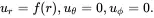 (3.13)
(3.13)
The corresponding strain field obtained from (2.142) is then given by
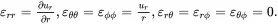 (3.14)
(3.14)
The stress field follows from stress-strain relations expressed in the form (see (2.160) for the Cartesian equivalent)
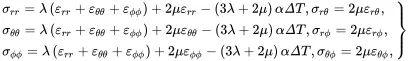 (3.15)
(3.15)
where λ and μ are Lamé’s constants and where α is now the linear coefficient of thermal expansion. On using the equilibrium equations (2.130)–(2.133), it can be shown that, within the spherical particle of radius a , the resulting bounded displacement and stress fields are given by
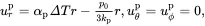 (3.16)
(3.16)
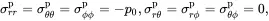 (3.17)
(3.17)
where kp= λp+23μp and μp are the bulk and shear moduli, respectively, for the particulate reinforcement, and where αp is the corresponding thermal expansion coefficient. Clearly the strain and stress distributions within the particle are both uniform. For the matrix region it can be shown that
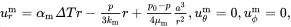 (3.18)
(3.18)
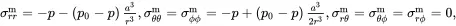 (3.19)
(3.19)
where km= λm+23μm and μm are the bulk and shear moduli, respectively, for the matrix, and where αm is the corresponding thermal expansion coefficient. The stress component σrr is automatically continuous across r = a having the value −p0. As the displacement component ur must also be continuous across this interface, the value of p 0must satisfy the relation
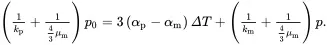 (3.20)
(3.20)
3.3.2 Applying Maxwell’s Methodology to Isotropic Multiphase Particulate Composites
Owing to the use of the far-field in Maxwell’s methodology, it is again possible to consider multiple types of spherical reinforcement. The perturbing effect in the matrix at large distances from the cluster of particles is estimated by superimposing the perturbations caused by each particle, regarded as being isolated, and regarding all particles to be located at the origin. The properties of particles of type i are denoted by a superscript (i).
Relations ( 3.19) for nonzero stresses in the matrix are generalised to
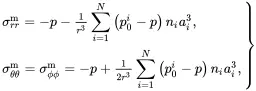 (3.21)
(3.21)
where p0i is the pressure at the particle/matrix interface when an isolated particle of species i is placed in infinite matrix material. From ( 3.20) the following value of p0i−p is obtained
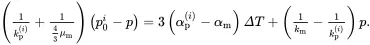 (3.22)
(3.22)
It then follows that the stress distribution in the matrix at large distances from the discrete cluster of particles shown in Figure 3.1(a) is approximately given by
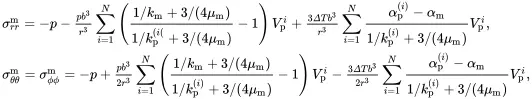 (3.23)
(3.23)
where the volume fractions Vpi of particles of type i defined by ( 3.1) have been introduced.
When ( 3.23) is applied to a single sphere of radius b , having the effective properties of a composite representing the multiphase cluster of particles embedded in matrix material (see Figure 3.1(b)), the exact matrix stress distribution, for given values of keff and αeff, is
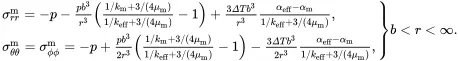 (3.24)
(3.24)
Maxwell’s methodology asserts that, at large distances from the cluster, the stress distributions ( 3.23) and ( 3.24), and hence the coefficients of p and ΔT, are identical leading to the following ‘mixtures’ rules for the functions 1/[1/k+3/(4μm)] and α/[1/k+3/(4μm)], respectively,
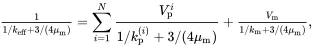 (3.25)
(3.25)
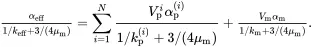 (3.26)
(3.26)
On using ( 3.1), the result ( 3.25) may be written as
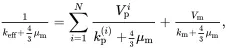 (3.27)
(3.27)
so that the effective bulk modulus of the multiphase particulate composite may instead be obtained from a ‘mixtures’ relation for the quantity 1/(k+43κm). On using ( 3.1) and ( 3.27), the effective bulk modulus may be estimated using
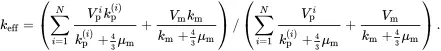 (3.28)
(3.28)
It follows from ( 3.26) and ( 3.27) that the corresponding relation for effective thermal expansion is
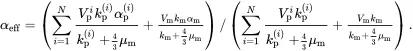 (3.29)
(3.29)
The bounds for effective bulk modulus of multiphase isotropic composites derived by Hashin and Shtrikman [6, Equations ( 3.37)–( 3.43)] and the bounds derived by Walpole [7, Equation (26)] are identical and may be expressed in the following simpler form having the same structure as the result ( 3.27) derived using Maxwell’s methodology
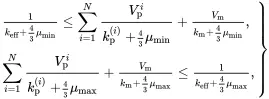 (3.30)
(3.30)
where the parameters kmin and μmin are the lowest values of bulk and shear moduli of all phases in the composite, respectively, whereas kmax and μmax are the highest values.
The bounds for effective thermal expansion involve the effective bulk modulus, and the specification of bounds is complex and beyond the scope of this chapter. An analysis has been undertaken showing numerically, for a very wide range of parameter values, that the effective thermal expansion obtained using Maxwell’s methodology lies between the absolute bounds for all volume fractions of spherical particle distributions that are consistent with isotropic properties.
Читать дальше

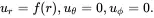 (3.13)
(3.13)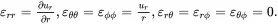 (3.14)
(3.14)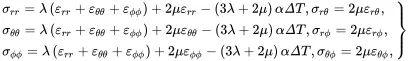 (3.15)
(3.15)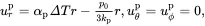 (3.16)
(3.16)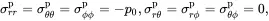 (3.17)
(3.17)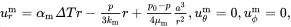 (3.18)
(3.18)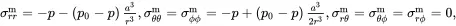 (3.19)
(3.19)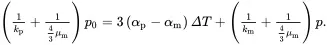 (3.20)
(3.20)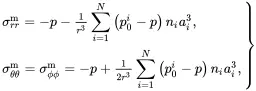 (3.21)
(3.21)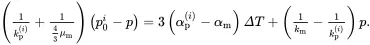 (3.22)
(3.22)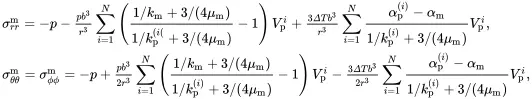 (3.23)
(3.23)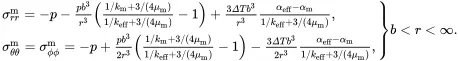 (3.24)
(3.24)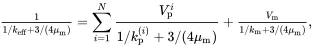 (3.25)
(3.25)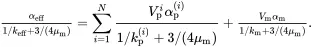 (3.26)
(3.26)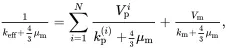 (3.27)
(3.27)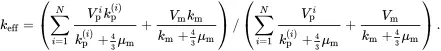 (3.28)
(3.28)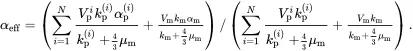 (3.29)
(3.29) (3.30)
(3.30)










