New, NoteworthyWe discuss the Vigenère cipher and show how it can be broken by finding the length of the keyword and then the keyword itself. We explain clearly the simple principles involved without getting bogged down in lengthy formulae. We also give a detailed but accessible description of the famous Enigma system used in World War II both from the mechanical and the mathematical point of view.
Since the early stages of human civilization, there has been a need to protect sensitive information from falling into the wrong hands. To achieve such secrecy, mankind has relied on a branch of mathematics known as cryptography, which is the study of designing methods to securely transmit information over nonsecure channels. In order to achieve this goal, one must first encipher, or scramble, the intended message to prevent an eavesdropper from obtaining any useful information, should the message be intercepted. The message (referred to as plain text) is scrambled into cipher textusing a predetermined key, known to both the sender and receiver. The encrypted message is constructed in such a way so as to be resilient against attack, while allowing the intended recipient to decipher, or unscramble the message with ease. The methods we will be investigating in this section to accomplish this task may be outdated and in some cases obsolete, but they can still provide us with valuable insight into some techniques that are still in use today.
While Julius Caesar was building his empire, he needed a method to transmit vital messages without risk of the enemy obtaining any crucial information. To achieve this goal, he employed one of the first known ciphering methods. The idea was to substitute each letter of the plain text with the letter appearing three spaces to the right in the alphabet, i.e. a is enciphered to D, b is enciphered to E, and z is enciphered to C (the alphabet wraps around). Thus, “six” is enciphered to “VLA.”
In practice, this can be easily achieved using a simple device consisting of two disks, such as the one shown in Figure 2.1. Both disks have the alphabet engraved on their perimeter, and they can rotate with respect to each other. If we assign the inner disk to represent the plain text alphabet and the outer disk to represent the cipher text alphabet, enciphering is accomplished simply by rotating the outer disk by three letters counter clockwise and reading off the cipher text corresponding to the plain text. To decipher the message, one must only reverse the procedure. The “key” of the cipher is just the number of letters that the outer disk is shifted by, and is denoted by k. Both sender and recipient are in possession of this common secret key.
For a numerical explanation, suppose we label  by the numbers
by the numbers  . Using Caesar's key of three, the plain text message “six” is enciphered as follows:
. Using Caesar's key of three, the plain text message “six” is enciphered as follows:
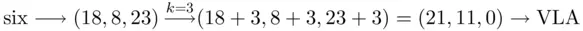
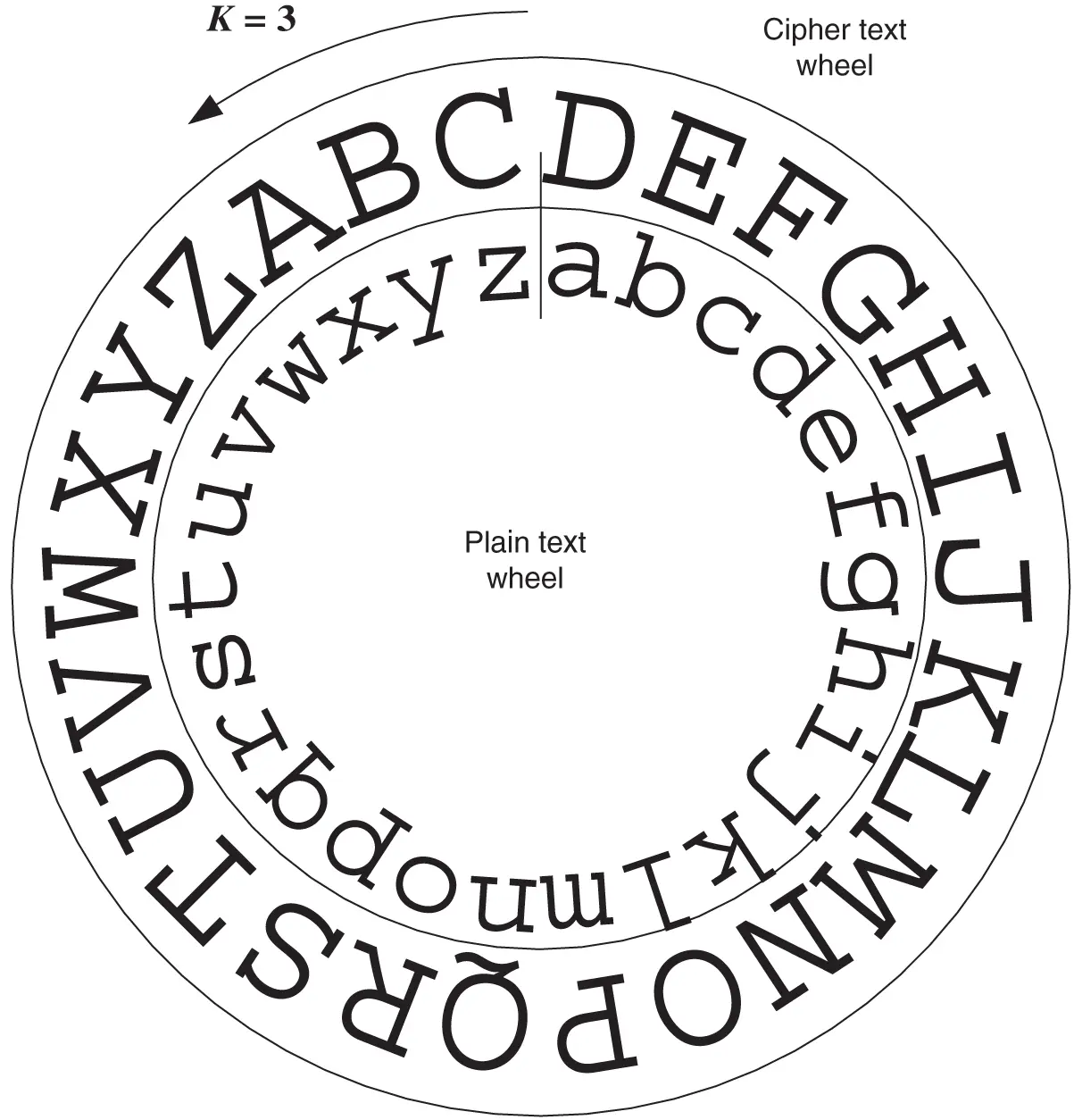
Figure 2.1Caesar cipher wheel.
Note that in the above example, 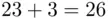 . We replace 26 by
. We replace 26 by 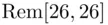 which is the remainder when we divide by 26 (see Chapter 19for details). In this case, the remainder is 0, corresponding to the letter A. Similarly,
which is the remainder when we divide by 26 (see Chapter 19for details). In this case, the remainder is 0, corresponding to the letter A. Similarly, 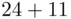 becomes
becomes 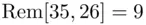 . The number 9 corresponds to the letter J.
. The number 9 corresponds to the letter J.
To decipher the message, reverse the operation (shift left by 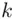 spaces):
spaces):
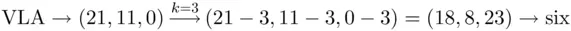
In this case, we have 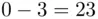 . If
. If 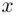 is a negative number, then it is replaced by
is a negative number, then it is replaced by 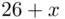 . So, for example
. So, for example  gets replaced by
gets replaced by 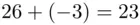 . The reasoning is that
. The reasoning is that 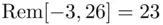 since
since 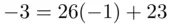 . Alternatively, (see Chapter 19) we have
. Alternatively, (see Chapter 19) we have 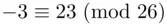 .
.
The Caesar cipher is a simple example of a type of cipher known as a monoalphabeticcipher. Monoalphabetic ciphers belong to a class of ciphers known as substitution ciphers, in which all of the plain text characters in the message are substituted for another letter. Mathematically speaking, the enciphering process of a monoalphabetic cipher can be represented by the mapping of a plain text character to a cipher text character:
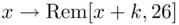
Similarly, deciphering is represented by the mapping
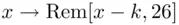
where 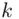 is the cipher key, with
is the cipher key, with 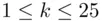 . In the case of the Caesar cipher,
. In the case of the Caesar cipher, 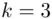 . If
. If 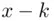 is negative, then, as explained above,
is negative, then, as explained above, 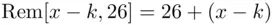 .
.
Читать дальше

 by the numbers
by the numbers  . Using Caesar's key of three, the plain text message “six” is enciphered as follows:
. Using Caesar's key of three, the plain text message “six” is enciphered as follows: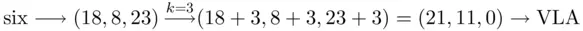

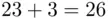 . We replace 26 by
. We replace 26 by 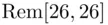 which is the remainder when we divide by 26 (see Chapter 19for details). In this case, the remainder is 0, corresponding to the letter A. Similarly,
which is the remainder when we divide by 26 (see Chapter 19for details). In this case, the remainder is 0, corresponding to the letter A. Similarly, 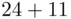 becomes
becomes 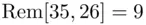 . The number 9 corresponds to the letter J.
. The number 9 corresponds to the letter J.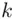 spaces):
spaces):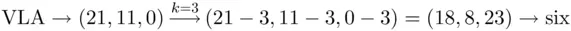
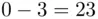 . If
. If 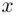 is a negative number, then it is replaced by
is a negative number, then it is replaced by 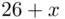 . So, for example
. So, for example  gets replaced by
gets replaced by 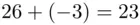 . The reasoning is that
. The reasoning is that 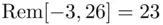 since
since 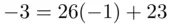 . Alternatively, (see Chapter 19) we have
. Alternatively, (see Chapter 19) we have 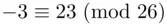 .
.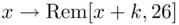
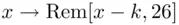
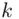 is the cipher key, with
is the cipher key, with 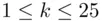 . In the case of the Caesar cipher,
. In the case of the Caesar cipher, 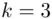 . If
. If 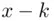 is negative, then, as explained above,
is negative, then, as explained above, 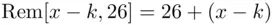 .
.










