5 Chapter 5Figure 5.1 A nitrogen atom approaching an oxygen molecule must have enough k...Figure 5.2 A nitrogen atom will sweep out a volume V = vπ ( r N + r O) 2Figure 5.3 (a) Relative change in the reaction rate as a function of activat...Figure 5.4 Progress in the reaction CO 2(aq)+ H 2O → H 2CO 3with time, as meas...Figure 5.5 Structure of L-isoleucine and D-alloisoleucine. Solid...Figure 5.6 The relationship between enthalpy of reaction and the barrier ene...Figure 5.7 Comparison of observed and predicted rates of the aragonite ⇋ cal...Figure 5.8 Log of the rate constant vs. inverse of temperature for a variety...Figure 5.9 Relative volume of dolomite as a function of time predicted at 62...Figure 5.10 A volume of dimension d x with fluxes through the planes at x and...Figure 5.11 Three possible concentration gradients. In (a), ∂ 2 c/∂x ...Figure 5.12 Concentration profiles at three different times resulting from o...Figure 5.13 An extended initial distribution can be thought of as consisting...Figure 5.14 Distribution of a diffusing species initially confined to −∞ < x Figure 5.15 A zoned plagioclase crystal in a lava from the Azores viewed wit...Figure 5.16 Distribution of Ni in a spherical olivine grain with an initial ...Figure 5.17 Change in the bulk concentration of Sr in a 2 mm diameter calcit...Figure 5.18 Electron microprobe traverses across the contact of basaltic liq...Figure 5.19 Four types of diffusion mechanisms in solids. After Henderson (1...Figure 5.20 Schematic plot of log diffusion rate against inverse of temperat...Figure 5.21 Schematic plot of log diffusion rate against inverse of temperat...Figure 5.22 On a microscopic scale, the surface of a mineral exhibits a numb...Figure 5.23 Free energy as a function of crystal radius for small crystals f...Figure 5.24 Calculated nucleation rate of diopside in diopside melt as a fun...Figure 5.25 Photomicrograph of an intergrowth of clinopyroxene and plagiocla...Figure 5.26 Illustration of the balance of forces as a spherical crystal or ...Figure 5.27 Variation of Sr and Rb concentrations from a plagioclase–liquid ...Figure 5.28 Left: Photomicrograph of a fossiliferous limestone from Texas (L...Figure 5.29 a. Distribution of grain sizes normalized to mean grain diameter...Figure 5.30 Variation of adsorption density of Sr on FeOH as a function of S...Figure 5.31 Oxygenation of vanadyl at pH 4 and PO 2= 1 atm in experiments of...Figure 5.32 Mechanism of oxygenation of surface-bound vanadyl. In step (1) v...Figure 5.33 Cartoon of proton-promoted dissolution of an oxide such as quart...Figure 5.34 Log of the rate of Al 2O 3dissolution plotted against the log of ...Figure 5.35 Quartz dissolution and precipitation rates at 200°C in near-neut...Figure 5.36 Experimentally determined dissolution rates of common minerals a...Figure 5.37 Comparison of olivine (forsterite) and feldspar (albite) structu...Figure 5.38 Enstatite (MgSiO 3) and forsterite (Mg 2SiO 4) dissolution rates as...Figure 5.39 (a). Albite dissolution rates measured by Hellman and Tisserand ...Figure 5.40 Log of steady-state dissolution (a) and growth (b) of calcite as...Figure 5.41 Steady-state diagenesis. Concentration at a fixed depth x 1below...Figure 5.42 Concentration profiles in a sediment in which the composition of...Figure 5.43 Fluxes through a box in a sedimentary layer of unit lateral dime...Figure 5.44 Dissolved sulfate concentrations in sediments from the Saanich I...
6 Chapter 6Figure 6.1 Activities of different species in the carbonate system as a func...Figure 6.2 Titration curve (solid red line) for a one liter 0.005 M Na 2CO 3...Figure 6.3 Buffer intensity as a function of pH for several ideal natural sy...Figure 6.4 Buffer capacity of a carbonate solution in equilibrium with atmos...Figure 6.5 Illustration of ion pair and complex formation. Two types of ion ...Figure 6.6 Predominant aquo-, hydroxo-, and oxo-complexes as a function of p...Figure 6.7 Fraction of Pb complexed as PbOH +as a function of pH.Figure 6.8 pH and −log α, as a function of total copper concentration in aqu...Figure 6.9 Classification of the elements with respect to complex formation ...Figure 6.10 Stability constants for transition metal sulfate and organic com...Figure 6.11 Concentration of calcium ion in equilibrium with calcite at 25°C...Figure 6.12 Comparison of the evolution of systems with constant 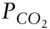 (open sys...Figure 6.13 Predominance diagrams for Mg-bearing phases in equilibrium with ...Figure 6.14 Stability of magnesite, dolomite, calcite, and brucite in equili...Figure 6.15 Stability diagram showing the stable solid Fe-bearing phases in ...Figure 6.16 Log activity of dissolved silica in equilibrium with quartz and ...Figure 6.17 Solubility of metal hydroxides as a function of pH. After Stumm ...Figure 6.18 Log activity of dissolved aluminum species and total Al (solid r...Figure 6.19 Solubility of goethite as a function of pH. Solubility of indivi...Figure 6.20 Total dissolved Al activity in equilibrium with gibbsite, pyroph...Figure 6.21 Stability diagram for the system K 2O−Al 2O 3−SiO 2−H 2O at 25°C. Aft...Figure 6.22 Stability diagram for the system K 2O−Na 2O−CaO−Al 2O 3−SiO 2−H 2O at ...Figure 6.23 Structure of gibbsite and brucite. (a) Plan (vertical) view. (b)...Figure 6.24 Structure of kaolinite. (a) Plan view of the tetrahedral layer. ...Figure 6.25 Structure of pyrophyllite.Figure 6.26 Structure of muscovite (KAl 3Si 3O 10(OH) 2). The structure of the c...Figure 6.27 Structure of chlorite.Figure 6.28 (a) Metal ions (small red spheres) and oxygens (large gray spher...Figure 6.29 Complex formation of solid surfaces may occur when (a) a metal r...Figure 6.30 Binding of ligands (anions) on the surface of hydrous ferric oxi...Figure 6.31 Calculated adsorption of Pb 2+on hydrous ferric oxide for th...Figure 6.32 Calculated adsorption (Θ, fraction of sites occupied) of metals ...Figure 6.33 Inner sphere surface complexes involve some degree of covalent b...Figure 6.34 (a) Surface charge of some common sedimentary materials as a fun...Figure 6.35 Surface charge on FeOOH as a function of pH for different ionic ...Figure 6.36 (a) Titration of a suspension of α−FeOOH (goethite) (6 g/liter)...Figure 6.37 Variation in electrical potential and ions with distance from a ...Figure 6.38 The double layer surrounding clay particles.Figure 6.39 Surface speciation of hydrous ferric oxide for I = 0.1 M calcul...Figure 6.40 Comparison of calculated adsorption of Pb on hydrous ferric oxid...
(open sys...Figure 6.13 Predominance diagrams for Mg-bearing phases in equilibrium with ...Figure 6.14 Stability of magnesite, dolomite, calcite, and brucite in equili...Figure 6.15 Stability diagram showing the stable solid Fe-bearing phases in ...Figure 6.16 Log activity of dissolved silica in equilibrium with quartz and ...Figure 6.17 Solubility of metal hydroxides as a function of pH. After Stumm ...Figure 6.18 Log activity of dissolved aluminum species and total Al (solid r...Figure 6.19 Solubility of goethite as a function of pH. Solubility of indivi...Figure 6.20 Total dissolved Al activity in equilibrium with gibbsite, pyroph...Figure 6.21 Stability diagram for the system K 2O−Al 2O 3−SiO 2−H 2O at 25°C. Aft...Figure 6.22 Stability diagram for the system K 2O−Na 2O−CaO−Al 2O 3−SiO 2−H 2O at ...Figure 6.23 Structure of gibbsite and brucite. (a) Plan (vertical) view. (b)...Figure 6.24 Structure of kaolinite. (a) Plan view of the tetrahedral layer. ...Figure 6.25 Structure of pyrophyllite.Figure 6.26 Structure of muscovite (KAl 3Si 3O 10(OH) 2). The structure of the c...Figure 6.27 Structure of chlorite.Figure 6.28 (a) Metal ions (small red spheres) and oxygens (large gray spher...Figure 6.29 Complex formation of solid surfaces may occur when (a) a metal r...Figure 6.30 Binding of ligands (anions) on the surface of hydrous ferric oxi...Figure 6.31 Calculated adsorption of Pb 2+on hydrous ferric oxide for th...Figure 6.32 Calculated adsorption (Θ, fraction of sites occupied) of metals ...Figure 6.33 Inner sphere surface complexes involve some degree of covalent b...Figure 6.34 (a) Surface charge of some common sedimentary materials as a fun...Figure 6.35 Surface charge on FeOOH as a function of pH for different ionic ...Figure 6.36 (a) Titration of a suspension of α−FeOOH (goethite) (6 g/liter)...Figure 6.37 Variation in electrical potential and ions with distance from a ...Figure 6.38 The double layer surrounding clay particles.Figure 6.39 Surface speciation of hydrous ferric oxide for I = 0.1 M calcul...Figure 6.40 Comparison of calculated adsorption of Pb on hydrous ferric oxid...
7 Chapter 7Figure 7.1 Three-dimensional histogram illustrating the abundance of the el...Figure 7.2 Goldschmidt's classification of the elements.Figure 7.3 The geochemical periodic table, in which elements are grouped acc...Figure 7.4 (a) Solubility of the rare gases in melts of varying composition ...Figure 7.5 Ionic radii of the lanthanide rare earth elements (3+ state excep...Figure 7.6 Concentrations of the rare earths in the carbonaceous chondritic ...Figure 7.7 A rare earth plot showing rare earth patterns for average upper c...Figure 7.8 Shale-normalized REE patterns of a Pacific pelagic sediment (V21-...Figure 7.9 Chondrite-normalized abundances of the noble metals in ore deposi...Figure 7.10 Ionic radius (picometers) vs. ionic charge contoured for clinopy...Figure 7.11 Effects of temperature and water in the melt on trace element pa...Figure 7.12 Experimentally determined clinopyroxene–liquid and plagioclase–l...Figure 7.13 Because increasing pressure increases the amount of jadeite (NaA...Figure 7.14 Variation of the zinc olivine/liquid partition coefficient as a ...Figure 7.15 Comparison of Zn olivine/melt partition coefficients of Kohn and...Figure 7.16 Effect of tetrahedral aluminum mole fraction and Na 2O melt conce...Figure 7.17 Comparison of calculated REE patterns for a representative andes...Figure 7.18 Rare earth mineral–melt partition coefficients for mafic magmas....Figure 7.19 Geometry of the d orbitals.Figure 7.20 (a) Orientation of ligands and Cartesian coordinates for a metal...Figure 7.21 (a) Orientation of ligands and Cartesian coordinates for a metal...Figure 7.22 Arrangement of ligands and energy levels for (a) an octahedral s...Figure 7.23 Schematic phase diagram for the system forsterite–Ni olivine sho...Figure 7.24 Variation in C ℓ /C owith degree of melting, F , for various ...Figure 7.25 Rare earth patterns of 7% batch and aggregate fractional partial...Figure 7.26 Comparison of continuous and fractional melting for D = 0.0001 a...Figure 7.27 Representation of melting of an ascending packet of mantle in te...Figure 7.28 Relationship between extent of melting, F, and temperature in pe...Figure 7.29 Relationship between dihedral angle, θ , and melt distributi...Figure 7.30 Three-dimensional network formed by melt along triple junctions ...Figure 7.31 (a) Melting regime under a mid-ocean ridge. Red lines show the f...Figure 7.32 Variation of relative trace element concentration in a liquid un...Figure 7.33 Magma chamber undergoing in situ crystallization. The solidifica...Figure 7.34 Comparison of the effects of in situ and fractional crystallizat...Figure 7.35 Schematic illustration of a steady-state and periodically refill...Figure 7.36 Concentration of Ni and La in closed system fractional crystalli...Figure 7.37 La and Ni concentrations plotted against MgO concentration in a ...Figure 7.38 Plot of the ratio of two incompatible elements (one with D = 0.0...
Читать дальше

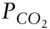 (open sys...Figure 6.13 Predominance diagrams for Mg-bearing phases in equilibrium with ...Figure 6.14 Stability of magnesite, dolomite, calcite, and brucite in equili...Figure 6.15 Stability diagram showing the stable solid Fe-bearing phases in ...Figure 6.16 Log activity of dissolved silica in equilibrium with quartz and ...Figure 6.17 Solubility of metal hydroxides as a function of pH. After Stumm ...Figure 6.18 Log activity of dissolved aluminum species and total Al (solid r...Figure 6.19 Solubility of goethite as a function of pH. Solubility of indivi...Figure 6.20 Total dissolved Al activity in equilibrium with gibbsite, pyroph...Figure 6.21 Stability diagram for the system K 2O−Al 2O 3−SiO 2−H 2O at 25°C. Aft...Figure 6.22 Stability diagram for the system K 2O−Na 2O−CaO−Al 2O 3−SiO 2−H 2O at ...Figure 6.23 Structure of gibbsite and brucite. (a) Plan (vertical) view. (b)...Figure 6.24 Structure of kaolinite. (a) Plan view of the tetrahedral layer. ...Figure 6.25 Structure of pyrophyllite.Figure 6.26 Structure of muscovite (KAl 3Si 3O 10(OH) 2). The structure of the c...Figure 6.27 Structure of chlorite.Figure 6.28 (a) Metal ions (small red spheres) and oxygens (large gray spher...Figure 6.29 Complex formation of solid surfaces may occur when (a) a metal r...Figure 6.30 Binding of ligands (anions) on the surface of hydrous ferric oxi...Figure 6.31 Calculated adsorption of Pb 2+on hydrous ferric oxide for th...Figure 6.32 Calculated adsorption (Θ, fraction of sites occupied) of metals ...Figure 6.33 Inner sphere surface complexes involve some degree of covalent b...Figure 6.34 (a) Surface charge of some common sedimentary materials as a fun...Figure 6.35 Surface charge on FeOOH as a function of pH for different ionic ...Figure 6.36 (a) Titration of a suspension of α−FeOOH (goethite) (6 g/liter)...Figure 6.37 Variation in electrical potential and ions with distance from a ...Figure 6.38 The double layer surrounding clay particles.Figure 6.39 Surface speciation of hydrous ferric oxide for I = 0.1 M calcul...Figure 6.40 Comparison of calculated adsorption of Pb on hydrous ferric oxid...
(open sys...Figure 6.13 Predominance diagrams for Mg-bearing phases in equilibrium with ...Figure 6.14 Stability of magnesite, dolomite, calcite, and brucite in equili...Figure 6.15 Stability diagram showing the stable solid Fe-bearing phases in ...Figure 6.16 Log activity of dissolved silica in equilibrium with quartz and ...Figure 6.17 Solubility of metal hydroxides as a function of pH. After Stumm ...Figure 6.18 Log activity of dissolved aluminum species and total Al (solid r...Figure 6.19 Solubility of goethite as a function of pH. Solubility of indivi...Figure 6.20 Total dissolved Al activity in equilibrium with gibbsite, pyroph...Figure 6.21 Stability diagram for the system K 2O−Al 2O 3−SiO 2−H 2O at 25°C. Aft...Figure 6.22 Stability diagram for the system K 2O−Na 2O−CaO−Al 2O 3−SiO 2−H 2O at ...Figure 6.23 Structure of gibbsite and brucite. (a) Plan (vertical) view. (b)...Figure 6.24 Structure of kaolinite. (a) Plan view of the tetrahedral layer. ...Figure 6.25 Structure of pyrophyllite.Figure 6.26 Structure of muscovite (KAl 3Si 3O 10(OH) 2). The structure of the c...Figure 6.27 Structure of chlorite.Figure 6.28 (a) Metal ions (small red spheres) and oxygens (large gray spher...Figure 6.29 Complex formation of solid surfaces may occur when (a) a metal r...Figure 6.30 Binding of ligands (anions) on the surface of hydrous ferric oxi...Figure 6.31 Calculated adsorption of Pb 2+on hydrous ferric oxide for th...Figure 6.32 Calculated adsorption (Θ, fraction of sites occupied) of metals ...Figure 6.33 Inner sphere surface complexes involve some degree of covalent b...Figure 6.34 (a) Surface charge of some common sedimentary materials as a fun...Figure 6.35 Surface charge on FeOOH as a function of pH for different ionic ...Figure 6.36 (a) Titration of a suspension of α−FeOOH (goethite) (6 g/liter)...Figure 6.37 Variation in electrical potential and ions with distance from a ...Figure 6.38 The double layer surrounding clay particles.Figure 6.39 Surface speciation of hydrous ferric oxide for I = 0.1 M calcul...Figure 6.40 Comparison of calculated adsorption of Pb on hydrous ferric oxid...










