1 ...6 7 8 10 11 12 ...31 Introduction of CRISPR‐Cpf1 also known as CRISPR‐Cas12a further diversified the genome engineering methods ( Figure 1.2). Cpf1 is an endonuclease which belongs to the class II CRISPR family (Alok et al. 2020; Zaidi et al. 2017). It was identified from Prevotella and Francisella1 , therefore named as named as Cpf1. This system become popular as it was able to fill the gaps of previous genome editing tools and can substitute the CRISPR‐Cas9 in an efficient way (Moon et al. 2018). It is smaller in size than Cas9 and required a shorter CRISPR RNA for proper functioning (Liu et al. 2017). Unlike the CRISPR/Cas9, tracrRNA is no longer necessary to process Cpf1 associated mature CRISPR RNAs (Zetsche et al. 2015). Further, in contrast to the G rich PAM at 3′ end in CRISPR Cas9, it requires a T‐rich PAM sequence at the 5′‐end to perform cleavage efficiently, which enables the targeting of AT‐rich regions in the genome. Further, Cpf1 creates staggered cuts where insertion of a DNA fragment is easily possible via HDR (Gao et al. 2017). The off‐target binding of CRIPSR‐Cpf1 is comparatively less than CRISPR‐Cas9 which could be an additional benefit (Kim et al. 2016; Kleinstiver et al. 2016; Yan et al. 2017). A number of studies showed the application of CRISPR‐Cpf1 for targeted genome editing in various eukaryotes including plants (Kim et al. 2017; Zetsche et al. 2015). It has also been used for multiple targets in the genome (Wang et al. 2017).
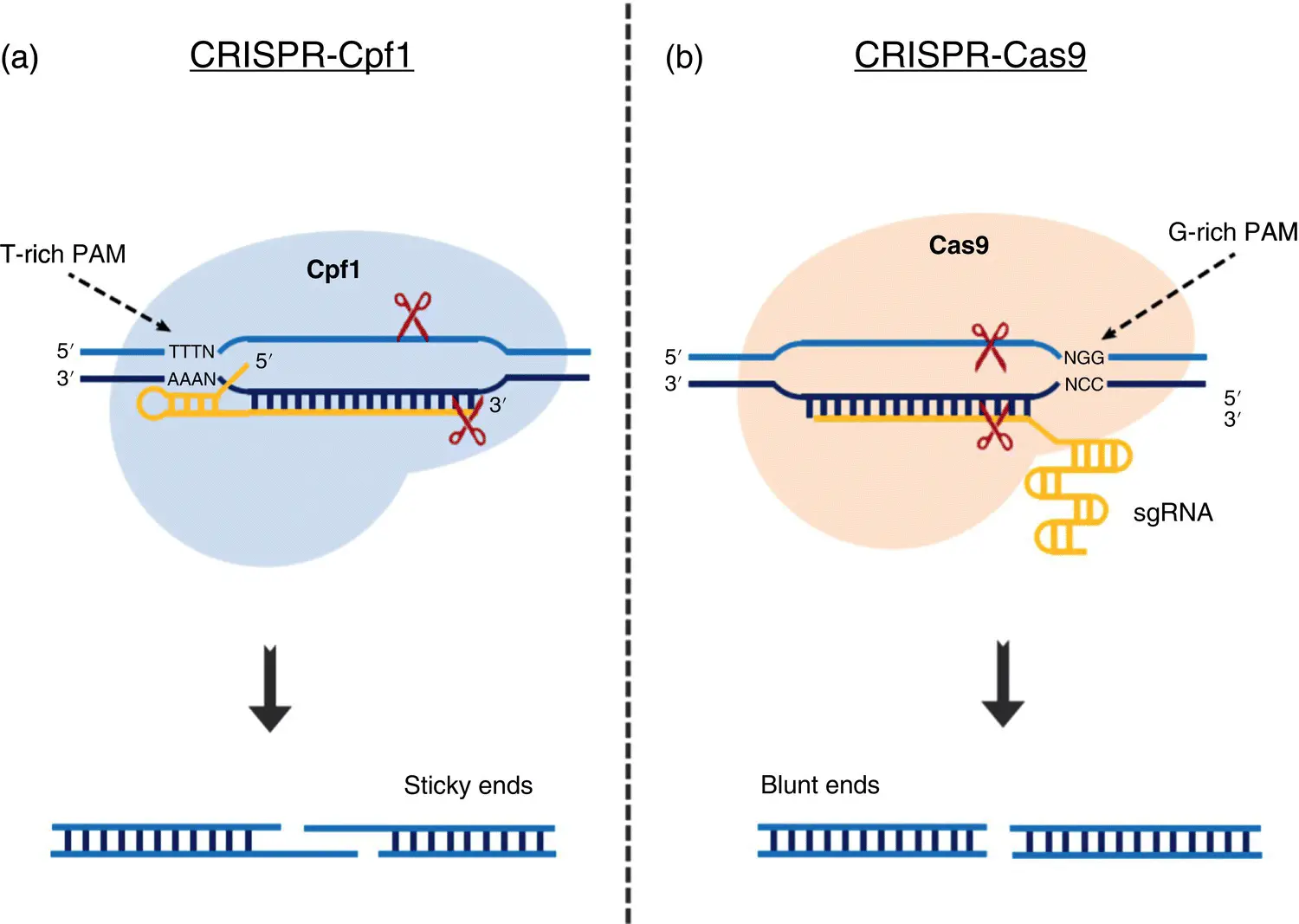
Figure 1.2 Comparison of various features of CRISPR‐Cpf1 (a) and CRISPR‐Cas9.
Source: Adapted from Zaidi et al. (2017) © 2017. Reproduced with the permission of Elsevier.
Genome‐editing technologies enable us to make precise changes in the genome of any living organism. These changes may be diverse‐insertion, deletion or even replacement of a particular stretch of DNA from the genome. Targeting these changes in accordance with our needs has always been the ambition of the scientific community. It was a challenging job until the development of recent genome‐editing technologies. Among these, the most popular and successful ones till now have been ZFNs, TALENs, and CRISPR‐Cas9. The breakthrough in the field of genome editing came after the discovery of CRISPR/Cas9 system as it is an RNA‐ guided and easy‐to‐design system. This system is fascinatingly repurposed as a genome editing tool and is till now the most efficient, cost effective and least demanding genome editing technique. Moreover, the recent addition of CRISPR‐Cpf1 that is a variant of the CRISPR‐Cas system further diversified the application of genome engineering tools by overcoming the various shortcomings of earlier systems.
Ms. Sushmita is grateful to DST‐INSPIRE fellowship Program, DST, New Delhi, India for providing financial support. Authors are also thankful to CSIR, New Delhi for financial support in the form of “FBR Genome Editing Network Project” (MLP‐007).
Institute's Manuscript Number is 'CSIR‐NBRI_MS/2020/06/24.
1 Ainley, W.M., Sastry‐Dent, L., Welter, M.E. et al. (2013). Trait stacking via targeted genome editing. Plant Biotechnology Journal 11: 1126–1134.
2 Alok, A., Sandhya, D., Jogam, P. et al. (2020). The rise of the CRISPR/Cpf1 system for efficient genome editing in plants. Frontiers in Plant Science 11: 264.
3 Andersson, M., Turesson, H., Nicolia, A. et al. (2017). Efficient targeted multiallelic mutagenesis in tetraploid potato (Solanum tuberosum) by transient CRISPR‐Cas9 expression in protoplasts. Plant Cell Reports 36 (1): 117–128.
4 Bae, K.H., Do Kwon, Y., Shin, H.C. et al. (2003). Human zinc fingers as building blocks in the construction of artificial transcription factors. Nature Biotechnology 21 (3): 275–280.
5 Bae, S., Park, J., and Kim, J.S. (2014). Cas‐OFFinder: a fast and versatile algorithm that searches for potential off‐target sites of Cas9 RNA‐guided endonucleases. Bioinformatics 30 (10): 1473–1475.
6 Boch, J., Scholze, H., Schornack, S. et al. (2009). Breaking the code of DNA binding specificity of TAL‐type III effectors. Science 326: 1509–1512.
7 Brazelton, V.A. Jr., Zarecor, S., Wright, D.A. et al. (2015). A quick guide to CRISPR sgRNA design tools. GM Crops and Food 6 (4): 266–276.
8 Briggs, A.W., Rios, X., Chari, R. et al. (2012). Iterative capped assembly: rapid and scalable synthesis of repeat‐module DNA such as TAL effectors from individual monomers. Nucleic Acids Research 40 (15): e117–e117.
9 Butler, N.M., Baltes, N.J., Voytas, D.F., and Douches, D.S. (2016). Geminivirus‐mediated genome editing in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) using sequence‐specific nucleases. Frontiers in Plant Science 7: 1045.
10 Butt, H., Eid, A., Ali, Z. et al. (2017). Efficient CRISPR/Cas9‐mediated genome editing using a chimeric single‐guide RNA molecule. Frontiers in Plant Science 8: 1441.
11 Cai, C.Q., Doyon, Y., Ainley, W.M. et al. (2009). Targeted transgene integration in plant cells using designed zinc finger nucleases. Plant Molecular Biology 69: 699–709.
12 Cermak, T., Doyle, E.L., Christian, M. et al. (2011). Efficient design and assembly of custom TALEN and other TAL effector‐based constructs for DNA targeting. Nucleic Acids Research 39 (12): e82–e82.
13 Chandrasekaran, J., Brumin, M., Wolf, D. et al. (2016). Development of broad virus resistance in non‐transgenic cucumber using CRISPR/Cas9 technology. Molecular Plant Pathology 17 (7): 1140–1153.
14 Charrier, A., Vergne, E., Dousset, N. et al. (2019). Efficient targeted mutagenesis in apple and first time edition of pear using the CRISPR‐Cas9 system. Frontiers in Plant Science 10: 40.
15 Chen, H., Choi, J., and Bailey, S. (2014). Cut site selection by the two nuclease domains of the Cas9 RNA‐guided endonuclease. Journal of Biological Chemistry 289 (19): 13284–13294.
16 Chen, K., Wang, Y., Zhang, R. et al. (2019). CRISPR/Cas genome editing and precision plant breeding in agriculture. Annual Review of Plant Biology 70: 667–697.
17 Chen, W., Dong, Y., Saqib, H.S.A. et al. (2020). Functions of duplicated glucosinolate sulfatases in the development and host adaptation of Plutella xylostella. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 119: 103316.
18 Cho, S.W., Kim, S., Kim, Y. et al. (2014). Analysis of off‐target effects of CRISPR/Cas‐derived RNA‐guided endonucleases and nickases. Genome Research 24: 132–141.
19 Christian, M., Cermak, T., Doyle, E.L. et al. (2010). Targeting DNA double‐strand breaks with TAL effector nucleases. Genetics 186: 757–761.
20 Christian, M., Qi, Y., Zhang, Y., and Voytas, D.F. (2013). Targeted mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana using engineered TAL effector nucleases. G3: Genes, Genomes, Genetics 3 (10): 1697–1705.
21 Clasen, B.M., Stoddard, T.J., Luo, S. et al. (2016). Improving cold storage and processing traits in potato through targeted gene knockout. Plant Biotechnology Journal 14 (1): 169–176.
22 Cong, L., Ran, F.A., Cox, D. et al. (2013). Multiplex genome engineering using CRISPR/Cas systems. Science 339: 819–823.
23 Coordinators, N.R. (2013). Database resources of the national center for biotechnology information. Nucleic Acids Research 41 (Database issue): D8.
24 Cradick, T.J., Qiu, P., Lee, C.M. et al. (2014). COSMID: a web‐based tool for identifying and validating CRISPR/Cas off‐target sites. Molecular Therapy – Nucleic Acids 3: e214.
25 Curtin, S.J., Zhang, F., Sander, J.D. et al. (2011). Targeted mutagenesis of duplicated genes in soybean with zinc‐finger nucleases. Plant Physiology 156 (2): 466–473.
Читать дальше













