Example 1.15 A bag contains six Scrabble tiles with the letters A-D-M-N-O-R. You reach into the bag and take out tiles one at a time. What is the probability that you will spell the word R-A-N-D-O-M?How many possible words can be formed? All the letters are distinct and a “word” is a permutation of the set of six letters. There are possible words. Only one of them spells R-A-N-D-O-M, so the desired probability is
Example 1.16 Scrabble continued. Change the previous example. After you pick a tile from the bag, write down that letter and then return the tile to the bag. So every time you reach into the bag, it contains the six original letters. What is the probability that you spell R-A-N-D-O-M now when drawing six tiles?With the change, there are possible words, and only one still spells R-A-N-D-O-M, so the desired probability is
Sampling with and without replacement
The last examples highlight two different sampling methods called sampling without replacement and sampling with replacement . When sampling with replacement, a unit that is selected from a population is returned to the population before another unit is selected. When sampling without replacement, the unit is not returned to the population after being selected. When solving a probability problem involving sampling (such as selecting cards or picking balls from urns), make sure you know the sampling method before computing the related probability.
Example 1.17 When national polling organizations conduct nationwide surveys, they often select about 1000 people sampling without replacement. If is the number of people in a target population, then by the multiplication principle there are possible ordered samples. For national polls in the United States, where , the number of people age 18 or over, is about 250 million, that gives about 250,000,000 possible ordered samples, which is a mind-boggling 2.5 with 8000 zeros after it.
As defined, permutations tell us the number of possible arrangements of 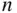 objects where all objects are distinguishable and order matters when sampling without replacement. As in the last example, perhaps we only want to arrange
objects where all objects are distinguishable and order matters when sampling without replacement. As in the last example, perhaps we only want to arrange 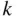 of the
of the 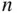 objects,
objects, 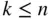 , sampling without replacement where order matters. What changes when we want to know the number of permutations of
, sampling without replacement where order matters. What changes when we want to know the number of permutations of 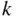 objects out of
objects out of  ?
?
The first object can still be any of the 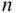 objects, while the second can be any of the remaining
objects, while the second can be any of the remaining 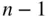 objects, etc. However, rather than continuing to the last of the
objects, etc. However, rather than continuing to the last of the 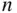 objects, we stop at the
objects, we stop at the  th object. Considering the pattern, the
th object. Considering the pattern, the 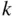 th object can be any of the remaining
th object can be any of the remaining 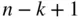 objects at that point. Thus, the number of possible arrangements is
objects at that point. Thus, the number of possible arrangements is  which is more easily written as
which is more easily written as 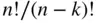 We illustrate this in the following examples.
We illustrate this in the following examples.
Example 1.18 A club with seven members needs to elect three officers (president, vice president, and secretary/treasurer) for the upcoming year. Members can only hold one position. How many sets of officers are possible?Thinking through the problem, the president can be any of the seven members. Once the president is in place, the vice president can be any of the remaining six members, and finally, the secretary/treasurer can be any of the remaining five members. By the multiplication rule, the number of possible sets of officers is . We obtain the same result with and , as .
Example 1.19 A company decides to create inventory stickers for their product. Each sticker will consist of three digits (0–9) which cannot repeat among themselves, two capital letters which cannot repeat, and another three digits that cannot repeat amongst themselves. For example, valid stickers include 203AZ348 and 091BE289, but 307JM449 is not valid. How many different possible stickers can the company make?We use both permutations and the multiplication rule to solve the problem. For the three digits, there are possible options and we need in order. This occurs twice. For each set of digits, there are thus arrangements possible. For the capital letters, there are options with . Thus, the number of possible arrangements is . Combining this we find the number of possible stickers is . The company can keep inventory on up to almost 337 million objects with this scheme for stickers.
In the last section, you learned how to count ordered lists and permutations. Here we count unordered sets and subsets. For example, given a set of 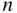 distinct objects, how many subsets of size
distinct objects, how many subsets of size 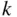 can we select when sampling without replacement? To proceed, we first show a simple yet powerful correspondence between subsets of a set and binary sequences, or lists. This correspondence will allow us to relate counting results for sets to those for lists, and vice versa.
can we select when sampling without replacement? To proceed, we first show a simple yet powerful correspondence between subsets of a set and binary sequences, or lists. This correspondence will allow us to relate counting results for sets to those for lists, and vice versa.
A binary sequence is a list, each of whose elements can take one of two values, which we generically take to be zeros and ones. Our questions about subsets of size 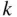 drawn from
drawn from 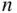 distinct objects is equivalent to asking: how many binary sequences of length
distinct objects is equivalent to asking: how many binary sequences of length 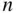 contain exactly
contain exactly  ones?
ones?
To illustrate, consider a group of 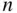 people lined up in a row and numbered 1 to
people lined up in a row and numbered 1 to 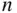 . Each person holds a card. On one side of the card is a 0; on the other side is a 1. Initially, all the cards are turned to 0. The
. Each person holds a card. On one side of the card is a 0; on the other side is a 1. Initially, all the cards are turned to 0. The 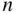 cards from left to right form a binary list.
cards from left to right form a binary list.
Читать дальше

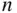 objects where all objects are distinguishable and order matters when sampling without replacement. As in the last example, perhaps we only want to arrange
objects where all objects are distinguishable and order matters when sampling without replacement. As in the last example, perhaps we only want to arrange 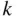 of the
of the 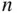 objects,
objects, 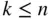 , sampling without replacement where order matters. What changes when we want to know the number of permutations of
, sampling without replacement where order matters. What changes when we want to know the number of permutations of 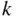 objects out of
objects out of  ?
?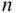 objects, while the second can be any of the remaining
objects, while the second can be any of the remaining 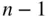 objects, etc. However, rather than continuing to the last of the
objects, etc. However, rather than continuing to the last of the 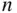 objects, we stop at the
objects, we stop at the  th object. Considering the pattern, the
th object. Considering the pattern, the 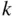 th object can be any of the remaining
th object can be any of the remaining 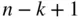 objects at that point. Thus, the number of possible arrangements is
objects at that point. Thus, the number of possible arrangements is  which is more easily written as
which is more easily written as 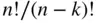 We illustrate this in the following examples.
We illustrate this in the following examples. distinct objects, how many subsets of size
distinct objects, how many subsets of size 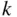 can we select when sampling without replacement? To proceed, we first show a simple yet powerful correspondence between subsets of a set and binary sequences, or lists. This correspondence will allow us to relate counting results for sets to those for lists, and vice versa.
can we select when sampling without replacement? To proceed, we first show a simple yet powerful correspondence between subsets of a set and binary sequences, or lists. This correspondence will allow us to relate counting results for sets to those for lists, and vice versa.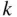 drawn from
drawn from 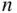 distinct objects is equivalent to asking: how many binary sequences of length
distinct objects is equivalent to asking: how many binary sequences of length 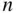 contain exactly
contain exactly  ones?
ones?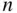 people lined up in a row and numbered 1 to
people lined up in a row and numbered 1 to 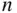 . Each person holds a card. On one side of the card is a 0; on the other side is a 1. Initially, all the cards are turned to 0. The
. Each person holds a card. On one side of the card is a 0; on the other side is a 1. Initially, all the cards are turned to 0. The 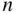 cards from left to right form a binary list.
cards from left to right form a binary list.










