2.10.2 Changes in enthalpy due to reactions and change of state
We cannot measure the absolute enthalpy of substances, but we can determine the enthalpy changes resulting from transformations of a system, and they are of great interest in thermodynamics. For this purpose, a system of relative enthalpies of substances has been established. Since enthalpy is a function of both temperature and pressure, the first problem is to establish standard conditions of temperature and pressure to which these enthalpies apply. These conditions, by convention, are 298.15 K and 0.1 MPa (25°C and 1 bar). Under these conditions the elements are assigned enthalpies of 0. Standard state enthalpy of formation , or heat of formation, from the elements, ΔH° , can then be determined for compounds by measuring the heat evolved in the reactions that form them from the elements (e.g., Example 2.2). For example, the heat of formation of water is determined from the energy released at constant pressure in the reaction: H 2+ ½O 2→ H 2O, which yields a ΔH° of −285.83 kJ/mol, where water is in the liquid state. The minus sign indicates heat is liberated in the reaction , that is, the reaction is exothermic (a reaction that consumes heat is said to be endothermic ).
Having established such a system, the enthalpy associated with a chemical reaction is easily calculated using Hess's law, which is:
(2.115) 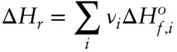
where ν iis the stoichiometric coefficient for the i thspecies. In other words, the enthalpy of reaction is just the total enthalpy of the products less the total enthalpy of the reactants. The use of Hess's law is illustrated in Example 2.5below.
The heat of vaporization of a substance is the energy required to convert that substance from liquid to gas, i.e., to boil it. If the reaction H 2+ ½O 2→ H 2O is run to produce water vapor, the ΔH° turns out to be −241.81 kJ/mol. The difference between the enthalpy of formation of water and vapor, 44.02 kJ/mol, is the heat consumed in going from liquid water to water vapor. This is exactly the amount of energy that would be required to boil 1 mole of water. Analogously, the heat of melting (or fusion) is the enthalpy change in the melting of a substance. Because reaction rates are often very slow, and some compounds are not stable at 298 K and 1 MPa, it is not possible to measure the enthalpy for every compound. However, the enthalpies of formation for these compounds can generally be calculated indirectly.
Example 2.5Enthalpies (or heats) of reaction and Hess's law
What is the energy consumed or evolved in the hydration of corundum (Al 2O 3) to form gibbsite (Al(OH) 3)? The reaction is:
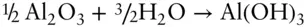
Answer: We use Hess's law . To use Hess's law, we need the standard state enthalpies for water, corundum, and gibbsite. These are: Al 2O 3: −1675.70 kJ/mol, H 2O: −285.83 and Al(OH) 3: −1293.13. The enthalpy of reaction is 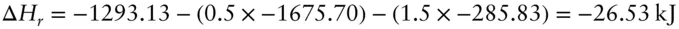 .
.
This is the enthalpy of reaction at 1 bar and 298 K. Suppose you were interested in this reaction under metamorphic conditions such as 300°C and 50 MPa. How would you calculate the enthalpy of reaction then?
2.10.3 Entropies of reaction
Since
(2.62) 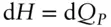
and
(2.57) 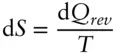
then at constant pressure
(2.116) 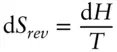
Thus, at constant pressure, the entropy change in a reversible reaction is simply the ratio of enthalpy change to temperature.
Entropies are additive properties and entropies of reaction can be calculated in the same manner as for enthalpies, so Hess's law applies:
(2.117) 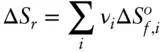
The total entropy of a substance can be calculated as:
(2.118) 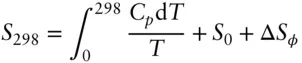
Table 2.2 Standard state thermodynamic data for some important minerals.
| Phase/ Compound |
Formula |
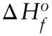 kJ/mol kJ/mol |
S OJ/K-mol |
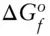 kJ/mol kJ/mol |
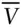 cc/mol* cc/mol* |
a |
C Pb |
c |
| H 2O g |
H 2O (gas) |
−241.81 |
188.74 |
−228.57 |
24789.00 |
30.54 |
0.01029 |
0 |
| H 2O l |
H 2O (liquid) |
−285.84 |
69.92 |
−237.18 |
18.10 |
29.75 |
0.03448 |
0 |
| CO 2 |
CO 2 |
−393.51 |
213.64 |
−394.39 |
24465.10 |
44.22 |
0.00879 |
861904 |
| Calcite |
CaCO 3 |
−1207.30 |
92.68 |
−1130.10 |
36.93 |
104.52 |
0.02192 |
2594080 |
| Graphite |
C |
0 |
5.740 |
|
5.298 |
|
|
|
| Diamond |
C |
1.86 |
2.37 |
|
3.417 |
|
|
|
| Aragonite |
CaCO 3 |
−1207.21 |
90.21 |
−1129.16 |
34.15 |
84.22 |
0.04284 |
1397456 |
| α-Qz |
SiO 2 |
−910.65 |
41.34 |
−856.24 |
22.69 |
46.94 |
0.03431 |
1129680 |
| β-Qz |
SiO 2 |
−910.25 |
41.82 |
−856.24 |
|
60.29 |
0.00812 |
0 |
| Cristobalite |
SiO 2 |
−853.10 |
43.40 |
−853.10 |
25.74 |
58.49 |
0.01397 |
1594104 |
| Coesite |
SiO 2 |
−851.62 |
40.38 |
−851.62 |
20.64 |
46.02 |
0.00351 |
1129680 |
| Periclase |
MgO |
−601.66 |
26.94 |
−569.38 |
11.25 |
42.59 |
0.00728 |
619232 |
| Magnetite |
Fe 3O 4 |
−1118.17 |
145.73 |
−1014.93 |
44.52 |
91.55 |
0.20167 |
0 |
| Spinel |
MgAl 2O 4 |
−2288.01 |
80.63 |
−2163.15 |
39.71 |
153.86 |
0.02684 |
4062246 |
| Hematite |
Fe 2O 3 |
−827.26 |
87.61 |
−745.40 |
30.27 |
98.28 |
0.07782 |
1485320 |
| Corundum |
Al 2O 3 |
−1661.65 |
50.96 |
−1568.26 |
25.58 |
11.80 |
0.03506 |
3506192 |
| Kyanite |
Al 2SiO 5 |
−2581.10 |
83.68 |
−2426.91 |
44.09 |
173.18 |
0.02853 |
5389871 |
| Andalusite |
Al 2SiO 5 |
−2576.78 |
92.88 |
−2429.18 |
51.53 |
172.84 |
0.02633 |
5184855 |
| Sillimanite |
Al 2SiO 5 |
−2573.57 |
96.78 |
−2427.10 |
49.90 |
167.46 |
0.03092 |
4884443 |
| Almandine |
Fe 3Al 2Si 3O 12 |
−5265.50 |
339.93 |
−4941.73 |
115.28 |
408.15 |
0.14075 |
7836623 |
| Grossular |
Ca 3Al 2Si 3O 12 |
−6624.93 |
254.68 |
−6263.31 |
125.30 |
435.21 |
0.07117 |
11429851 |
| Albite |
NaAlSi 3O 8 |
−3921.02 |
210.04 |
−3708.31 |
100.07 |
258.15 |
0.05816 |
6280184 |
| K-feldspar |
KAlSi 3O 8 |
−3971.04 |
213.93 |
−3971.4 |
108.87 |
320.57 |
0.01804 |
12528988 |
| Anorthite |
CaAl 2Si 2O 8 |
−4215.60 |
205.43 |
−3991.86 |
100.79 |
264.89 |
0.06190 |
7112800 |
| Jadeite |
NaAlSi 2O 6 |
−3011.94 |
133.47 |
−2842.80 |
60.44 |
201.67 |
0.04770 |
4966408 |
| Diopside |
CaMgSi 2O 6 |
−3202.34 |
143.09 |
−3029.22 |
66.09 |
221.21 |
0.03280 |
6585616 |
| Enstatite |
MgSiO 3 |
−1546.77 |
67.86 |
−1459.92 |
31.28 |
102.72 |
0.01983 |
2627552 |
| Wollatonite |
CaSiO 3 |
−1632.0 |
82.03 |
−1656.45 |
39.93 |
139.58 |
0.00236 |
1401200 |
| Forsterite |
Mg 2SiO 4 |
−2175.68 |
95.19 |
−2056.70 |
43.79 |
149.83 |
0.02736 |
3564768 |
| Clinozoisite |
Ca 2Al 3Si 3O 12(OH) |
−68798.42 |
295.56 |
−6482.02 |
136.2 |
787.52 |
0.10550 |
11357468 |
| Tremolite |
Ca 2MgSi 8O 22(OH) 2 |
−12319.70 |
548.90 |
−11590.71 |
272.92 |
188.22 |
0.05729 |
4482200 |
| Chlorite |
MgAl(AlSi 3)O 10(OH) 8 |
−8857.38 |
465.26 |
−8207.77 |
207.11 |
696.64 |
0.17614 |
15677448 |
| Pargasite |
NaCa 2Mg 4Al 3Si 8O 22(OH) 2 |
−12623.40 |
669.44 |
−11950.58 |
273.5 |
861.07 |
0.17431 |
21007864 |
| Phlogopite |
KMg 3AlSi 3O 10(OH) 2 |
−6226.07 |
287.86 |
−5841.65 |
149.66 |
420.95 |
0.01204 |
8995600 |
| Muscovite |
KAl 3Si 3O 10(OH) 2 |
−5972.28 |
287.86 |
−5591.08 |
140.71 |
408.19 |
0.110374 |
10644096 |
| Gibbsite |
Al(OH) 3 |
−1293.13 |
70.08 |
−1155.49 |
31.96 |
36.19 |
0.19079 |
0 |
| Boehmite |
AlO(OH) |
−983.57 |
48.45 |
−908.97 |
19.54 |
60.40 |
0.01757 |
0 |
| Brucite |
Mg(OH) 2 |
−926.30 |
63.14 |
−835.32 |
24.63 |
101.03 |
0.01678 |
2556424 |
Data for the standard state of 298.15 K and 0.1 MPa. ΔH fis the molar heat (enthalpy) of formation from the elements; S° is the standard state entropy; V is the molar volume; a, b and c are constants for the heat capacity ( C p) computed as: C p= a + bT − cT –2J/K-mol.
Читать дальше

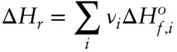
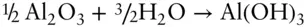
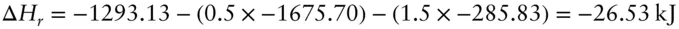 .
.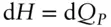
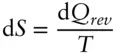
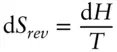
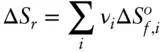
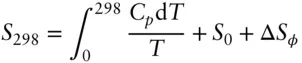
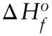 kJ/mol
kJ/mol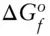 kJ/mol
kJ/mol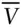 cc/mol*
cc/mol*










