11 Index
12 About the Authors
13 Advertisement Page
14 Connect with Dummies
15 End User License Agreement
1 Chapter 2 TABLE 2-1 The pH Scale and the Associated Hydrogen Ion Concentration TABLE 2-2 The K aValues for Biologically Important Acids
2 Chapter 3 TABLE 3-1 Possible Bonds of Carbon and Selected Nonmetals TABLE 3-2 Acid-Base Properties of Biologically Important Functional Groups
3 Chapter 4TABLE 4-1 pK aValues for the Amino Acids
4 Chapter 6TABLE 6-1 Six Basic Types of EnzymesTABLE 6-2 Some Possible Types of Oxidation and Reduction ReactionsTABLE 6-3 Idealized Kinetics Data
5 Chapter 8TABLE 8-1 Common Fatty Acids
6 Chapter 12TABLE 12-1 Relationships between 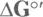 and KTABLE 12-2 Energy Released
and KTABLE 12-2 Energy Released 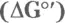 by Some High-Energy MoleculesTABLE 12-3 ATP Yield for Each Step in the Metabolism of GlucoseTABLE 12-4 ATP Yield for Each Step in the Metabolism of Stearic Acid
by Some High-Energy MoleculesTABLE 12-3 ATP Yield for Each Step in the Metabolism of GlucoseTABLE 12-4 ATP Yield for Each Step in the Metabolism of Stearic Acid
7 Chapter 13TABLE 13-1 Some Physiological Reduction Potentials (E’°)TABLE 13-2 Essential and Nonessential Amino Acids
8 Chapter 14TABLE 14-1 Ten Enzymes Necessary for Inosine SynthesisTABLE 14-2 Glucogenic and Ketogenic Amino AcidsTABLE 14-3 Essential and Nonessential Amino Acids
9 Chapter 15TABLE 15-1 Some Genetic Diseases in Humans
10 Chapter 16TABLE 16-1 The Standard Genetic Code
11 Chapter 17TABLE 17-1 Base-Pairing Rules for the Wobble Hypothesis
1 Chapter 1FIGURE 1-1: Simplified prokaryotic cell.FIGURE 1-2: Simplified illustration of an animal cell.FIGURE 1-3: Simplified illustration of a plant cell.
2 Chapter 2FIGURE 2-1: Structure of a water molecule.FIGURE 2-2: Structure of a typical amphipathic (both water-loving and water-hat...FIGURE 2-3: Structure of a micelle, composed of amphipathic molecules, with the...
3 Chapter 3FIGURE 3-1: Top: straight chain hydrocarbon expanded and condensed. Middle: bra...FIGURE 3-2: Examples of alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, and aromatic hydrocarbons.FIGURE 3-3: Oxygen- and sulfur-containing functional groups.FIGURE 3-4: Some nitrogen-containing functional groups.FIGURE 3-5: Phosphorous-containing functional groups.FIGURE 3-6: Acetals, hemiacetals, hemiketals, and ketals.FIGURE 3-7: Cis and trans isomers.FIGURE 3-8: The structure of glucose, a sugar with four chiral carbon atoms.FIGURE 3-9: The construction of a Fischer projection.FIGURE 3-10: Fischer projection formulas distinguish stereoisomers.
4 Chapter 4FIGURE 4-1: A zwitterion’s formation.FIGURE 4-2: (a) zwitterion form, (b) protonated form, and (c) deprotonated form...FIGURE 4-3: Different ways of drawing the Fischer projections of the amino acid...FIGURE 4-4: Nonpolar amino acids.FIGURE 4-5: Polar amino acids.FIGURE 4-6: Acidic amino acids.FIGURE 4-7: Basic amino acids.FIGURE 4-8: Two of the less common amino acids.FIGURE 4-9: Joining two cysteine molecules to form cystine.FIGURE 4-10: The formation of a peptide bond.FIGURE 4-11: Resonance stabilization of a peptide bond.FIGURE 4-12: A tripeptide.
5 Chapter 5FIGURE 5-1: Repeating sequence of the protein backbone.FIGURE 5-2: Structure of bovine insulin.FIGURE 5-3: Hydrogen bonding between two peptide bonds.FIGURE 5-4: The generic structure of an  -helix with its corresponding ribbon d...FIGURE 5-5: Parallel and antiparallel
-helix with its corresponding ribbon d...FIGURE 5-5: Parallel and antiparallel  -pleated sheet structures.FIGURE 5-6: Some tertiary structures appearing in proteins.
-pleated sheet structures.FIGURE 5-6: Some tertiary structures appearing in proteins.
6 Chapter 6FIGURE 6-1: General form, unbalanced, of two transferase catalyzed reactions.FIGURE 6-2: General form of two hydrolase catalyzed reactions.FIGURE 6-3: General form of two lyase catalyzed reactions.FIGURE 6-4: Examples of isomerase reactions catalyzed by a racemase and an epim...FIGURE 6-5: Reactions illustrating the action of the ligases pyruvate carboxyla...FIGURE 6-6: The Lock and Key Model of enzyme catalysis.FIGURE 6-7: The Induced-Fit Model of enzyme catalysis.FIGURE 6-8: Effect of an enzyme on a reaction.FIGURE 6-9: Plot of reaction rate, V, versus substrate concentration, [substrat...FIGURE 6-10: A Lineweaver-Burk plot.FIGURE 6-11: A Woolf plot.FIGURE 6-12: An Eadie-Hofstee plot.FIGURE 6-13: A Lineweaver-Burk plot indicating noncompetitive inhibition.FIGURE 6-14: A Lineweaver-Burk plot indicating competitive inhibition.
7 Chapter 7FIGURE 7-1: The relationship between the three-dimensional structure around a c...FIGURE 7-2: Structure of D-glucose.FIGURE 7-3: Structures of the D-aldohexoses.FIGURE 7-4: Structures of the D-ketohexoses.FIGURE 7-5: A pyranose ring.FIGURE 7-6: The Haworth projections for the pyranose structures of D-glucose.FIGURE 7-7: A furanose ring.FIGURE 7-8: Two forms of D-fructose.FIGURE 7-9: Two representations of the structure of D-ribose.FIGURE 7-10: D-ribitol.FIGURE 7-11: D-ribonic acid, an aldonic acid.FIGURE 7-12: D-ribouronic acid, a uronic acid.FIGURE 7-13: D-ribose-1-phosphate.FIGURE 7-14: Glyceraldehyde and dihydroxyacetone.FIGURE 7-15: The arrows point to the positions of the alcohol groups leading to...FIGURE 7-16: The structure of maltose with a  (1-4) linkage present.FIGURE 7-17: Cellobiose showing its
(1-4) linkage present.FIGURE 7-17: Cellobiose showing its  (1-4) linkage.FIGURE 7-18: Structure of sucrose, formed by joining
(1-4) linkage.FIGURE 7-18: Structure of sucrose, formed by joining  -D-glucose and
-D-glucose and  -D-fructo...FIGURE 7-19: Disaccharide repeating units in hyaluronate and heparin.FIGURE 7-20: Symbolic representations of the members of the D-aldose family.FIGURE 7-21: The relative positions of the
-D-fructo...FIGURE 7-19: Disaccharide repeating units in hyaluronate and heparin.FIGURE 7-20: Symbolic representations of the members of the D-aldose family.FIGURE 7-21: The relative positions of the 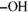 groups in the bottom row of Figure...FIGURE 7-22: The overall pattern in Figure 7-20.
groups in the bottom row of Figure...FIGURE 7-22: The overall pattern in Figure 7-20.
8 Chapter 8FIGURE 8-1: The relationships among the many types of lipids.FIGURE 8-2: Representation of a soap.FIGURE 8-3: Structure of glycerol.FIGURE 8-4: Structure of a typical fat: Upper chains are saturated; bottom chai...FIGURE 8-5: Examples of the general formulas of a phosphatidylethanolamine and ...FIGURE 8-6: Alcohol components of lipids.FIGURE 8-7: Structure of sphingosine.FIGURE 8-8: A simplified representation of a lipid bilayer.FIGURE 8-9: An integral protein that doesn’t pass through the membrane.FIGURE 8-10: An integral protein passing through the membrane.FIGURE 8-11: Basic structure of a steroid.FIGURE 8-12: Structures of arachidonic acid and a typical prostaglandin, thromb...
9 Chapter 9FIGURE 9-1: Basic purine structure (top) and basic pyrimidine structure (bottom...FIGURE 9-2: Adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), thymine (T), and uracil (U)...FIGURE 9-3: Structures of the 5-carbon sugars present in nucleic acids.FIGURE 9-4: Structure of phosphoric acid.FIGURE 9-5: General reaction for the formation of a nucleoside.FIGURE 9-6: Structure of the nucleoside adenosine.FIGURE 9-7: Simplified representation of the formation of a nucleotide.FIGURE 9-8: Structure of adenosine monophosphate (AMP).FIGURE 9-9: Simplified representation of the joining of two nucleotides.FIGURE 9-10: 5’ and 3’ carbon atoms on adenosine monophosphate.FIGURE 9-11: Hydrogen bonds (dotted lines) form between adenine (right) and thy...FIGURE 9-12: Hydrogen bonds (dotted lines) form between guanine (right) and cyt...FIGURE 9-13: Hydrogen bonds (dotted lines) form between adenine (right) and ura...FIGURE 9-14: The secondary structure of DNA.
Читать дальше

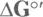 and KTABLE 12-2 Energy Released
and KTABLE 12-2 Energy Released 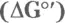 by Some High-Energy MoleculesTABLE 12-3 ATP Yield for Each Step in the Metabolism of GlucoseTABLE 12-4 ATP Yield for Each Step in the Metabolism of Stearic Acid
by Some High-Energy MoleculesTABLE 12-3 ATP Yield for Each Step in the Metabolism of GlucoseTABLE 12-4 ATP Yield for Each Step in the Metabolism of Stearic Acid -helix with its corresponding ribbon d...FIGURE 5-5: Parallel and antiparallel
-helix with its corresponding ribbon d...FIGURE 5-5: Parallel and antiparallel  -pleated sheet structures.FIGURE 5-6: Some tertiary structures appearing in proteins.
-pleated sheet structures.FIGURE 5-6: Some tertiary structures appearing in proteins. (1-4) linkage present.FIGURE 7-17: Cellobiose showing its
(1-4) linkage present.FIGURE 7-17: Cellobiose showing its  (1-4) linkage.FIGURE 7-18: Structure of sucrose, formed by joining
(1-4) linkage.FIGURE 7-18: Structure of sucrose, formed by joining  -D-glucose and
-D-glucose and  -D-fructo...FIGURE 7-19: Disaccharide repeating units in hyaluronate and heparin.FIGURE 7-20: Symbolic representations of the members of the D-aldose family.FIGURE 7-21: The relative positions of the
-D-fructo...FIGURE 7-19: Disaccharide repeating units in hyaluronate and heparin.FIGURE 7-20: Symbolic representations of the members of the D-aldose family.FIGURE 7-21: The relative positions of the 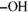 groups in the bottom row of Figure...FIGURE 7-22: The overall pattern in Figure 7-20.
groups in the bottom row of Figure...FIGURE 7-22: The overall pattern in Figure 7-20.










