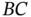1 Cover
2 Title Page Business Experiments with R B. D. McCullough Drexel University
3 Copyright
4 Dedication
5 Preface Suggested Courses Using This Book
6 Acknowledgments
7 Bruce McCullough
8 About the Companion Website
9 1 Why Experiment? 1.1 Case: Life Expectancy and Newspapers 1.2 Case: Credit Card Defaults 1.3 Case: Salk Polio Vaccine Trials 1.4 What Is a Business Experiment? 1.5 Improving Website Designs 1.6 A Brief History of Experiments 1.7 Chapter Exercises 1.8 Learning More 1.9 Statistics Refresher
10 2 Analyzing A/B Tests: Basics 2.1 Case: Improving Response to Sales Calls (Two‐Sample Test of Means) 2.2 Case: Email Response Test (Two‐Sample Test of Proportions) 2.3 Case: Comparing Landing Pages (Two‐Sample Test of Means, Again) 2.4 Case: Display Ad Clickthrough Rate 2.5 Case: Hotel Ad Test 2.6 Chapter Exercises 2.7 Learning More Notes
11 3 Designing A/B Tests with Large Samples 3.1 The Average Treatment Effect Exercises 3.2 Internal and External Validity Exercises 3.3 Designing Conclusive Experiments Exercises 3.4 The Lady Tasting Tea Exercises 3.5 Testing a New Checkout Button Exercises 3.6 Chapter Exercises 3.7 Learning More
12 4 Analyzing A/B Tests: Advanced Techniques 4.1 Case: Audio/Video Test Reprise (One‐Sided Tests) 4.2 Case: Typing Test (Paired ‐Test) 4.3 A/B/n Tests 4.4 Minimum Detectable Effect 4.5 Subgroup Analysis 4.6 Simpson's Paradox 4.7 Test and Roll 4.8 Chapter Exercises 4.9 Learning More 4.10 Axppendix on One‐Sided CIs, Tests, and Sample Sizes
13 5 Designing Tests with Small Samples 5.1 Case: Call Center Scripts (ANOVA) 5.2 Case: Facebook Geo‐Testing (Latin Square Design) 5.3 Dealing with Covariate Imbalance 5.4 Chapter Exercises 5.5 Learning More
14 6 Analyzing Designs via Regression 6.1 Experiments and Linear Regression 6.2 Dummies, Effect Coding, and Orthogonality 6.3 Case: Loan Experiment Revisited (Interactions) 6.4 Case: Direct Mail (Three‐Way Interactions) 6.5 Pretreatment Covariates in Regression 6.6 Chapter Exercises 6.7 Learning More 6.8 Appendix: The Covariance Matrix of the Regression Coefficients
15 7 Two‐Level Full Factorial Experiments 7.1 Case: The Postcard Example 7.2 Case: Email Campaign 7.3 The Determinant of a Matrix 7.4 Aliasing 7.5 Blocking (Again) 7.6 Mee's Blunders 7.7 Chapter Exercises 7.8 Learning More 7.9 Appendix on aliasMatrix and colorMap
16 8 Two‐Level Screening Designs 8.1 Preliminaries 8.2 Case: Puncture Resistance (Small Screening Experiment) 8.3 Case: College Giving (Big Screening Experiment) 8.4 How to Set Up a Screening Experiment 8.5 Creating a Screening Design 8.6 Chapter Exercises 8.7 Learning More
17 9 Custom Design of Experiments 9.1 Case: Selling Used Cars at Auction I (Small Custom Screening) 9.2 Case: Selling Used Cars at Auction II (Custom Experiment) 9.3 Custom Experiment with Blocking 9.4 Custom Screening Experiments 9.5 More Than Two Levels 9.6 Chapter Exercises 9.7 Learning More
18 10 Epilogue 10.1 The Sequential Nature of Experimentation 10.2 Approaches to Sequential Experimentation
19 References
20 Index
21 End User License Agreement
1 Chapter 1 Table 1.1 Credit default rates for men and women. Table 1.2 Credit default rates by marital status. Table 1.3 Results of first Salk vaccine field trial. Table 1.4 Results of second Salk vaccine field trial. Table 1.5 Factors and levels for financial services example. Table 1.6 Summary of web test results.
2 Chapter 2 Table 2.1 Data from sales calls test. Table 2.2 Summary statistics for audio and video sales calls. Table 2.3 Errors in hypothesis tests.Table 2.4 Data from email response test.Table 2.5 Confidence intervals for the difference in response rate between em...Table 2.6 Power for two‐sample comparison of proportions, 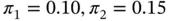 .Table 2.7 Summary statistics for sales.Table 2.8 Results of hotel display ad test.
.Table 2.7 Summary statistics for sales.Table 2.8 Results of hotel display ad test.
3 Chapter 4Table 4.1 Summary statistics on sales for subgroup data, zeros excluded..Table 4.2 Contingency table for aggregate A/B test.Table 4.3 Contingency table for subgroup “loan = yes” A/B test.Table 4.4 Contingency table for subgroup “amount 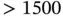 ” A/B test.Table 4.5 Admission to Berkeley graduate school by sex.Table 4.6 Credit default rates for men and women.Table 4.7 Kidney stone success rates.Table 4.8 Simpson's paradox in batting averages.Table 4.9 Simpson's paradox in voting.Table 4.10 Simpson's paradox in editing.Table 4.11 Simpson's paradox: septic shock example.Table 4.12 One‐sided alternatives and intervals.
” A/B test.Table 4.5 Admission to Berkeley graduate school by sex.Table 4.6 Credit default rates for men and women.Table 4.7 Kidney stone success rates.Table 4.8 Simpson's paradox in batting averages.Table 4.9 Simpson's paradox in voting.Table 4.10 Simpson's paradox in editing.Table 4.11 Simpson's paradox: septic shock example.Table 4.12 One‐sided alternatives and intervals.
4 Chapter 5Table 5.1 One‐way ANOVA on call center scripts.Table 5.2 Crosstab of counts for scripts A, B, C, and D and agents 1, 2, 3, 4...Table 5.3 One‐way ANOVA with blocking on call center data.Table 5.4 Tukey HSD intervals for call center data with blocking.Table 5.5 Initial experimental design for DigiPuppets.Table 5.6 Latin square design for DigiPuppets.Table 5.7 ANOVA on Latin square for DigiPuppets.Table 5.8 Standard form for Latin square design.Table 5.9 Another orthogonal Latin square design.Table 5.10 A bad choice for a Latin square design.Table 5.11 Randomizing a Latin square design: assign random numbers to rows a...Table 5.12 Data for new product example.Table 5.13 Latin square for background music exposure.Table 5.14 ANOVA results for distance1 (left) and distance2 (right).Table 5.15 ANOVA on combined distances.Table 5.16 Control and treatment means for various sample sizes.
5 Chapter 6Table 6.1 ANOVA table for car rental data.Table 6.2 Regression results on car rental data.Table 6.3 Simple experiment.Table 6.4 Numeric data for Table 6.3.Table 6.5 Regression results for simple experiment with dummy variables.Table 6.6 Regression results for simple experiment with effect‐coded variable...Table 6.7  table of responses to factors
table of responses to factors 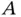 and
and 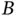 .Table 6.8 Response to interest rate and annual fee.Table 6.9 Effect coding vs. dummy coding.Table 6.10 Results of regressions on effect coding, dummies, and interactions...Table 6.11 Mnemonics for remembering level effect coding.Table 6.12 Design matrix for loan experiment.Table 6.13 Regression with all interactions, loan experiment.Table 6.14 Design matrix for credit card case.Table 6.15 Model matrix for credit card case.Table 6.16 Effects for credit card data set.Table 6.17 Regression results for credit card model.Table 6.18 Predictions (fitted values) for credit card model.
.Table 6.8 Response to interest rate and annual fee.Table 6.9 Effect coding vs. dummy coding.Table 6.10 Results of regressions on effect coding, dummies, and interactions...Table 6.11 Mnemonics for remembering level effect coding.Table 6.12 Design matrix for loan experiment.Table 6.13 Regression with all interactions, loan experiment.Table 6.14 Design matrix for credit card case.Table 6.15 Model matrix for credit card case.Table 6.16 Effects for credit card data set.Table 6.17 Regression results for credit card model.Table 6.18 Predictions (fitted values) for credit card model.
6 Chapter 7Table 7.1 Postcard data.Table 7.2 Full factorial regression coefficients for postcard experiment.Table 7.3 Postcard regression, reduced model.Table 7.4 Choosing 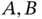 , and
, and 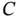 for main effects.Table 7.5 Are interactions consistent with main effects?.Table 7.6 Design matrix and predictions.Table 7.7 Postcard regression results, with replication.Table 7.8 Replicated postcard predictions with and without
for main effects.Table 7.5 Are interactions consistent with main effects?.Table 7.6 Design matrix and predictions.Table 7.7 Postcard regression results, with replication.Table 7.8 Replicated postcard predictions with and without 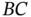
Читать дальше

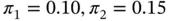 .Table 2.7 Summary statistics for sales.Table 2.8 Results of hotel display ad test.
.Table 2.7 Summary statistics for sales.Table 2.8 Results of hotel display ad test.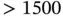 ” A/B test.Table 4.5 Admission to Berkeley graduate school by sex.Table 4.6 Credit default rates for men and women.Table 4.7 Kidney stone success rates.Table 4.8 Simpson's paradox in batting averages.Table 4.9 Simpson's paradox in voting.Table 4.10 Simpson's paradox in editing.Table 4.11 Simpson's paradox: septic shock example.Table 4.12 One‐sided alternatives and intervals.
” A/B test.Table 4.5 Admission to Berkeley graduate school by sex.Table 4.6 Credit default rates for men and women.Table 4.7 Kidney stone success rates.Table 4.8 Simpson's paradox in batting averages.Table 4.9 Simpson's paradox in voting.Table 4.10 Simpson's paradox in editing.Table 4.11 Simpson's paradox: septic shock example.Table 4.12 One‐sided alternatives and intervals. table of responses to factors
table of responses to factors 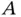 and
and 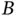 .Table 6.8 Response to interest rate and annual fee.Table 6.9 Effect coding vs. dummy coding.Table 6.10 Results of regressions on effect coding, dummies, and interactions...Table 6.11 Mnemonics for remembering level effect coding.Table 6.12 Design matrix for loan experiment.Table 6.13 Regression with all interactions, loan experiment.Table 6.14 Design matrix for credit card case.Table 6.15 Model matrix for credit card case.Table 6.16 Effects for credit card data set.Table 6.17 Regression results for credit card model.Table 6.18 Predictions (fitted values) for credit card model.
.Table 6.8 Response to interest rate and annual fee.Table 6.9 Effect coding vs. dummy coding.Table 6.10 Results of regressions on effect coding, dummies, and interactions...Table 6.11 Mnemonics for remembering level effect coding.Table 6.12 Design matrix for loan experiment.Table 6.13 Regression with all interactions, loan experiment.Table 6.14 Design matrix for credit card case.Table 6.15 Model matrix for credit card case.Table 6.16 Effects for credit card data set.Table 6.17 Regression results for credit card model.Table 6.18 Predictions (fitted values) for credit card model.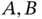 , and
, and 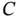 for main effects.Table 7.5 Are interactions consistent with main effects?.Table 7.6 Design matrix and predictions.Table 7.7 Postcard regression results, with replication.Table 7.8 Replicated postcard predictions with and without
for main effects.Table 7.5 Are interactions consistent with main effects?.Table 7.6 Design matrix and predictions.Table 7.7 Postcard regression results, with replication.Table 7.8 Replicated postcard predictions with and without