Allan T. Kirkpatrick - Internal Combustion Engines
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Allan T. Kirkpatrick - Internal Combustion Engines» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Internal Combustion Engines
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:5 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
Internal Combustion Engines: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Internal Combustion Engines»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
New engine technologies and concepts Effects of engine speed on performance and emissions Fluid mechanics of intake and exhaust flow in engines Turbocharger and supercharger performance analysis Chemical kinetic modeling, reaction mechanisms, and emissions Advanced combustion processes including low temperature combustion Piston, ring and journal bearing friction analysis The
expands on the combined analytical and numerical approaches used successfully in previous editions. Students and engineers are provided with several new tools for applying the fundamental principles of thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, and heat transfer to internal combustion engines.
Each chapter includes MATLAB programs and examples showing how to perform detailed engineering computations. The chapters also have an increased number of homework problems with which the reader can gauge their progress and retention. All the software is ‘open source’ so that readers can see in detail how computational analysis and the design of engines is performed. A companion website is also provided, offering access to the MATLAB computer programs.

 , enthalpy
, enthalpy 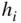 , and pressure
, and pressure 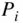 . Again, at this level of modeling, as the piston moves downward, it is assumed that the cylinder pressure
. Again, at this level of modeling, as the piston moves downward, it is assumed that the cylinder pressure 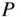 remains constant at the inlet pressure,
remains constant at the inlet pressure, 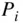 .
.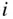 , the open‐system conservation of mass equation is
, the open‐system conservation of mass equation is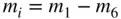
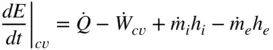
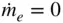 ,
,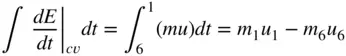
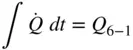

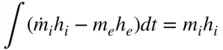
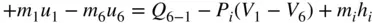
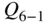 during the intake stroke is neglected,
during the intake stroke is neglected,
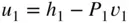 and
and 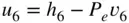 ,
,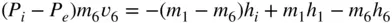
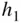 :
: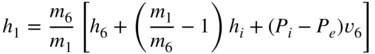
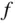 . From Equation ( 2.45),
. From Equation ( 2.45),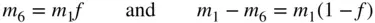
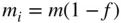
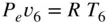
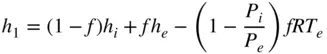
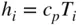 , then
, then










