Yves Tille - Sampling and Estimation from Finite Populations
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Yves Tille - Sampling and Estimation from Finite Populations» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Sampling and Estimation from Finite Populations
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:4 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
Sampling and Estimation from Finite Populations: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Sampling and Estimation from Finite Populations»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
Sampling and Estimation from Finite Populations Provides an up-to-date review of the theory of sampling Discusses the foundation of inference in survey sampling, in particular, the model-based and design-based frameworks Reviews the problems of application of the theory into practice Also deals with the treatment of non sampling errors
is an excellent book for methodologists and researchers in survey agencies and advanced undergraduate and graduate students in social science, statistics, and survey courses.

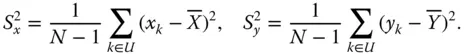
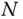 is not necessarily known and therefore can also be an estimation objective. However, as one can write
is not necessarily known and therefore can also be an estimation objective. However, as one can write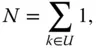
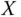 or
or 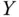 .
.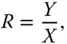
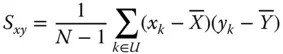

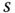 is simply a subset of the population
is simply a subset of the population 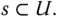 We also consider the set
We also consider the set 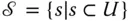 of all the possible samples. For instance, if
of all the possible samples. For instance, if 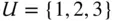 , then
, then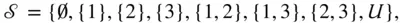
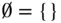 denotes the empty set.
denotes the empty set.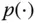 is a probability distribution on
is a probability distribution on 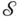 such that
such that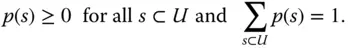
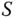 is a random variable whose values are the samples:
is a random variable whose values are the samples: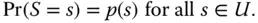
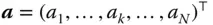 . The variable
. The variable 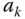 represents the number of times unit
represents the number of times unit 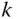 is selected in the sample. If the sample is without replacement then variable
is selected in the sample. If the sample is without replacement then variable 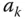 can only take the values 0 or 1 and therefore has a Bernoulli distribution. In general, random variables
can only take the values 0 or 1 and therefore has a Bernoulli distribution. In general, random variables 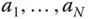 are not independent except in very special cases. The use of indicator variables
are not independent except in very special cases. The use of indicator variables 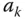 was introduced by Cornfield (1944) and greatly simplified the notation in survey sampling theory because it allows us to clearly separate the values of the variables
was introduced by Cornfield (1944) and greatly simplified the notation in survey sampling theory because it allows us to clearly separate the values of the variables 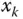 or
or 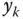 from the source of randomness
from the source of randomness  .
.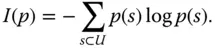
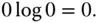
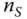 is the number of units selected in the sample. We can write
is the number of units selected in the sample. We can write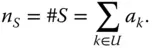
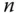 .
.










