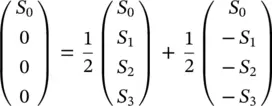Jakob J. Zyl - Introduction to the Physics and Techniques of Remote Sensing
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Jakob J. Zyl - Introduction to the Physics and Techniques of Remote Sensing» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Introduction to the Physics and Techniques of Remote Sensing
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:3 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
Introduction to the Physics and Techniques of Remote Sensing: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Introduction to the Physics and Techniques of Remote Sensing»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
delivers a comprehensive update to the authoritative textbook, offering readers new sections on radar interferometry, radar stereo, and planetary radar. It explores new techniques in imaging spectroscopy and large optics used in Earth orbiting, planetary, and astrophysics missions. It also describes remote sensing instruments on, as well as data acquired with, the most recent Earth and space missions.
Readers will benefit from the brand new and up-to-date concept examples and full-color photography, 50% of which is new to the series. You’ll learn about the basic physics of wave/matter interactions, techniques of remote sensing across the electromagnetic spectrum (from ultraviolet to microwave), and the concepts behind the remote sensing techniques used today and those planned for the future.
The book also discusses the applications of remote sensing for a wide variety of earth and planetary atmosphere and surface sciences, like geology, oceanography, resource observation, atmospheric sciences, and ionospheric studies. This new edition also incorporates:
A fulsome introduction to the nature and properties of electromagnetic waves An exploration of sensing solid surfaces in the visible and near infrared spectrums, as well as thermal infrared, microwave, and radio frequencies A treatment of ocean surface sensing, including ocean surface imaging and the mapping of ocean topography A discussion of the basic principles of atmospheric sensing and radiative transfer, including the radiative transfer equation Perfect for senior undergraduate and graduate students in the field of remote sensing instrument development, data analysis, and data utilization,
will also earn a place in the libraries of students, faculty, researchers, engineers, and practitioners in fields like aerospace, electrical engineering, and astronomy.

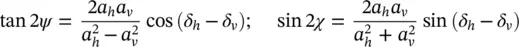
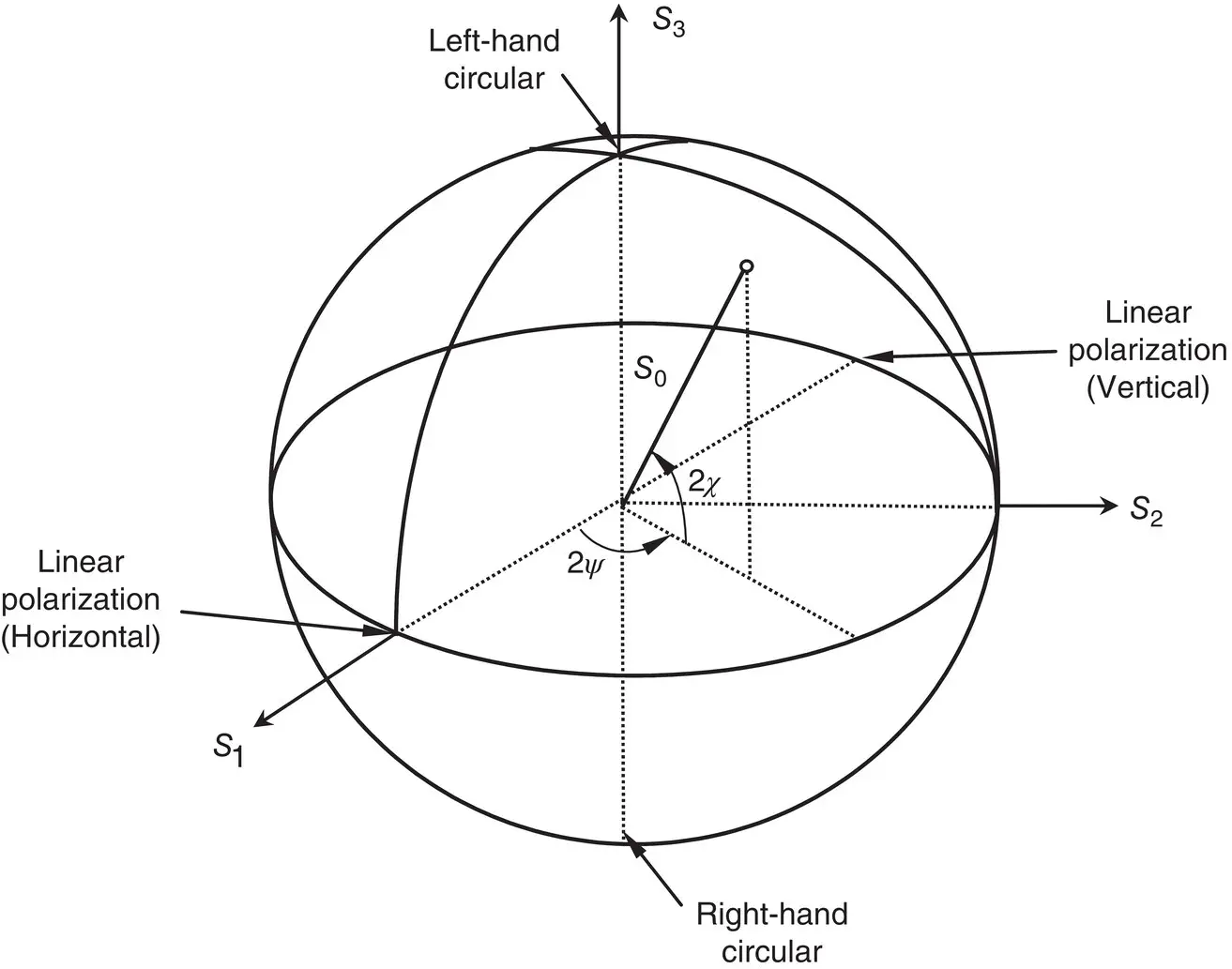
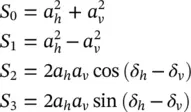 (2.15)
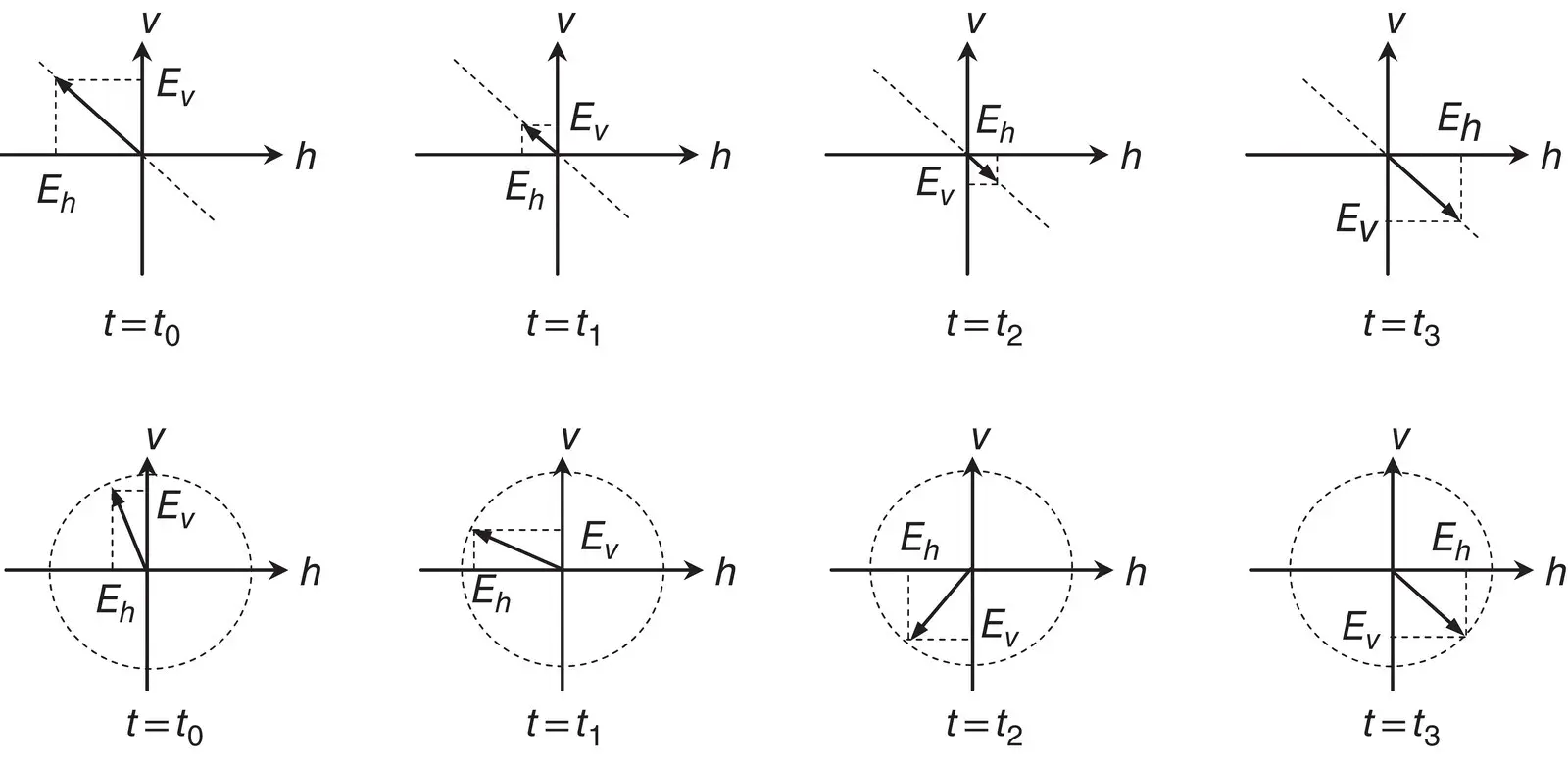
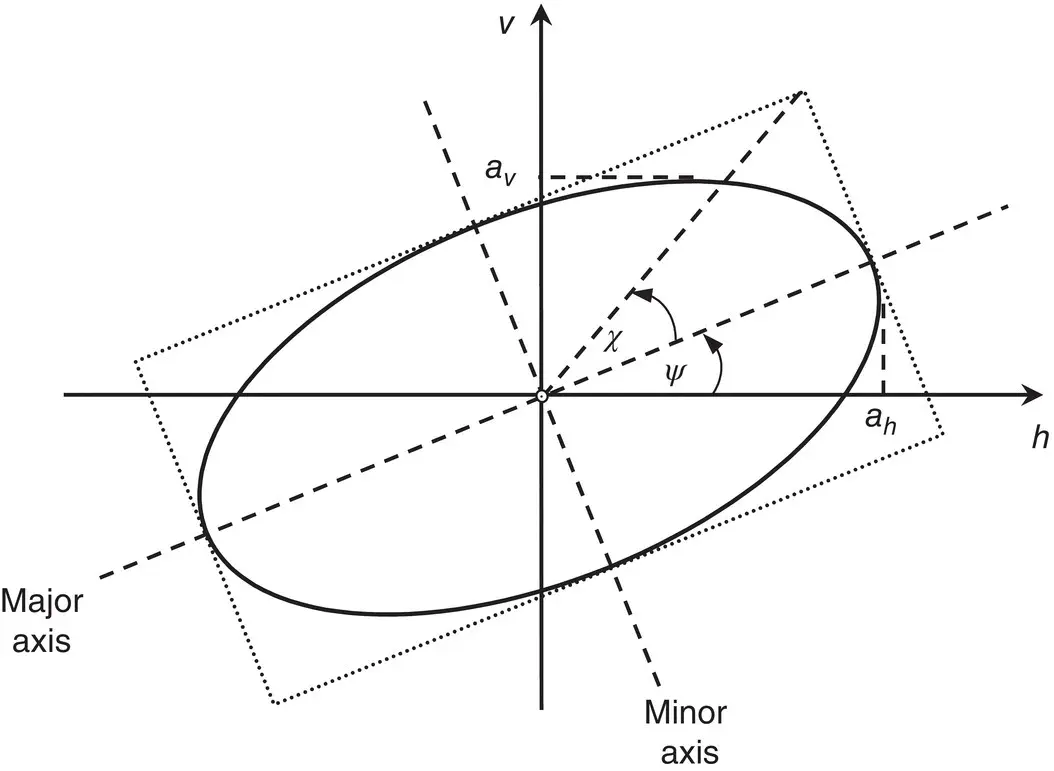
(2.15)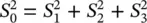 . Using the relations in (2.14)between the ellipse orientation and ellipticity angles and the wave amplitudes and relative phases, it can be shown that the Stokes parameters can also be written as
. Using the relations in (2.14)between the ellipse orientation and ellipticity angles and the wave amplitudes and relative phases, it can be shown that the Stokes parameters can also be written as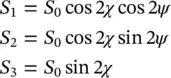
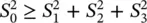 , with equality holding only for fully polarized waves. In the extreme case of an unpolarized wave, the Stokes parameters are S 0> 0; S 1= S 2= S 3= 0. It is always possible to describe a partially polarized wave by the sum of a fully polarized wave and an unpolarized wave. The magnitude of the polarized wave is given by
, with equality holding only for fully polarized waves. In the extreme case of an unpolarized wave, the Stokes parameters are S 0> 0; S 1= S 2= S 3= 0. It is always possible to describe a partially polarized wave by the sum of a fully polarized wave and an unpolarized wave. The magnitude of the polarized wave is given by 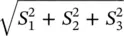 and the magnitude of the unpolarized wave is
and the magnitude of the unpolarized wave is 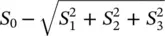 . Finally, it should be pointed out that the Stokes parameters of an unpolarized wave can be written as the sum of two fully polarized waves
. Finally, it should be pointed out that the Stokes parameters of an unpolarized wave can be written as the sum of two fully polarized waves