Consumption of a combination of prebiotics and probiotics appropriately selected can improve the beneficial effects of the compounds when used individually. Fructooligosaccharides and inulin can stimulate the growth of bifidobacterial in the intestine (bifidogenic effect) and suppress the activity of undesirable bacteria (Enterococcus faecalis, Escherichia coli , and Proteus genus). Consequently, there is a reduction in the pH values because the beneficial microorganisms produce acids, and an antagonist effect against harmful or pathogenic bacteria may be observed, with decreases in the concentration of toxic metabolites [77].
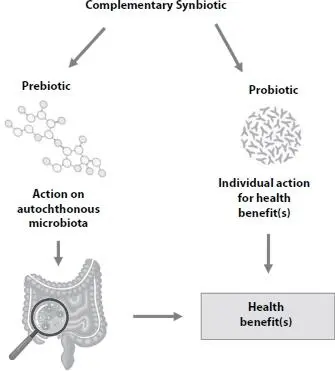
Figure 2.2 Mechanism of action of a complementary synbiotic.
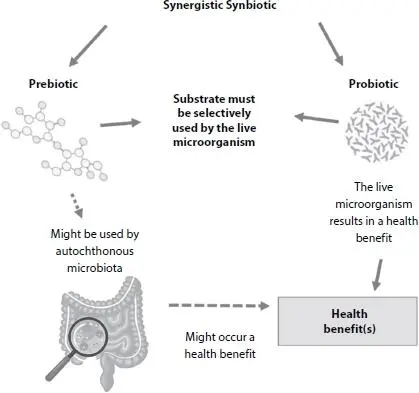
Figure 2.3 Mechanism of action of a synergistic synbiotic.
The synergistic activity between prebiotics probiotics and was considered efficient because they could improve the implantation and survival of probiotics in the gastrointestinal tract. Some health effects of orally administered combinations of live microorganisms and a prebiotic substrate are reported in Figure 2.4[15]. Randomized controlled trials have been reported including adults with overweight, metabolic diseases, obesity, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and type 2 diabetes mellitus [15]. In addition, the investigation of other outcomes also was conducted, such as surgical infections, irritable bowel syndrome, atopic dermatitis, chronic kidney disease, eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection, and management of gestational diabetes mellitus [15]. However, it is important to note that for a formulation to be called synbiotic, there needs to be evidence to prove the selective use by the host microbiota (complementary synbiotic) or by the live microorganism that is co-administered (synergistic synbiotic) [15].
Synbiotics have as the main benefit the increase in the permanence of probiotics in the gastrointestinal environment. Synbiotics can control infections, which is associated with the formation of compounds during the fermentation process in the large intestine by probiotic cultures [78]. They can improve the functionality of epithelial barriers and modify the ecosystem of bacteria [79]. Prebiotics can improve the microbiota of the large intestine, while probiotics can also act in the small intestine. In an ideal synbiotic product, a synergistic action is observed between beneficial microorganisms (probiotics) and the selected substrate (prebiotics), increasing the activity of the probiotic culture. The increases in the probiotic activity is associated with greater health benefits [80, 81].
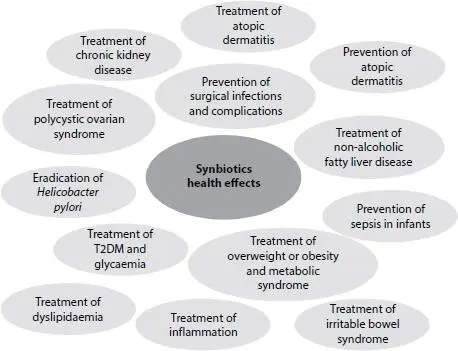
Figure 2.4 Synbiotics health benefits tested with human trials. Adapted from Swanson et al . [15].
2.5 Synbiotic Dairy Functional Foods
Functional dairy foods represent an excellent alternative of foods that presents additional beneficial properties to consumers. Probiotics, prebiotics, or their combination (synbiotics) are the primary three categories of functional dairy products [82]. The balanced combinations of probiotics and prebiotics, resulting in ingredients with the functional characteristics of both groups are reported as synbiotics. In the literature, several workers are reporting the production of synbiotic dairy products, since they represent an excellent way to carry live and active cultures. Table 2.4describes examples of the application of probiotic bacteria in association with prebiotics (synbiotics) in dairy products. Dairy beverages and yogurt are the most explored matrices since the use of synbiotic in dairy products can multiply the positive effects of this kind of food on the host. In a randomized study, individuals who consumed yogurt added with isomaltooligosaccharide (0.6%) and B. lactis Bi-07 and L. acidophilus NCFM as probiotic cultures showed higher populations of bifidobacterial and lactobacilli in the colon. In addition, synbiotic yogurt may have immunomodulatory properties [83]. The ability of synbiotic fermented milk containing isomaltooligosaccharide (1%) and Lacticaseibacillus paracasei 01 (10 8CFU/mL) to defend epithelial cells (in vitro) was evaluated. The synbiotic fermented beverage was capable of protect the intestinal cells [84]. In addition, kefir supplementation with isomaltooligosaccharide (4%) reduced the fermentation time and improved the acidification rate. The reduction in the fermentation time may provide lower costs to the industries [85].
Table 2.4 Examples of synbiotic dairy products. Adapted from Dantas et al. [47].
| Product |
Probiotic strain |
Prebiotic |
Raw material |
Reference |
| Cheese |
Enterococcus faecium NRRL B-2354, Bifidobacterium longum NRRL B-41409, Lacticaseibacillus paracasei subsp. paracasei NRRL B-4560 |
Inulin and oligofructose |
Goat milk |
[93] |
| Cream cheese |
Bifidobacterium animalis subsp lactis Bb-12 and Lactobacillus acidophilus LA-05 |
Inulin |
Goat milk |
[87] |
| Chevrotin cheese |
Bifidobacterium lactis |
Inulin |
Cow and goat milk |
[94] |
| Fresh cheese |
Bifidobacterium lactis BB-12 |
Inulin |
Cryoconcentrated milk |
[95] |
| Mascarpone cheese |
Bifidobacterium lactis BB-12 |
Inulin |
Milk cream |
[96] |
| Greek-type yogurt |
Microencapsulated Bifidobacterium lactis BB-12 |
Inulin |
Cow milk |
[97] |
| Cupuaçu yogurt |
Lactobacillus acidophilus LA-5 |
Inulin |
Goat milk and cupuassu |
[98] |
| Yogurt |
Lactobacillus acidophilus L10 DSM, Lactobacillus acidophilus L10 NCFM, Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis Bl04, Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis HN019 |
Powdered passion fruit peel (potential prebiotic) |
Skimmed milk powder, whole milk powder |
[99] |
| Yogurt |
Lactobacillus acidophilus, Bifidobacterium bifidium |
Lactulose, oligofructose, and inulin |
Buffalo milk |
[100] |
| Chocolate milk beverage |
Bifidobacterium lactis |
A mix of inulin and oligofructose |
Goat milk, goat whey |
[101] |
| Milk beverage |
Lacticaseibacillus paracasei |
Inulin and oligofructose |
Cow milk |
[102] |
| Milk beverage |
Bifidobacterium lactis BB-12, Lactobacillus acidophilus LA-5 |
Oligofructose |
Cow milk and whey |
[103] |
| Peach ice cream |
Bifidobacterium lactis BB-12 |
Inulin |
Cow milk |
[104] |
| Ice cream |
Bifidobacterium lactis and Lacticaseibacilluscasei microencapsulated with sodium alginate and Camellia sinensis extract. |
Camellia sinensis (potential prebiotic) |
Cow milk and milk cream |
[105] |
| Ice cream |
Pediococcus pentosaceus UAM22 |
Inulin |
Cow milk and whey protein |
[106] |
| Dairy chocolate dessert |
Lacticaseibacillus paracasei subsp. paracasei LBC 81 |
Fructooligosaccharide |
Cow milk |
[86] |
Due to high overall liking, dairy chocolate desserts can be innovative synbiotic products [86]. The addition of inulin to a synbiotic creamy cheese and ice cream processed with goat milk resulted in improved texture properties (consistency), which was associated with its high capacity of holding water, resulting in decreased syneresis and important changes in texture and viscosity. In this way, probiotics and inulin could be used to manufacture creamy goat cheese with maintenance of the overall quality characteristics of the product and improving its functional potential [87].
Читать дальше













