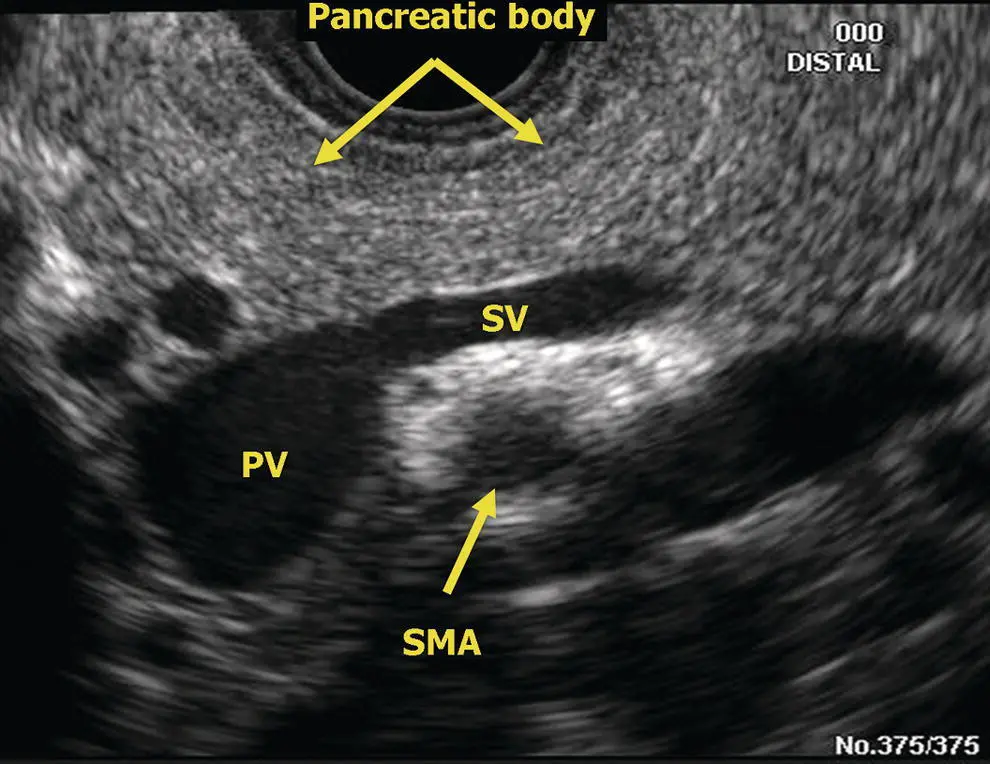
Figure 6.1 Radial EUS: pancreatic body and portal/splenic vein confluence. PV, portal vein; SMA, superior mesenteric artery; SV, splenic vein.
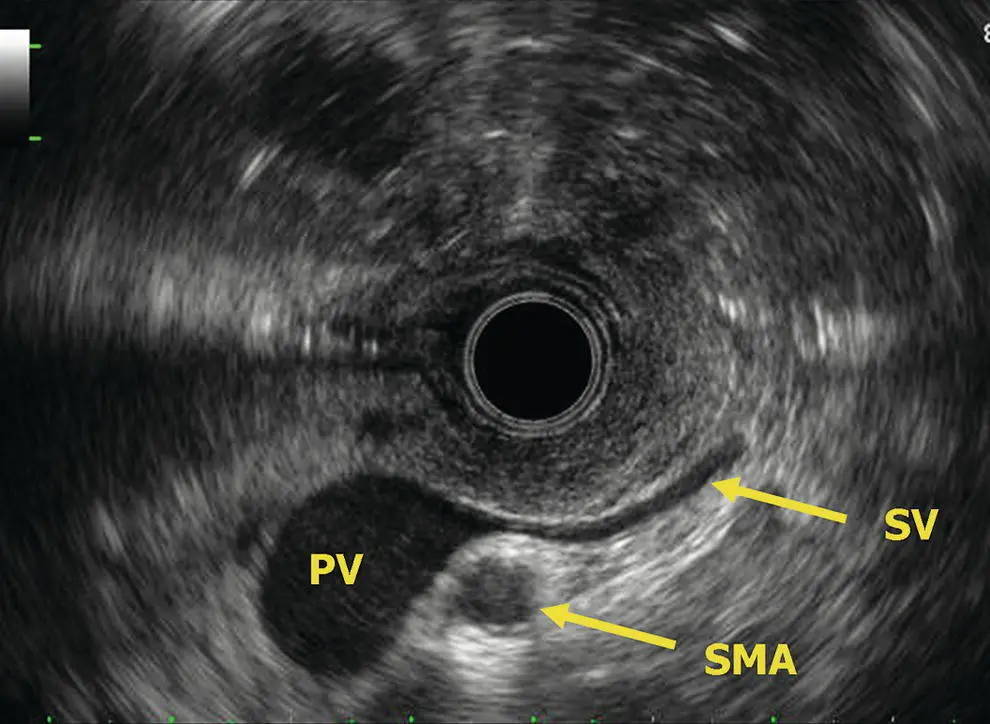
Figure 6.2 Radial EUS: portal/splenic vein confluence. PV, portal vein; SMA, superior mesenteric artery; SV, splenic vein.
Linear examination of the pancreas
The linear endosonographic examination of the pancreas through the stomach differs fundamentally from the radial examination in that complete imaging of the pancreas must be provided by rotating the shaft of the scope. Since the retroperitoneal structures are all posterior to the stomach, clockwise (rightward) rotation of the echoendoscope will point the echoendoscope towards the patient’s left and counterclockwise (leftward) rotation towards their right side. To find the pancreas in the stomach, one starts at the abdominal aorta near the gastroesophageal junction and follows its course distally until the take‐off of the celiac artery is visible. Usually, the more oblique take‐off of the superior mesenteric artery is apparent just distal to this. Further advancement of the instrument distally will find the pancreas neck/body nestled between the “V” of the celiac and superior mesenteric artery. The splenic artery will course tortuously in and out of the pancreas body/tail, but the splenic vein usually has a straight course and is the larger, deeper and more ovoid of the two vessels ( Figure 6.11). The pancreas is interrogated sequentially from the neck to the body and tail through the stomach at this level by rotating the echoendoscope to the right (clockwise) with slight withdrawal following the splenic vein and splenic artery as they run into the hilum of the spleen. The pancreas neck, body, and tail will appear be the tissue found between the splenic vein and the posterior gastric wall. The pancreatic duct is usually seen in cross‐section through the stomach ( Figure 6.12). A normal caliber duct will appear as a small, sometimes difficult to see, echolucent dot in the middle of the pancreatic parenchyma. Rotation to the left at the level of the celiac axis and body of the pancreas brings into view the pancreatic neck with the portal vein confluence deep to it. The splenic vein merges into the confluence from the patient’s left and the superior mesenteric vein runs caudad from the portal vein confluence. A little further leftward rotation of the echoendoscope may produce views of the right border of the pancreatic neck looking down towards the pancreatic head. Sometimes, longitudinal views of the pancreatic duct can be obtained from this view.
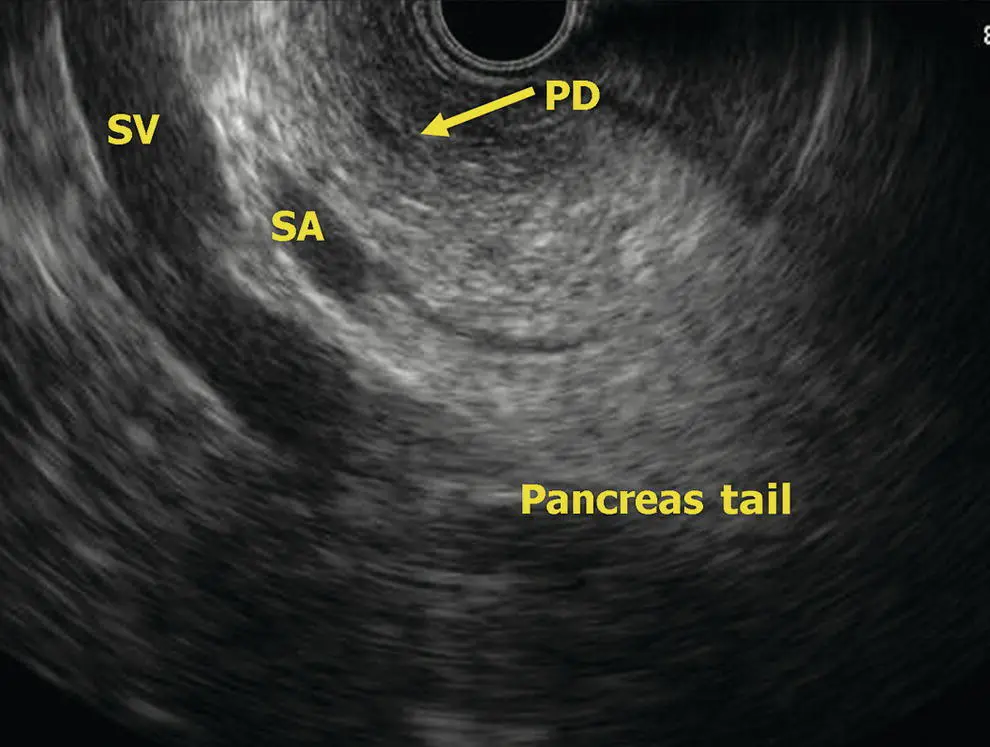
Figure 6.3 Radial EUS: pancreas tail. PD, pancreatic duct; SA, splenic artery; SV, splenic vein.
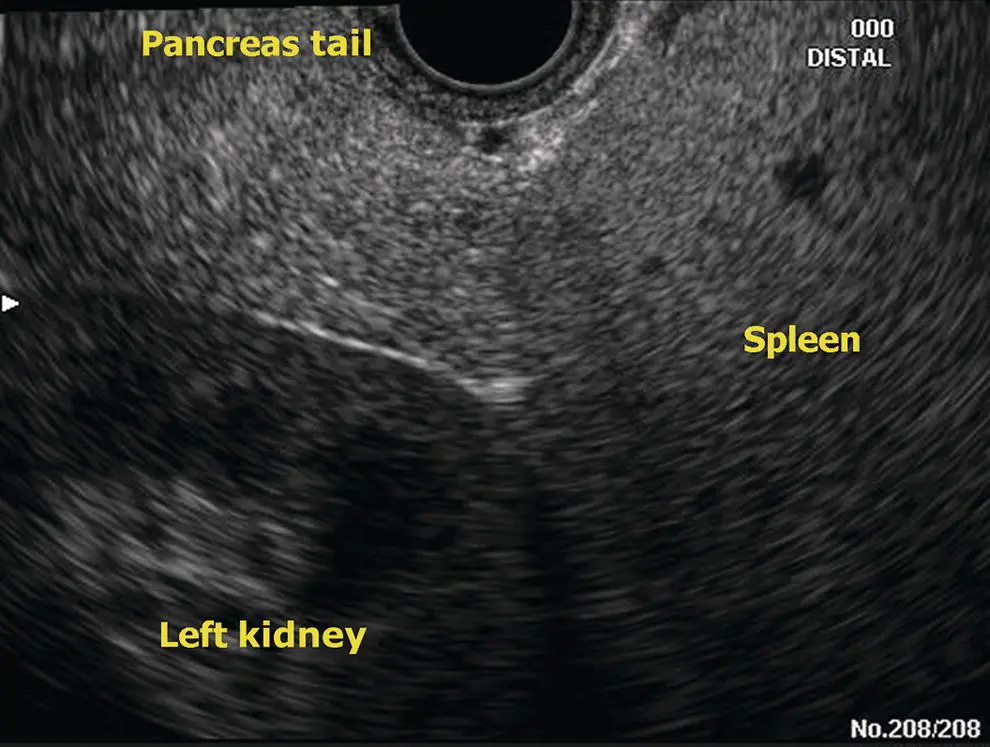
Figure 6.4 Radial EUS: pancreas tail.
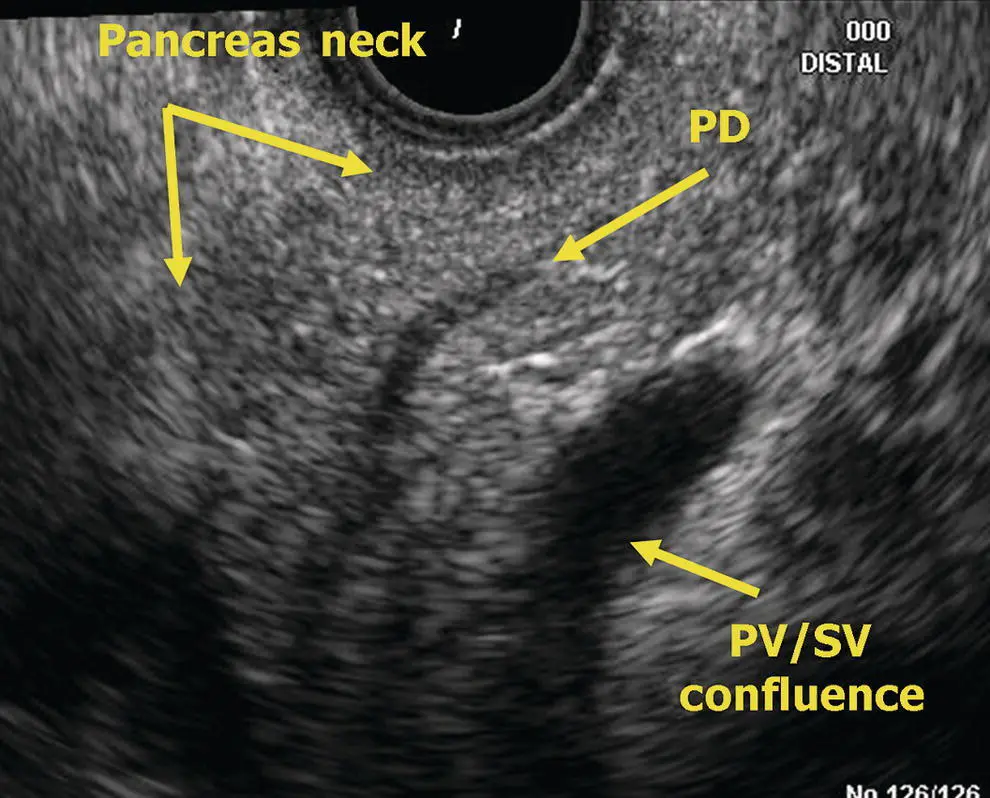
Figure 6.5 Radial EUS: pancreas neck. PD, pancreatic duct; PV, portal vein; SV, splenic vein.
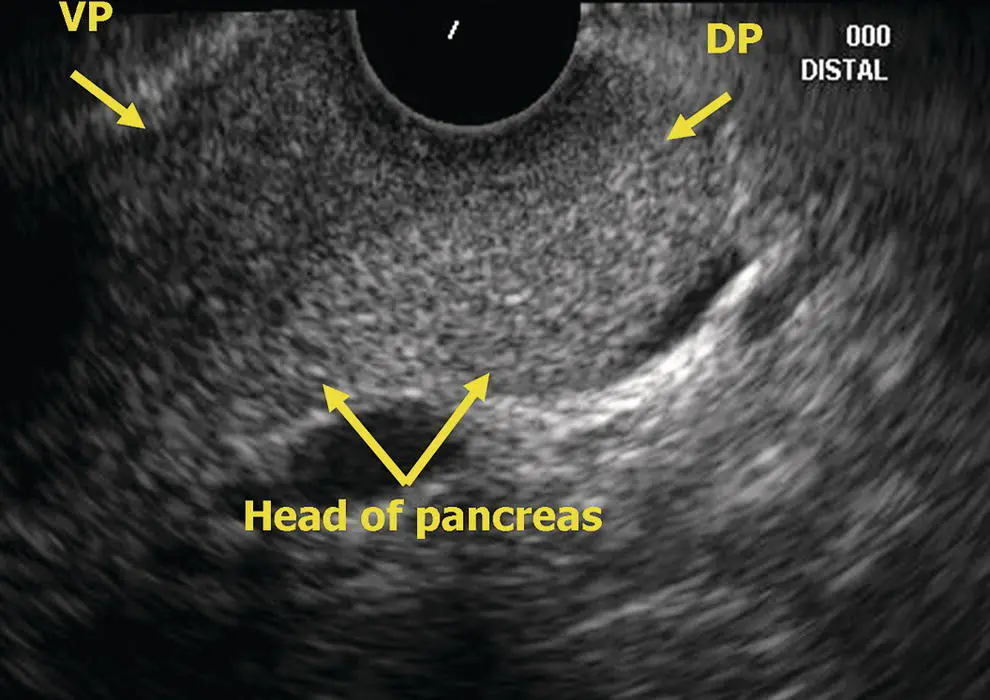
Figure 6.6 Radial EUS: head of pancreas. DP, dorsal pancreas; VP, ventral pancreas.
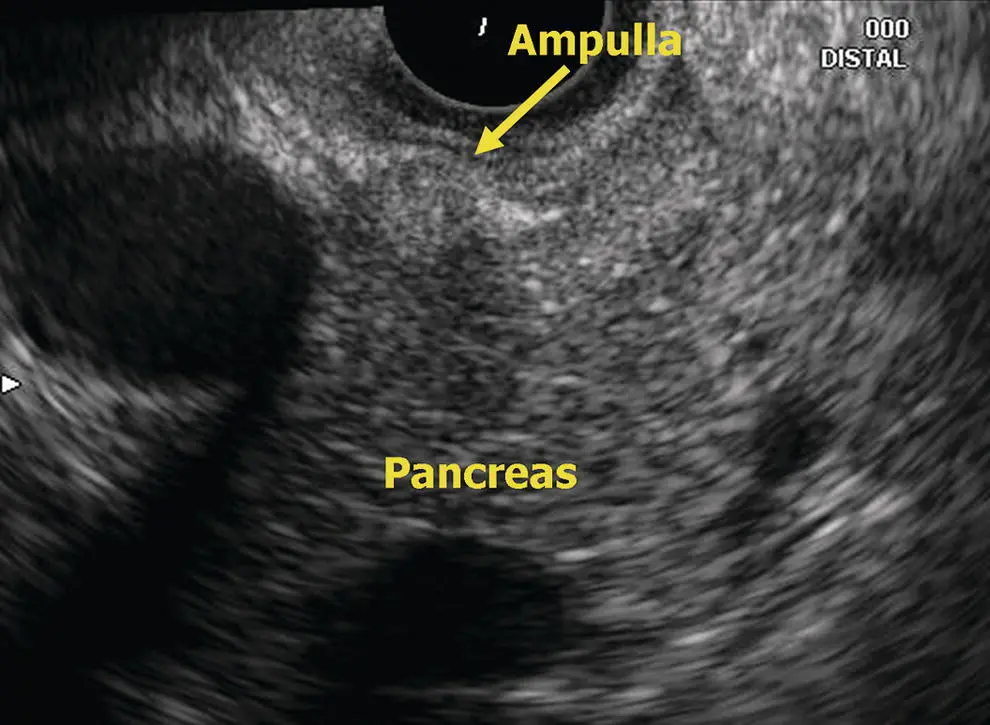
Figure 6.7 Radial EUS: ampulla.
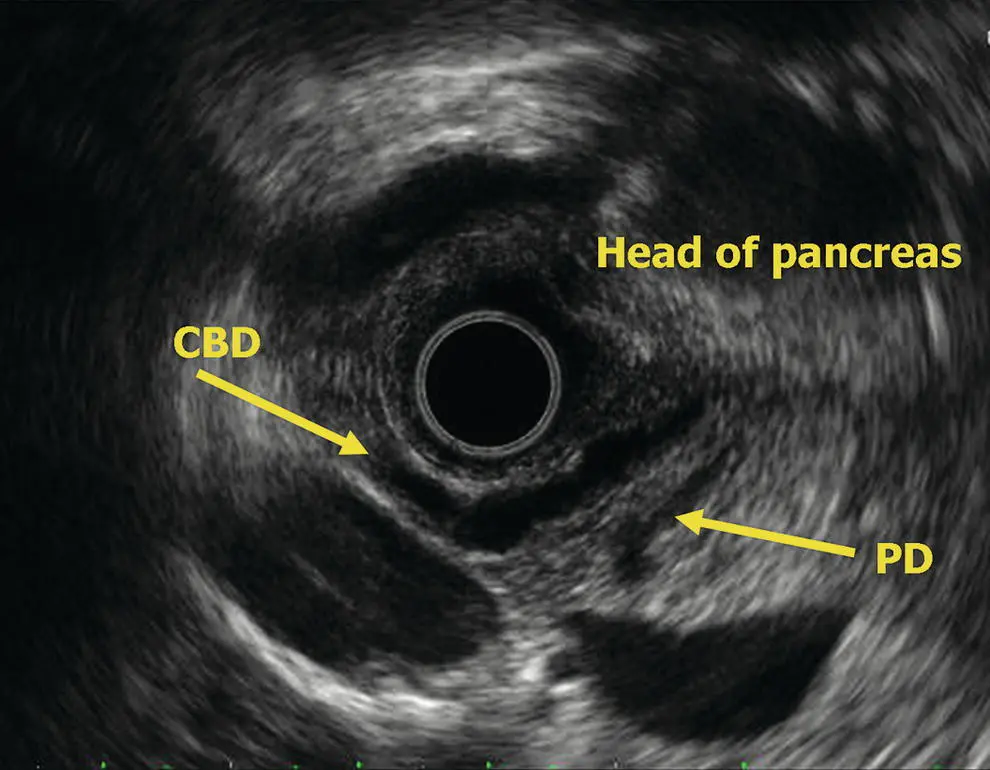
Figure 6.8 Radial EUS: head of pancreas. CBD, common bile duct; PD, pancreatic duct.
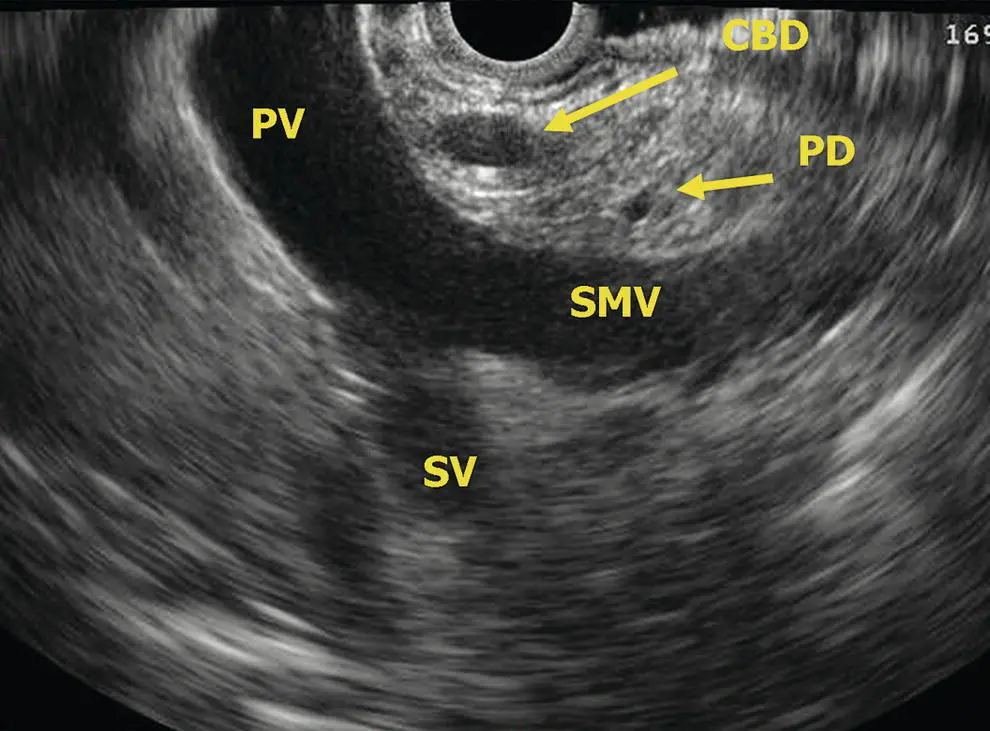
Figure 6.9 Radial EUS: head of pancreas, vasculature. CBD, common bile duct; PD, pancreatic duct; PV, portal vein; SMV, superior mesenteric vein; SV, splenic vein.
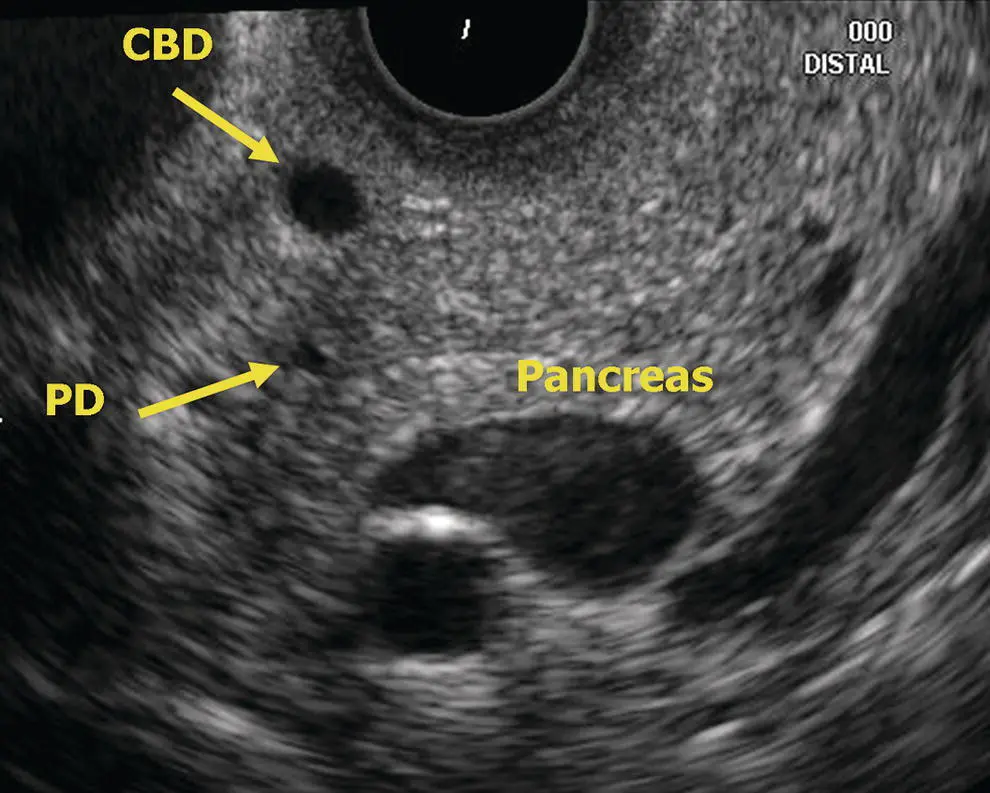
Figure 6.10 Radial EUS: head of pancreas. CBD, common bile duct; PD, pancreatic duct.
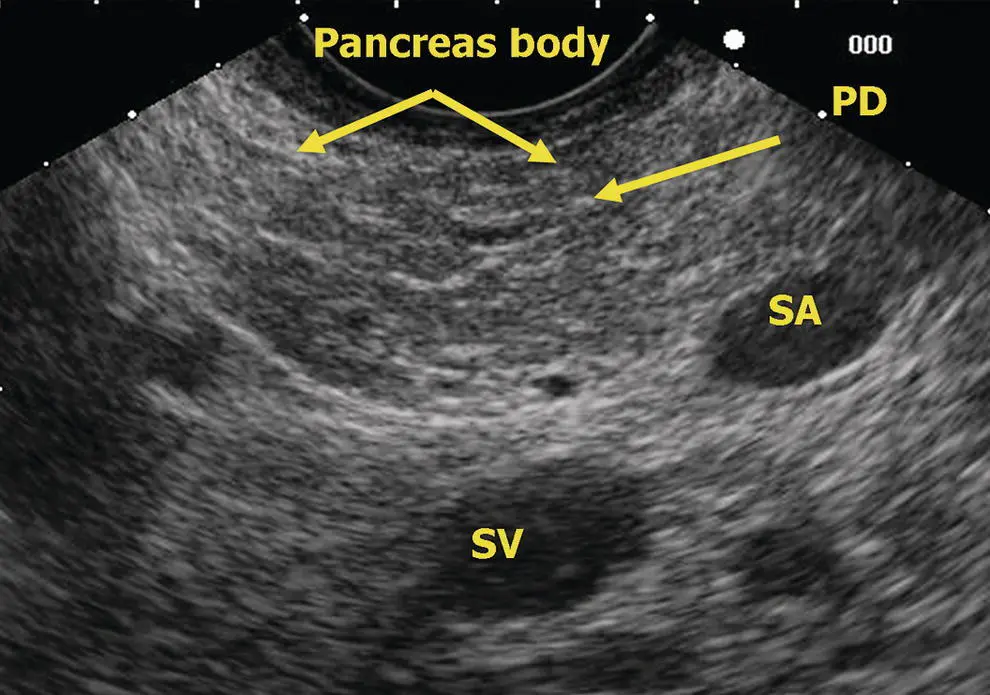
Figure 6.11 Linear EUS: pancreas body. PD, pancreatic duct; SA, splenic artery; SV, splenic vein.
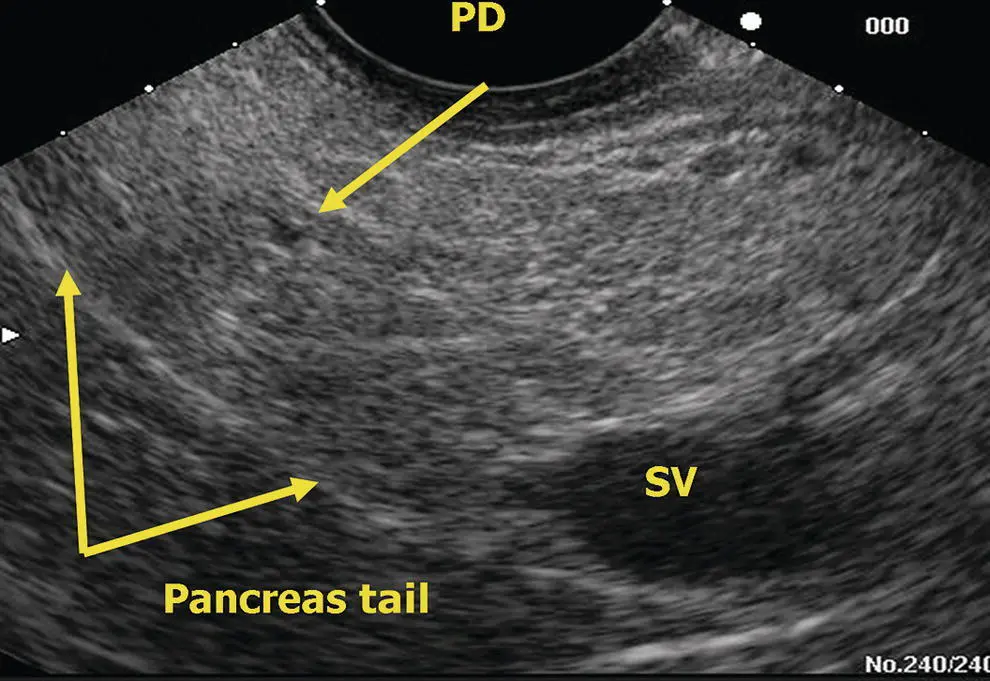
Figure 6.12 Linear EUS: pancreas tail. PD, pancreatic duct; SV, splenic vein.
As with radial endosonography, the linear duodenum presents the endosonographer with the most variability in endosonographic relationships of vessels, ducts, and periduodenal organs. There is a marked transition in the direction of the scope tip and therefore anatomic views between entering the duodenal bulb in a “long position,” where the scope tip is pointing cephalad and posterior, and a “short position” when withdrawing from the second portion of the duodenum, where the scope tip is pointing caudad. Generally, we try to start by inserting the linear echoendoscope deep into the second portion of the duodenum. With the echoendoscope in a short position in the second portion of the duodenum, the scope is designed to be facing the medial wall of the duodenum near the region of the ampulla ( Figure 6.13). On slightly rotating the scope right or left with very gentle withdrawal, usually the pancreatic duct will be seen first traveling relatively perpendicularly away from the transducer. The CBD will be seen to originate from the ampulla between the duodenal lumen and the pancreatic duct ( Figure 6.14). The pancreatic parenchyma seen at the level of the ampulla represents primarily the ventral pancreas. The relative echolucency of the ventral anlage commonly seen by radial endosonography may be less apparent by linear endoscopic ultrasound (EUS). At this level, if vessels are seen deep to the pancreatic head they are usually the superior mesenteric vein and artery. If one inserts the echoendoscope deeper into the third portion of the duodenum, the uncinate portion of the pancreas nestled among the vessels of the mesenteric root may be seen. Because this is a difficult view to get with a radial instrument, this view using a linear instrument is sometimes the only way in which deep uncinate tumors may be seen. From the ampullary region, further gradual withdrawal and rotation to the left (counterclockwise) will follow the course of the tubular structures of the porta hepatis. The pancreatic head will appear as the tissue between the superior mesenteric vein/portal vein and the duodenal wall.
Читать дальше
























