William M. White - Geochemistry
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «William M. White - Geochemistry» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Geochemistry
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:5 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
Geochemistry: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Geochemistry»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
, undergraduate and graduate students will find each of the core principles of geochemistry covered. From defining key principles and methods to examining Earth’s core composition and exploring organic chemistry and fossil fuels, this definitive edition encompasses all the information needed for a solid foundation in the earth sciences for beginners and beyond.
For researchers and applied scientists, this book will act as a useful reference on fundamental theories of geochemistry, applications, and environmental sciences. The new edition includes new chapters on the geochemistry of the Earth’s surface (the “critical zone”), marine geochemistry, and applied geochemistry as it relates to environmental applications and geochemical exploration.
● A review of the fundamentals of geochemical thermodynamics and kinetics, trace element and organic geochemistry
● An introduction to radiogenic and stable isotope geochemistry and applications such as geologic time, ancient climates, and diets of prehistoric people
● Formation of the Earth and composition and origins of the core, the mantle, and the crust
● New chapters that cover soils and streams, the oceans, and geochemistry applied to the environment and mineral exploration
In this foundational look at geochemistry, new learners and professionals will find the answer to the essential principles and techniques of the science behind the Earth and its environs.

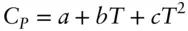
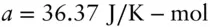 ,
, 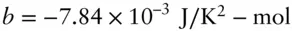 , and
, and 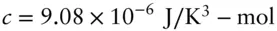 , and the enthalpy of vaporization at 100°C is 40.6 kJ/mol, calculate the S and H changes when 1 mol of liquid water at 100°C and 1 atm is converted to steam and brought to 200°C and 3 atm. Assume that with respect to volume, steam behaves as an ideal gas (which, in reality, it is certainly not).
, and the enthalpy of vaporization at 100°C is 40.6 kJ/mol, calculate the S and H changes when 1 mol of liquid water at 100°C and 1 atm is converted to steam and brought to 200°C and 3 atm. Assume that with respect to volume, steam behaves as an ideal gas (which, in reality, it is certainly not).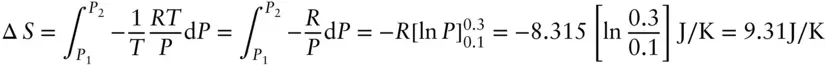
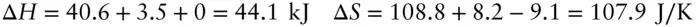
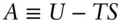
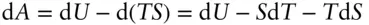
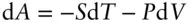
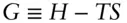
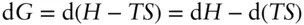
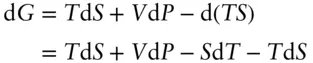
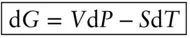

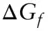 , is related to the enthalpy and entropy change of reaction:
, is related to the enthalpy and entropy change of reaction: