Robert P. Dobrow - Probability
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Robert P. Dobrow - Probability» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Probability
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:4 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
Probability: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Probability»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
distinguished researchers Drs. Robert Dobrow and Amy Wagaman deliver a thorough introduction to the foundations of probability theory. The book includes a host of chapter exercises, examples in R with included code, and well-explained solutions. With new and improved discussions on reproducibility for random numbers and how to set seeds in R, and organizational changes, the new edition will be of use to anyone taking their first probability course within a mathematics, statistics, engineering, or data science program.
New exercises and supplemental materials support more engagement with R, and include new code samples to accompany examples in a variety of chapters and sections that didn’t include them in the first edition.
The new edition also includes for the first time:
A thorough discussion of reproducibility in the context of generating random numbers Revised sections and exercises on conditioning, and a renewed description of specifying PMFs and PDFs Substantial organizational changes to improve the flow of the material Additional descriptions and supplemental examples to the bivariate sections to assist students with a limited understanding of calculus Perfect for upper-level undergraduate students in a first course on probability theory, is also ideal for researchers seeking to learn probability from the ground up or those self-studying probability for the purpose of taking advanced coursework or preparing for actuarial exams.

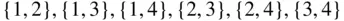
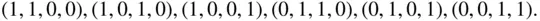
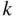 -element subset, there are
-element subset, there are 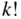 ordered lists that can be formed by permuting the elements of that subset. For instance, the three-element subset
ordered lists that can be formed by permuting the elements of that subset. For instance, the three-element subset 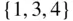 yields the
yields the 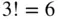 lists: (1,3,4), (1,4,3), (3,1,4), (3,4,1), (4,1,3), and (4,3,1).
lists: (1,3,4), (1,4,3), (3,1,4), (3,4,1), (4,1,3), and (4,3,1). made up of the elements
made up of the elements  is equal to
is equal to 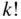 times the number of
times the number of 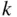 -element subsets of
-element subsets of  By the multiplication principle, there are
By the multiplication principle, there are  such lists. Thus, the number of
such lists. Thus, the number of 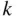 -element subsets of
-element subsets of  is equal to
is equal to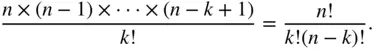
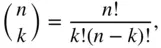
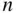 choose
choose  .” On calculators, the option may be shown as “
.” On calculators, the option may be shown as “ 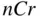 .”
.”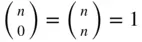
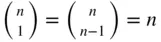

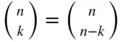
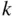 objects from
objects from 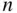 is equal to the number of permutations of
is equal to the number of permutations of 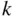 objects out of
objects out of 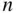 objects divided by the factorial of
objects divided by the factorial of 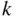 , the size of the subset desired (the number of permutations of the
, the size of the subset desired (the number of permutations of the 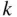 objects). This is accounting for the fact that in combinations, we do not care about the order of the objects in the subset.
objects). This is accounting for the fact that in combinations, we do not care about the order of the objects in the subset.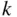 -element subsets and binary lists with exactly
-element subsets and binary lists with exactly 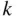 ones, we have the following.
ones, we have the following.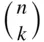
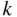 -element subsets of
-element subsets of  .
.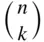 binary lists of length
binary lists of length 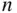 with exactly
with exactly 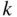 ones.
ones. ways to select a subset of
ways to select a subset of 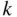 objects from a set of
objects from a set of 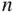 objects when the order the objects are selected in does not matter.
objects when the order the objects are selected in does not matter.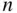 and
and 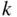 , where
, where 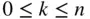 . For
. For 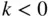 or
or 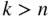 , set
, set 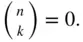 Common values of binomial coefficients are given in Table 1.4.
Common values of binomial coefficients are given in Table 1.4.










