3 Find the values of the following thermo‐physical parameters at and (xf= 40 000 ppm); boiling point elevation (BPE), μ, v, k, hfg, cp, u, s, ρ. Explain the reason behind the differences.
4 Find the values of the following thermo‐physical parameters at under two salinities; xf = 20 000 and 40 000 ppm for; BPE, μ, v, k, hfg, cp, u, s, ρ. Explain the reason behind the differences.
5 Calculate entropy generation and irreversibility per mass of feedwater flow rate.
Example 1.6 Performance of Feed Pump
Feedwater is pumped from 100 kPa, 30 °C, 1.5 kg/s to 3 MPa, if pump efficiency is 75%:
Find:
1 Actual work input
2 Reversible work
3 Exergy destruction (irreversibility)
4 Second law efficiency
1 Working fluid water:State 1then h2 = 131.4 kJ/kg and s2 = 0.4423 kJ/(kg K).
2 Wrev = Ψ2 − Ψ1
3 Exergy destruction (irreversibility):
4 Exergetic efficiency:
Extra activity:
Student can perform the following:
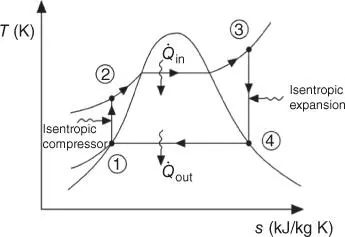
1 Sketch T–v, P–v, and T–s diagram for actual and isentropic processes.
2 Resolve example using seawater (x = 40 000 ppm) as feed. Refer to Appendix A.
3 Compare results of feed seawater against water. Explain and comment.
Example 1.7 Exergy Analysis of Rankine Cycle (Review)
Simple Rankine cycle operates with isentropic expansion and isentropic compressor to produce net power of 1750 kW, and steam boiler operates isobarically at 6 MPa pressure; using fuel oil as a fuel, the combustion of fuel produces heat that is added at a source temperature of 800 K, and the produced steam enters steam turbine at 500 °C and 6 MPa to be expand isentropically to 20 kPa as it leaves steam turbine.
The condenser operates at 20 kPa using seawater cooling water at 4 °C (winter season).
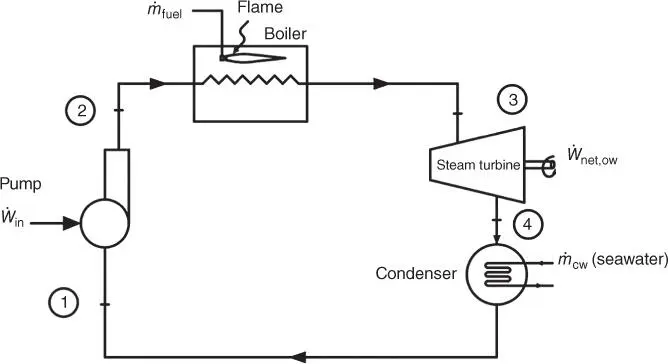
Find:
1 Rate of heat supply in the boiler.
2 Rate of heat rejection in the condenser.
3 Cycle thermal efficiency.
4 Availability at each state (To = 298 K)
5 Exergy destruction in each component assuming heat is added from a source at 800 °C and rejected at 4 °C.
6 Cycle second law efficiency.
1 v1 = vf @ 20 kPa = 0.001 017 m3/kgEnergy balance (first law):Since Δs = 0 (s2 = s1) at state 3 h3 = 3423.1 kJ/kg and s3 = 6.8826 kJ/(kg K) again the isentropic expansion turbine (s3 = s4) givesh4 = 2264.7 kJ/kg with quality x4 = 0.8552.Energy balance in turbine:and cycle Wnet = Wt − WpthenThe rate of heat added in the boiler (due to fuel burning)
2 Rate of rejected heat:
3
4 The thermal availability (exergy) for control volume system defined aswhere kinetic and potential exergies are neglected and ho and so are measured at environmental state (298 K).Exergy at state:One can notice that Ψ3 is the highest (explain).
5 Exergy destruction (irreversibility) for steady flow process type is (isentropic process which is adiabatic and reversible type)where qin = h3 − h2 = 3165.6 kJ/kg and where qout = h4 − h1 = 2016.1 kJ/kg.Total amount of exergy destruction (irreversibility):Note that 40% of energy added (4818 kW) is destructed (wasted) due to irreversible processes, the reasons behind irreversibilities in any thermal system are combustion, heat transfer, mixing, friction, and non‐quasi equilibrium processes.
6 The second law efficiency can be defined as (Carnot efficiency) then
Extra activity:
Student can perform the following:
1 Explain the exergy value of fluid stream at each state.
2 Explain the sources of irreversibilities in boiler. How can we reduce them?
3 Calculate exergetic efficiency using the following three forms: (called rational) Compare and discuss.
4 Resolve example assuming that seawater is at 30 °C (summer season). Explain results, and compare.
5 Find the required fuel flow rate during summer using fuel oil and natural gas, and calculate the amount of emitted emissions: CO2 and SO2.
1 1 MAL (2013). IDA Desalting Plants Inventory. Global Water Intelligence (GWI). Oxford, UK: Media Analytics Ltd.
2 2 Desalination in Water Treatment (IDA2014). www.IDAdesal.org.
3 3 Youssef, P.G., AL‐Dadah, R.K., and Mahmoud, S.M. (2014). Comparative analysis of desalination technologies. Energy Procedia 61: 2604–2607.
4 4 Alkaisi, A., Mossad, R., and Barforoush, A.S. (2017). A review of the water desalination systems integrated with renewable energy. Energy Procedia 110: 268–274.
5 5 U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (2018). Edition of the Drinking Water Standards and Health Advisories. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
1 1.1 What is the recent global world capacity of desalted water? State the value of desalting water capacity in your country.
2 1.2 In which year world capacity of desalted water using RO start to overcome thermal‐type (MEE and MSF) production? Highlight on facts and reasons.
3 1.3 Can freezing desalination technology be considered as a thermal type? Explain.
4 1.4 Sketch and explain the following processes on T–v, P–v, and T–s diagrams:Boiling.Flashing.Condensation.
5 1.5 List the top 10 countries that produce desalted water. What is the rank of your country? List the sources of fresh water in your country.
6 1.6 Search through the literature to obtain the following worldwide recent statistics:Potable water production.Number of desalination plants.Contribution of each type of desalination technology.Potable water production cost, specify the cost in your country, compare, and comment.
7 1.7 Define and explain the following glossary:Corrosion.Scaling.Fouling.TDS.Turbidity.pH.
8 1.8 Present in table form the actual values of salinities in seven selected seas, oceans, and gulfs around the world, and provide information for the nearest one to your country.
9 1.9 Present in table form freshwater consumption per capita in seven different countries. What is the consumption per capita in your country? Explain.
10 1.10 Define the following thermal performance parameters.Recovery ratio.Gain ratio.Performance ratio.Concentration factor.Specific energy consumption.Specific exergy consumption.
11 1.11 Write an essay on the following desalination systems explaining the historical developments, and provide industrial examples:Thermal systems.Membrane systems.Wastewater systems.
12 1.12 Differentiate between home and industry wastewater, and explain in terms of composition.
13 1.13 Elaborate on the principles of wastewater desalination process. Can desalted product be considered as potable water? Explain and comment.
14 1.14 Search through the literature and highlight on three major proposed nonconventional desalination systems that can be considered as a promising and futuristic one.
15 1.15 Explain the following feed seawater thermo‐physical properties:Density.Viscosity.Specific heat.Enthalpy.Thermal conductivity.Boiling point elevation (BPE).Latent heat (hfg).Provide real values for three types of feedwater salinities (Appendix A).
Читать дальше







![Andrew Radford - Linguistics An Introduction [Second Edition]](/books/397851/andrew-radford-linguistics-an-introduction-second-thumb.webp)







