2 Examine desalination system under different operating conditions and design parameters using sensitivity analysis (parametric study).
3 Assess and evaluate different conventional and hybrid desalination configurations using conventional and renewable types of energy.
4 Train student to select one research paper (per topic) from a referred journal for reproduction in the light of 4E's.
The textbook is recommended for senior undergraduate and graduate engineering students during a one‐semester course (14 weeks). Student must have knowledge and background in the following fields: thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, and heat mass transfer as a prerequisite.
There are several sections, examples, and problems that can be considered as advanced types, which are suitable for graduate level course.
On the other side, parts of the textbook can be used by practicing engineers in the field of desalination plant industry. Student needs to download the following software in order to solve examples:
1 ROSA
2 Nitto
3 Engineering Equation Solver (EES)
The textbook's suggested plan in a one‐semester‐course is shown in the following Table 1.
Table 1Suggested desalination course plan (14 weeks).
| Chapter |
Topics |
Number of weeks |
Number of hours (1 wk = 3 h) |
| 1 |
Introduction |
1 |
3 |
| 2 |
MEE |
1.33 |
4 |
| 3 |
MSF |
1.33 |
4 |
| 4 |
VC |
1 |
3 |
| 5 |
MF, UF, NF, and RO |
2 |
6 |
| 6 |
ED and EDR |
1 |
3 |
| 7 |
MD |
1 |
3 |
| 8 |
FO, PV, and dialysis |
1 |
3 |
| 9 |
Renewable energy |
1.33 |
4 |
| 10 |
Hybrid system |
1 |
3 |
|
|
Σ = 12 |
+2 wk for quizzes, exams, and project presentation |
At the end, special thanks to my students whom I learned from and to engineer Alfadel Taqi for his valuable contribution in software computational calculations. I wish that the textbook will be useful and helpful for both students and faculty members, whom I ask them kindly to contact me in case of any suggestions.
Kuwait
2020
Prof. Fuad Nesf Alasfour ( fuadnalasfour@gmail.com)
1 Introduction
1.1 What Is Desalination?
Desalination is a process of separating and removing unwanted dissolved salts and minerals from feedwater sources such as seawater, brackish water, or wastewater.
The aim of desalination process is to produce a stream of fresh water (potable) with high quality (purity) according to the standards of World Health Organization (WHO), which state that the accepted maximum limit of total dissolved salts (TDS) in fresh water is 500 ppm (500 mg/l); if we take seawater (called feed or saline) as an example with a salinity of 35 000 ppm, feed can be desalted through two main industrial processes: (i) thermal desalination technologies where feed phase changes through evaporation and condensation processes and (ii) membrane desalination technologies where separation of salts achieved through using semipermeable membrane without feed phase change. In either process, potable water is produced, and salty water (called brine or concentrate) is rejected from desalination system; the rejected brine salinity varies in concentration based on technology, and it can reach up to 90 000 ppm.
Today, desalination industry plays a vital role in society development and economic growth, and worldwide freshwater consumption rate is approximately doubled every 20 years, where the availability of natural water sources is depleted. According to UN report and in the light of global population growth, statistics showed that one‐third of world's population lives under a state of insufficient potable water resources and in communities that suffer from scarcity and water stress. As prehuman body, water is essentially needed for building tissues, blood circulation, and maintaining stable blood temperature, and based on human weight it is recommended that a human drinks 8–14 glasses of water every day. Today desalination industries tend to provide safe drinking water to achieve and maintain sustainable human life and minimize negative environmental impacts. As per industry, there are eight major water‐consuming industrial sectors: power generation, food, pharmaceutical, mining, oil, petrochemical, electronics, and paper.
There are several types of “well‐proven” industrial desalination technologies that have been used in the last seven decades. Note that the major parameters that affect desalination technology performance are feed type and its thermal‐physical characteristics, in addition to the required desalted water quality (purity).
Figure 1.1shows the classification of desalination systems based on separation processes. Note that such processes can be operated by conventional energy type such as fossil fuel (thermal and electrical) or by renewable energy types such as solar, wind, and geothermal ( Chapter 9).
Statistics by IDA for year 2015 shows that there are 18 426 desalination plants worldwide, producing 86.8 × 10 6m 3/d and serving more than 300 × 10 6in 150 countries per day, and such production can provide potable water for municipal, industrial, and agriculture sectors. Today Gulf countries produce around 57% of world desalination capacity [2].
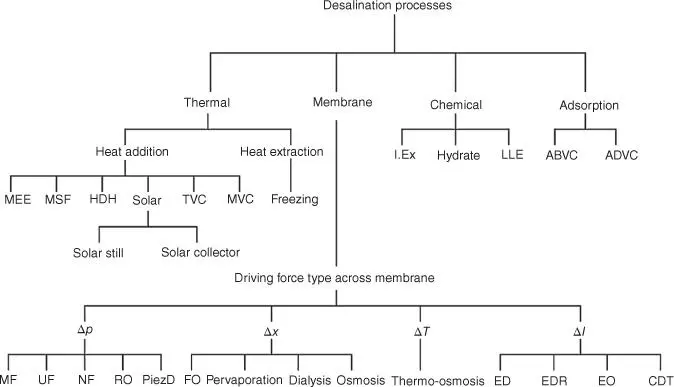
Figure 1.1Desalination processes based on separation type.
1.2 Aims of Desalination Processes
Several desalination technologies have been invented, developed, and employed during the last seven decades, and the potentials behind such industrial developments are:
1 Satisfy the global increase in freshwater demand for drinking, and in industrial and agriculture sectors, in addition to hygiene requirements.
2 Compensate the capacity of limited natural freshwater resources specially in arid and remote areas.
3 Reduce the values of elevated intensive energy cost of freshwater production.
4 Reduce the potential levels of emissions and minimize negative environmental impacts on human and climate in terms of greenhouse effect and acid rain.
5 Provide efficient large size desalination system with the ability of integration with other conventional or renewable energy types.
6 Achieve water quality based on WHO rules and regulations or other specific industrial standards.
7 Manage wastewater processes that are associated with municipal and industrial sectors.
1.3 Desalination Processes
There are four main industrial desalination processes that exist today to separate freshwater from feedwater, and separation processes can be achieved via:
1 Thermal processes
2 Membrane processes
3 Chemical processes
4 Adsorption processes
Figure 1.2shows the basic principles of general industrial desalination processes.
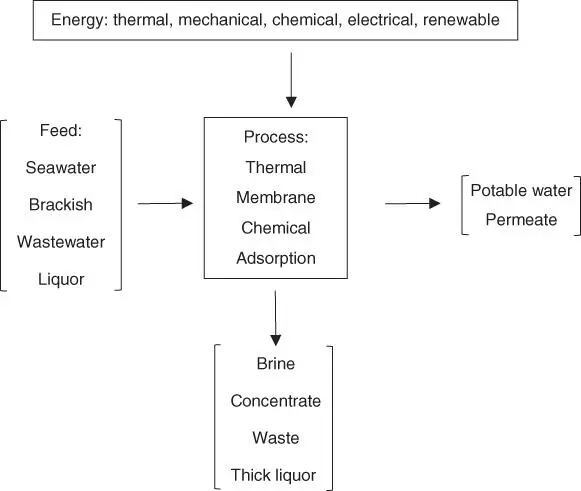
Figure 1.2Basic principles of desalination processes.
Feed can be in the form of seawater with high salinity that can reach a value of 45 000 ppm, or it can be in the form of brackish water or even wastewater that has been taken from industry or municipal.
The example of disposal fluid from desalination system can be in the following forms:
Читать дальше






![Andrew Radford - Linguistics An Introduction [Second Edition]](/books/397851/andrew-radford-linguistics-an-introduction-second-thumb.webp)







