The operation of glide plane repetition is shown in Figure 2.22c. Again, the magnitude of the translation will be of the order of the lattice parameters. Macroscopically, the glide plane in Figure 2.22c would show itself as a mirror plane.
Glide planes are described as axial glide planes if the translation parallel to the mirror is parallel to a single axis of the unit cell and equal to one‐half of the lattice parameter in that direction. Such glide planes are given the symbols a , b , or c , corresponding to the directions of the glide translations. A diagonal glide plane involves a translation of one‐half of a face diagonal or one‐half of a body diagonal (the latter in the tetragonal and cubic systems), and is given the symbol n . A diamond glide plane , given the symbol d , can only occur in orthorhombic F , tetragonal I , and cubic I and F lattices. In orthorhombic F lattices, this involves a translation of one‐quarter of a face diagonal, whereas in the tetragonal and cubic lattices this involves a translation of one-quarter of a body diagonal.
2.12.3 Combinations of Symmetry Operations to Form Space Groups
When we combine the operations of rotation with translation and look for the possible consistent combinations we can start with the point group and associate its symmetry elements with each lattice point of the lattices consistent with it. From the number of Bravais lattices and number of point groups detailed in Figures 1.19and 2.6it might be expected that 66 space groups could be obtained (2 triclinic, 6 monoclinic, 12 orthorhombic, 14 tetragonal, 5 trigonal with a rhombohedral lattice, 5 trigonal with a hexagonal lattice, 7 hexagonal, and 15 cubic). Seven additional ones arise because of cases in which the glide planes or screw axes automatically arising are different for different orientations of the point group with respect to the lattice; for example, in the tetragonal system 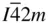 and
and 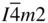 are distinct space groups. The 14 space groups for which this consideration is relevant are Cmm2 , Amm 2 (≡ C 2 mm ), P
are distinct space groups. The 14 space groups for which this consideration is relevant are Cmm2 , Amm 2 (≡ C 2 mm ), P 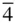 2 m , P
2 m , P 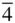 m 2,
m 2, 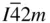 ,
, 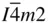 , P
, P 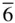 m 2, P
m 2, P 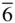 2 m , P 312, P 321, P 3 m 1, P 31 m , P
2 m , P 312, P 321, P 3 m 1, P 31 m , P 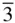 m 1 and P
m 1 and P 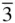 1 m . Therefore, there are 73 such space groups, referred to as arithmetic crystal classes in Section 1.3.4 of the sixth edition of the International Tables for Crystallography [3].
1 m . Therefore, there are 73 such space groups, referred to as arithmetic crystal classes in Section 1.3.4 of the sixth edition of the International Tables for Crystallography [3].
When the possibilities of introducing screw axes to replace pure rotational axes and glide planes to replace mirror planes are taken into consideration, the result is to produce the total of 230 different space groups [3]. Of particular note are the space groups in the trigonal crystal system. Of the 25 trigonal space groups, only seven have a rhombohedral unit cell ( R 3, R 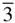 , R 32, R 3 m , R 3 c , R
, R 32, R 3 m , R 3 c , R 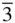 m , R
m , R 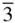 c ); the majority have a primitive hexagonal unit cell. Buerger [1] argues that ‘to refer one crystal of the trigonal class to rhombohedral axes, and another to hexagonal axes, because the lattice types are R and P respectively, leads to confusion’ (p. 106) and discourages the use of rhombohedral axes for this reason. It is certainly the case in the scientific literature that the use of rhombohedral axes for crystals where the space group is one of the seven rhombohedral space groups is markedly less prevalent than the use of hexagonal axes.
c ); the majority have a primitive hexagonal unit cell. Buerger [1] argues that ‘to refer one crystal of the trigonal class to rhombohedral axes, and another to hexagonal axes, because the lattice types are R and P respectively, leads to confusion’ (p. 106) and discourages the use of rhombohedral axes for this reason. It is certainly the case in the scientific literature that the use of rhombohedral axes for crystals where the space group is one of the seven rhombohedral space groups is markedly less prevalent than the use of hexagonal axes.
In centred cells, the possibility of a ‘double’ glide plane arises, given the symbol e . This symmetry operation is recognized officially in the fifth and sixth editions of the International Tables for Crystallography and incorporated into the conventional space group symbols of five orthorhombic space groups, Aem 2, Aea 2, Cmce , Cmme , and Ccce . In this operation, two glide reflections occur through the plane under consideration, with glide vectors perpendicular to one another related by a centring translation [3]. Seventeen space groups have these ‘double’ glide planes, recognized in the footnotes to Tables 2.1.2.2 and 2.1.2.3 of [3], but in 12 of these cases the ‘double’ glide planes are parallel to mirror planes. Therefore, their existence is not immediately apparent from the space group symbol because the mirror planes are stronger symmetry elements than the ‘double’ glide planes.
The arrangements of all of the symmetry elements in the 230 space groups are listed in the various editions of the International Tables for Crystallography . The numbers allocated to the various space groups are such that the space groups are in the sequence introduced by Schoenflies in 1891 [13], starting with the two triclinic space groups and finishing with the 36 cubic space groups.
Of particular interest to most materials scientists are the coordinates of general and special positions within each unit cell and diagrams showing the symmetry elements. More recent editions of the International Tables for Crystallography have extensive descriptions of space groups, which also include listings of maximal subgroups and minimal supergroups; these concepts will be discussed in general terms in Sections 2.14and 2.15.
2.12.4 The Relationship Between the Space Group Symbol and the Point Group Symmetry for a Crystal
The conventional space group symbol shows that the space groups have been built up by placing a point group at each of the lattice points of the appropriate Bravais lattice. Thus, for example, Fm 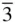 m (in full, F 4/ m
m (in full, F 4/ m 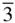 2/ m ) means the cubic face‐centred lattice with the point group m
2/ m ) means the cubic face‐centred lattice with the point group m 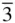 m associated with each lattice point; P 6 3/ mmc (in full, P 6 3/ m 2/ m 2/ c ) is a hexagonal primitive lattice derived from P 6 /mmm by replacing the sixfold rotation axis by 6 3and one of the mirror planes by a c ‐axis glide plane. P 6 3/ mmc and P 6 /mmm share the same point group symmetry. The point group symmetry of any crystal is derived immediately from the space group symbol by replacing screw axes by the appropriate rotational axes and glide planes by mirror planes in the space group symbol.
m associated with each lattice point; P 6 3/ mmc (in full, P 6 3/ m 2/ m 2/ c ) is a hexagonal primitive lattice derived from P 6 /mmm by replacing the sixfold rotation axis by 6 3and one of the mirror planes by a c ‐axis glide plane. P 6 3/ mmc and P 6 /mmm share the same point group symmetry. The point group symmetry of any crystal is derived immediately from the space group symbol by replacing screw axes by the appropriate rotational axes and glide planes by mirror planes in the space group symbol.
Читать дальше

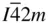 and
and 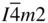 are distinct space groups. The 14 space groups for which this consideration is relevant are Cmm2 , Amm 2 (≡ C 2 mm ), P
are distinct space groups. The 14 space groups for which this consideration is relevant are Cmm2 , Amm 2 (≡ C 2 mm ), P 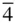 2 m , P
2 m , P 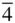 m 2,
m 2, 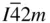 ,
, 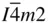 , P
, P 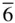 m 2, P
m 2, P 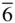 2 m , P 312, P 321, P 3 m 1, P 31 m , P
2 m , P 312, P 321, P 3 m 1, P 31 m , P 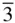 m 1 and P
m 1 and P 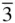 1 m . Therefore, there are 73 such space groups, referred to as arithmetic crystal classes in Section 1.3.4 of the sixth edition of the International Tables for Crystallography [3].
1 m . Therefore, there are 73 such space groups, referred to as arithmetic crystal classes in Section 1.3.4 of the sixth edition of the International Tables for Crystallography [3].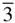 , R 32, R 3 m , R 3 c , R
, R 32, R 3 m , R 3 c , R 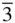 m , R
m , R 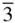 c ); the majority have a primitive hexagonal unit cell. Buerger [1] argues that ‘to refer one crystal of the trigonal class to rhombohedral axes, and another to hexagonal axes, because the lattice types are R and P respectively, leads to confusion’ (p. 106) and discourages the use of rhombohedral axes for this reason. It is certainly the case in the scientific literature that the use of rhombohedral axes for crystals where the space group is one of the seven rhombohedral space groups is markedly less prevalent than the use of hexagonal axes.
c ); the majority have a primitive hexagonal unit cell. Buerger [1] argues that ‘to refer one crystal of the trigonal class to rhombohedral axes, and another to hexagonal axes, because the lattice types are R and P respectively, leads to confusion’ (p. 106) and discourages the use of rhombohedral axes for this reason. It is certainly the case in the scientific literature that the use of rhombohedral axes for crystals where the space group is one of the seven rhombohedral space groups is markedly less prevalent than the use of hexagonal axes.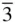 m (in full, F 4/ m
m (in full, F 4/ m 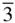 2/ m ) means the cubic face‐centred lattice with the point group m
2/ m ) means the cubic face‐centred lattice with the point group m 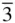 m associated with each lattice point; P 6 3/ mmc (in full, P 6 3/ m 2/ m 2/ c ) is a hexagonal primitive lattice derived from P 6 /mmm by replacing the sixfold rotation axis by 6 3and one of the mirror planes by a c ‐axis glide plane. P 6 3/ mmc and P 6 /mmm share the same point group symmetry. The point group symmetry of any crystal is derived immediately from the space group symbol by replacing screw axes by the appropriate rotational axes and glide planes by mirror planes in the space group symbol.
m associated with each lattice point; P 6 3/ mmc (in full, P 6 3/ m 2/ m 2/ c ) is a hexagonal primitive lattice derived from P 6 /mmm by replacing the sixfold rotation axis by 6 3and one of the mirror planes by a c ‐axis glide plane. P 6 3/ mmc and P 6 /mmm share the same point group symmetry. The point group symmetry of any crystal is derived immediately from the space group symbol by replacing screw axes by the appropriate rotational axes and glide planes by mirror planes in the space group symbol.










