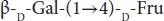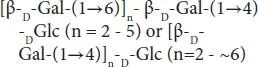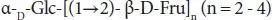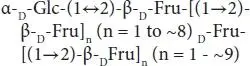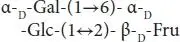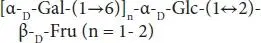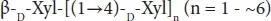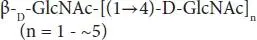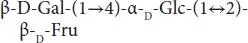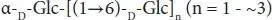1 ...8 9 10 12 13 14 ...31 In the same direction, the market for synbiotic products has also been increasing considerably. When a prebiotic and probiotic are used simultaneously in a product, the combination is called synbiotic. The updated definition of a synbiotic is “a mixture containing living microorganisms and substrate(s) used selectively by host microorganisms that confer a benefit to the host’s health” [15]. The requirement that the components should meet for evidence of its beneficial action and prove the dose established for prebiotics and probiotics individually, could represent a difficult scenario [15]. Thus, there are two different categories of synbiotics, the complementary and the synergistic synbiotic [15]. In a complementary synbiotic, the prebiotic and probiotic works independently in order to provide at least one health benefit, while a synergistic synbiotic is the mixture of the selectively utilized substrate (prebiotic) and a live microorganism (probiotic), which works together to achieve one or more health benefits [15]. With these new and defined terms and their confusion cleared up, it became much easier for the industry and researchers to explore and create new synbiotics.
In this sense, recently, it was observed an increased quantity of scientific studies using prebiotics or synbiotics ingredients with prospective health claims in dairy products. This chapter will present the main updates on prebiotic and synbiotic dairy products and their health benefits.
In 2017, the term prebiotic was redefined as “a substrate that is selectively used by host microorganisms that confer a health benefit” [10]. Prebiotics are often associated with carbohydrates of low molecular weight which are not digested in the human gastrointestinal tract and could positively improve the activity and composition of the microbiota of the intestine. However, the more recently definition of prebiotics opens opportunities to other compounds, such as polyunsaturated fatty acid, phytochemicals, linoleic acid, and phenolic compounds. Furthermore, it allows the utilization of prebiotics in many parts of the body besides the gastrointestinal tract and also other products, such as feed for poultry, aquaculture, and livestock [10]. In 2018, a group of scientists met again to analyse the advances in the prebiotics field, focusing on topics that affect research methodology, functionality, and geographical impacts [16]. Prebiotics are commonly highlighted in the studies, but the mechanisms of action and the health benefits need further evaluations [17].
Non-digestible carbohydrates, such as oligosaccharides, such as galactooligosaccharides (GOS), fructooligosaccharides (FOS), isomaltooligosaccharides (IMO), xylooligosaccharides (XOS), raffinose oligosaccharides (RFOs), mannan oligosaccharides (MOS), arabinoxylan oligosaccharides (AXOS), inulin, lactulose, and others, and polysaccharides (pectin, resistant starch, and dextrin) are considered food components with prebiotic properties ( Table 2.2) [12].
The prebiotics with established health effects are separated into three groups: I) oligosaccharides (GOS, inulin, FOS, IMO, XOS, isomaltulose, RFOS, among others), II) polyols (xylitol, lactulose, lactitol, mannitol), and III) fibers (dextrins, cellulose, β-glucans, pectins) [18]. They have a diversity of chemical compositions, and the differences in the units (monosaccharides) and the type of glycosidic bonds in the non-digestible carbohydrates enable the prebiotics to be classified in many classes of oli-gossacharides [19].
The intestinal microbiota ferments the prebiotic compounds and can produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFA), such as acetate, propionate, and butyrate. These compounds can enhance many physiological effects, such as the function of the intestine, the absorption of minerals, the regulation of the metabolism of glucose and lipids, and also could reduce the risk of colon cancer [10]. Some health effects of orally administered combinations of a prebiotic substrate are reported in Figure 2.1[10]. The consumption of prebiotics can favor the increase in the counts of beneficial bacteria and hinder the establishment of pathogenic bacteria, reducing the risk allergies and infections [18]. There are convincing and reproducible results in the literature of studies on animals that have consumed prebiotics demonstrating effectiveness in the reduction of risk or treatment of many diseases, e.g., irritable bowel syndrome, colon cancer, obesity, cardiovascular diseases and type 2 diabetes [16].
Table 2.2 Prebiotic substances, their source, and structure. Adapted from Sako and Tanaka [20].
| Designation |
Source |
Structure |
| Lactulose |
Lactose |
 |
| Galactooligosaccharides |
Lactose |
 |
| Fructooligosaccharides |
Sucrose |
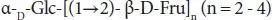 |
| Inulin-type fructans |
Inulin |
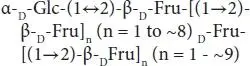 |
| Raffinose |
Beet |
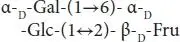 |
| Soy oligosaccharides |
Soy extract |
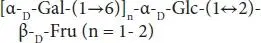 |
| Xylooligosaccharides |
Xylan |
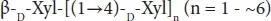 |
| Chitin oligosaccharides |
Chitin |
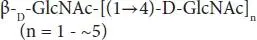 |
| Lactosaccharose |
Lactose, sucrose |
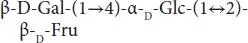 |
| Isomaltooligosaccharides |
Starch |
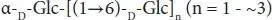 |
Fru, fructose; Gal, galactose; Xyl, xylose; Glc, glucose; Fuc, fucose; GlcNAc, N-acetylglucosamine; NeuAc, sialic acid.
Among the most studied prebiotics, lactulose, galactooligosaccharides, fructooligosaccharides, and inulin can be highlighted. Lactulose is a disaccharide produced synthetically through the chemical isomerization of lactose in alkaline conditions. Lactulose also appears naturally in milk, is not metabolized in the human digestive system, and is preferably used by lactobacilli and bifidobacteria [20]. Lactulose proved to be a prebiotic compound when 10 g was consumed daily by healthy adults, resulting in increases in the bifidobacterial counts, and decreases in clostridia counts [21]. Furthermore, the consumption of foods with lactulose (4 g), Ca (300 mg) and Mg (150 mg) by healthy adults (n = 24) resulted in increased absorption of magnesium and calcium [22]. The improvements in Ca absorption was also reported in postmenopausal women after consumption of lactulose for 9 days [23].
Читать дальше