow in Buildings Readers will also benefit from the inclusion of:
A thorough introduction to people-counting methods, including counting technology inside and outside buildings, passenger traffic components, and manual people-counting An examination of the passenger arrival process in building, including the Poisson arrival process and probability density function, and passenger arrivals in batches A consideration of daily vertical passenger traffic profiles, including two-way traffic profiles and the effects of inter-floor traffic An exploration of people flow solutions, including stairs, escalators, and elevators with collective and destination group control systems, as well as double-deck and multicar system People flow calculation and simulation models Elevator planning with ISO simulation method Elevator planning and evacuation of tall buildings Perfect for software designers in the private sector and academia,
will also earn a place in the libraries of elevator consultants, manufacturers, and architects who seek a one-stop reference for transportation devices from a functional and design perspective, as opposed to a hardware perspective.

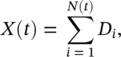
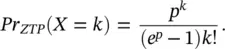
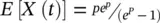 . The value for p and the suggested distributions for each building type can be solved by equalizing the observed mean value to the theoretical mean.
. The value for p and the suggested distributions for each building type can be solved by equalizing the observed mean value to the theoretical mean.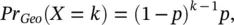
 .
.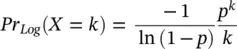
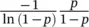 . The mean batch size was used to generate the zero‐truncated, the geometric and the logarithmic Poisson probabilities of Eqs. (3.8)– (3.10),respectively. All three given theoretical distributions are close to each other. The zero‐truncated and logarithmic distributions do not match with the mean distribution since the distributions vary considerably especially in observed hotels. The geometric distribution of Eq. (3.9)was found to fit best to the average daily batch size distribution (Sorsa et al. 2021).
. The mean batch size was used to generate the zero‐truncated, the geometric and the logarithmic Poisson probabilities of Eqs. (3.8)– (3.10),respectively. All three given theoretical distributions are close to each other. The zero‐truncated and logarithmic distributions do not match with the mean distribution since the distributions vary considerably especially in observed hotels. The geometric distribution of Eq. (3.9)was found to fit best to the average daily batch size distribution (Sorsa et al. 2021).