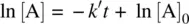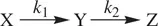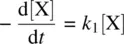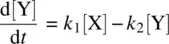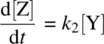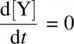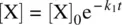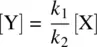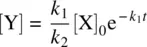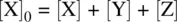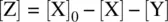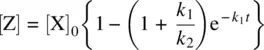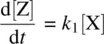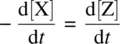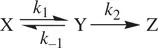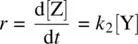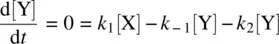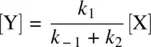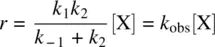1 ...7 8 9 11 12 13 ...23 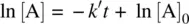
1.4.2 Reactive Intermediates and the Steady‐State Assumption
First, let us consider a reaction that consists of two consecutive irreversible unimolecular processes as shown in Reaction 1.28.
(1.28) 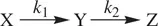
X is the reactant. Z is the product. Y is a reactive intermediate. k 1and k 2are rate constants for the two unimolecular processes. In order to determine the way in which the concentrations of the substances change over time, the rate equation for each of the substances is written down as follows (Eq. ) [2]:
(1.29) 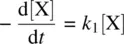
(1.30) 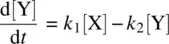
(1.31) 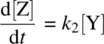
Equation 1.30shows the net rate of increase in the intermediate Y, which is equal to the rate of its formation ( k 1[X]) minus the rate of its disappearance ( k 2[Y]). Equation 1.31shows the rate of formation of the product Z. Since Z is produced only from the k 2step which is a unimolecular process, the rate equation for Z is first order in Y.
It is tedious to obtain the accurate solutions of the above simultaneous differential equations. Appropriate approximations may be employed to ease the situation [2].
In most of the stepwise organic reactions, the intermediates (such as radicals and carbocations) possess high energies and are unstable and highly reactive. Therefore, the formation of such an intermediate is usually relatively slow (with a high E a), while the subsequent transformation the intermediate experiences is relatively fast (with a low E a). Mathematically, k 1is much smaller than k 2( k 1≪ k 2). As a result, the concentration of the reactive intermediate (such as Y in Reaction 1.28 ) remains at a low level and it essentially does not change in the course of the overall reaction . This is referred to as the steady‐state approximation. The changes in concentrations of the reactant, intermediate, and product over time for Reaction 1.28are illustrated in Figure 1.2. It shows that the intermediate Y in Reaction 1.28remains in a steady‐state (an essentially constant low concentration) in the course of the overall reaction, formulated as
(1.32) 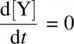
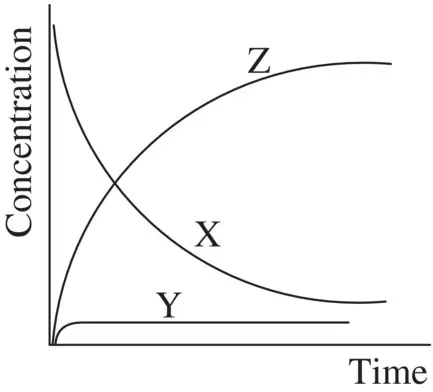
FIGURE 1.2 The changes in concentrations of the reactant (X), intermediate (Y), and product (Z) over time for Reaction 1.28. The intermediate Y is shown to remain in a steady‐state (d[Y]/d t = 0) in the course of the overall reaction.
In general, the steady‐state approximation is applicable to all types of reaction intermediates in organic chemistry . Equation 1.32is the mathematical form of the steady‐state assumption.
With the help of the steady‐state approximation, the dependence of concentrations of all the substances in Reaction 1.28on time can be obtained readily [2].
Integration of Equation 1.29leads to Equation 1.33(c.f. Eqs 1.9– 1.12).
(1.33) 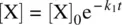
[X] 0is the initial concentration of X.
From Equation 1.30(rate equation for Y) and Equation 1.32(steady‐state assumption for Y), we have
(1.34) 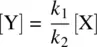
Substituting Equation 1.33for Equation 1.34, we have
(1.35) 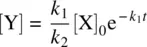
On the basis of the stoichiometry for Reaction 1.28, the initial concentration of the reactant X can be formulated as
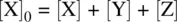
Therefore,
(1.36) 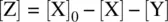
Combination of Equations gives Equation 1.37.
(1.37) 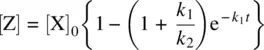
Equations show the dependence of concentrations of all the substances in Reaction 1.28on time [2].
Substituting Equation 1.34(derived from the steady‐state approximation for Y) for Equation 1.31gives Equation 1.38.
(1.38) 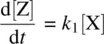
Comparing Equations 1.29and 1.38indicates that rate for consumption of the reactant X is approximately equal to rate for the formation of the product Z ( Eq. 1.39).
(1.39) 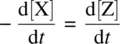
1.4.3 Rate‐Laws for Stepwise Reactions
Let us use the following consecutive reaction ( Reaction 1.40) that involves both reversible and irreversible elementary processes to demonstrate the general procedure for obtaining rate laws for stepwise reactions [3]:
(1.40) 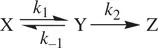
The rate ( r ) for the overall reaction can be expressed as an increase in concentration of the product (Z) per unit time ( Eq. 1.41):
(1.41) 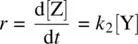
Since Z is produced only from the k 2step which is a unimolecular process, the rate equation for Z is first order in Y.
The steady‐state assumption is applied to the intermediate Y, and its rate equation is written as follows:
(1.42) 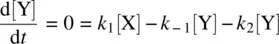
From Equation 1.42, we have
(1.43) 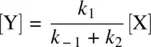
Substituting Equation 1.43for Equation 1.41leads to Equation 1.44, the rate law for Reaction 1.40.
(1.44) 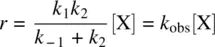
Читать дальше