Corn. —The chief product of their agriculture is corn. This becomes edible in the months of May and June and at this time it is eaten in great quantities. Then it is that the annual festival called the “Green Corn Dance” is celebrated. When the corn ripens, a quantity of it is laid aside and gradually used in the form of hominy and of what I heard described as an “exceedingly beautiful meal, white as the finest wheat flour.” This meal is produced by a slow and tedious process. The corn is hulled and the germ cut out, so that there is only a pure white residue. This is then reduced by mortar and pestle to an almost impalpable dust. From this flour a cake is made, which, is said to be very pleasant to the taste.
Sugar cane. —Another product of their agriculture is the sugar cane. In growing this they are the producers of perhaps the finest sugar cane grown in America; but they are not wise enough to make it a source of profit to themselves. It seems to be cultivated more as a passing luxury. It was at “Old Tommy’s” sugar field I met the forty-eight of the people of the Big Cypress Swamp settlement already mentioned. They had left their homes that they might have a pleasuring for a few weeks together, “camping out” and making and eating sirup. The cane which had been grown there was the largest I or my companion, Capt. F. A. Hendry, of Myers, had ever seen. It was two inches or more in diameter, and, as we guessed, seventeen feet or more in length. To obtain the sirup the Indians had constructed two rude mills, the cylinders of which, however, were so loosely adjusted that full half the juice was lost in the process of crushing the cane. The juice was caught in various kinds of iron and tin vessels, kettles, pails, and cans, and after having been, strained was boiled until the proper consistency was reached.
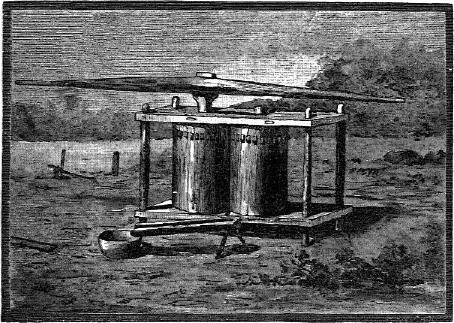
Sugar cane crusher.
At the time we were at the camp quite a quantity of the sirup had been made. It stood around the boiling place in kettles, large and small, and in cans bearing the labels of well known Boston and New York packers, which had been purchased at Myers. Of special interest to me was a platform near the boiling place, on which lay several deer skins, that had been taken as nearly whole as possible from the bodies of the animals, and utilized as holders of the sirup. They were filled with the sweet stuff, and the ground beneath was well covered by a slow leakage from them. “Key West Billy” offered me some of the cane juice to drink. It was clean looking and served in a silver gold lined cup of spotless brilliancy. It made a welcome and delicious drink. I tasted some of the sirup also, eating it Indian fashion, i.e., I pared some of their small boiled wild potatoes and, dipping them into the sweet liquid, ate them. The potato itself tastes somewhat like a boiled chestnut.
The sugar cane mill was a poor imitation of a machine the Indians had seen among the whites. Its cylinders were made of live oak; the driving cogs were cut from a much harder wood, the mastic, I was told; and these were so loosely set into the cylinders that I could take them out with thumb and forefinger. ( Fig. 68.)
It is not necessary to speak in particular of the culture of sweet potatoes, beans, melons, &c. At best it is very primitive. It is, however, deserving of mention that the Seminole have around their houses at least a thousand banana plants. When it is remembered that a hundred bananas are not an overlarge yield for one plant, it is seen how well off, so far as this fruit is concerned, these Indians are.
Table of Contents
Next in importance as an industry of the tribe (if it may be so called) is hunting. Southern Florida abounds in game and the Indians have only to seek in order to find it. For this purpose they use the rifle. The bow and arrow are no longer used for hunting purposes except by the smaller children. The rifles are almost all the long, heavy, small bore “Kentucky” rifle. This is economical of powder and lead, and for this reason is preferred by many to even the modern improved weapons which carry fixed ammunition. The Seminole sees the white man so seldom and lives so far from trading posts that he is not willing to be confined to the use of the prepared cartridge.
A few breech loading rifles are owned in the tribe. The shot gun is much disliked by the Seminole. There is only one among them, and that is a combination of shot gun with rifle. I made a careful count of their fire arms, and found that they own, of “Kentucky” rifles, 63; breech loading rifles, 8; shot gun and rifle, 1; revolvers, 2 total, 74.
Methods of hunting.—The Seminole always hunt their game on foot. They can approach a deer to within sixty yards by their method of rapidly nearing him while he is feeding, and standing perfectly still when he raises his head. They say that they are able to discover by certain movements on the part of the deer when the head is about to be lifted. They stand side to the animal. They believe that they can thus deceive the deer, appearing to them as stumps or trees. They lure turkeys within shooting distance by an imitation of the calls of the bird. They leave small game, such as birds, to the children. One day, while some of our party were walking near Horse Creek with Ka-tca-la-ni, a covey of quail whirred out of the grass. By a quick jerk the Indian threw his ramrod among the birds and billed one. He appeared to regard this feat as neither accidental nor remarkable.
I sought to discover how many deer the Seminole annually kill, but could get no number which I can call trustworthy. I venture twenty-five hundred as somewhere near a correct estimate.
Otter hunting is another of the Seminole industries. This animal has been pursued with the rifle and with the bow and arrow. Lately the Indians have heard of the trap. When we left Horse Creek, a request was made by one of them to our guide to purchase for him six otter traps for use in the Cat Fish Lake camp.
Table of Contents
Fishing is also a profitable industry. For this the hook and line are often used; some also use the spoon hook. But it is a common practice among them to kill the fish with bow and arrow, and in this they are quite skillful. One morning some boys brought me a bass, weighing perhaps sis pounds, which one of them had shot with an arrow.
Table of Contents
Stock raising, in a small way, may be called a Seminole industry. I found that at least fifty cattle, and probably more, are owned by members of the tribe and that the Seminole probably possess a thousand swine and five hundred chickens. The latter are of an excellent breed. At Cat Fish Lake an unusual interest in horses seems now to be developing. I found there twenty horses. I was told that there are twelve horses at Fish Eating Creek, and I judge that between thirty-five and forty of these animals are now in possession of the tribe.
Table of Contents
The unique industry, in the more limited sense of the word, of the Seminole is the making of the Koonti flour. Koonti is a root containing a large percentage of starch. It is said to yield a starch equal to that of the best Bermuda arrowroot. White men call it the “Indian bread root,” and lately its worth as an article of commerce has been recognized by the whites. There are now at least two factories in operation in Southern Florida in which the Koonti is made into a flour for the white man’s market. I was at one such factory at Miami and saw another near Orlando. I ate of a Koonti pudding at Miami, and can say that, as it was there prepared and served with milk and guava jelly, it was delicious. As might be supposed, the Koonti industry, as carried on by the whites, produces a far finer flour than that which the Indians manufacture. The Indian process, as I watched it at Horse Creek, was this: The roots were gathered, the earth was washed from them, and they were laid in heaps near the “Koonti log.”
Читать дальше













