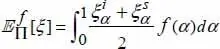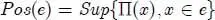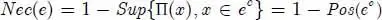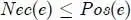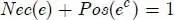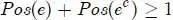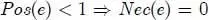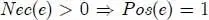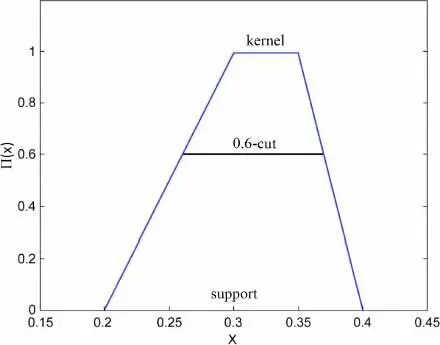
Figure 1.6. Illustration of a trapezoidal membership function in fuzzy set theory
As with previous approaches, a fundamental question concerns the propagation of uncertainties through a function g . As for any value α of the membership function, we can associate an interval; this is tantamount to ultimately performing interval analysis propagation at each level α. The methods discussed in the previous section apply in this way. Purely algebraic propagation is also possible for simple operations (additions, multiplications, powers). For a more detailed view of fuzzy set theory, the reader may refer to Zimmermann (2011).
One of the major drawbacks of fuzzy set theory lies, as for interval analysis, in the absence of a measure of uncertainty, which is equivalent to probability in probability theory. Uncertainty propagation is carried out at a level α, but the link with a measure allowing the quantification of the risk associated with this level α is still missing. In order to remedy this, a measure of uncertainty called possibility has been introduced. This has led to possibility theory, which will be presented in the next section.
1.7. Possibility theory
1.7.1. Theoretical context
Formally, possibility theory is defined on a possibility space Epos , defined as follows:
DEFINITION 1.16.– Let Ω be a set and E the set of the subsets of Ω. A function Π : E → ℝ is called a possibility measure (or possibility distribution function [PoDF]) if it satisfies the following axioms:
– the function has values between 0 and 1: ∀A ∈ E, 0 ≤ Π(A) ≤ 1;
– the image of the empty set is 0: Π(∅) = 0;
– the image of all the events in the universe is 1: Π(Ω) = 1;
– the function is monotonic: ∀A, B ∈ E, if A ⊆ B then Π (A) ≤ Π(B);
– the function is subadditive: .
DEFINITION 1.17.– Let Ω be a set, called universe, E the set of the subsets of Ω and Π a measure of possibility. The triplet (Ω, E, Π) is called the possibility space EPos .
Note that the possibility measure (or PoDF) Π provides a measure of the likelihood of each element of E . The membership functions introduced for fuzzy sets (for example, triangular, trapezoidal functions) are typically used as PoDFs.
DEFINITION 1.18.– Let ξ be an uncertain variable to which the possibility distribution Π is associated. Let 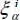 and
and 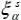 be the lower and upper bounds of the α-cut of ξ. Let f be a non-negative weighting function f : [0,1] → ℝ , monotonically decreasing and verifying the condition of normalization in the integral sense. The f-weighted possibilistic mean operator is:
be the lower and upper bounds of the α-cut of ξ. Let f be a non-negative weighting function f : [0,1] → ℝ , monotonically decreasing and verifying the condition of normalization in the integral sense. The f-weighted possibilistic mean operator is:
[1.11] 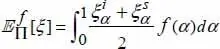
This operator is the equivalent of expectation in the context of probability theory. By introducing various weighting functions, different levels of importance can be assigned to the different α -cuts of the possibility distribution. There are also similar expressions existing for higher order moments in a possibility context.
In order to be able to compare the likelihood of different events, two quantities, the possibility and necessity of an event, are introduced.
DEFINITION 1.19.– Let ( Ω, E , Π ) be a space of possibility. We call the possibility and necessity of an event e ∈ E , respectively:
[1.12] 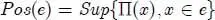
[1.13] 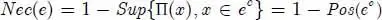
PROPERTY 1.2.– Let (Ω, E , Π) be a space of possibility and an event e ∈ E . We have the following properties:
[1.14] 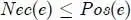
[1.15] 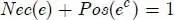
[1.16] 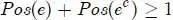
[1.17] 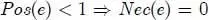
[1.18] 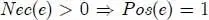
More intuitively, we can say that possibility measures the degree to which the facts do not contradict the assumption that an event can happen. If an event has a possibility of 1, it means that there is no reason to believe that the event cannot happen. It does not mean, however, that the event will certainly happen. In order for an event to be certain, both its possibility and its necessity must be equal to 1. On the other hand, if we consider that an event cannot happen, then it must be assigned a possibility of 0.
It should be noted that, similarly to what has been done in probability theory, a cumulative possibility function (CPoF), a cumulative necessity function (CNeF), a cumulative complementary possibility function (CCPoF) and a cumulative complementary necessity function (CCNeF) can be associated with a PoDF. Figure 1.7illustrates these different functions with an example.
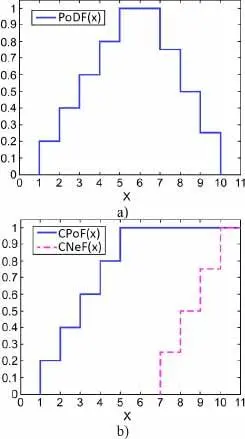
Figure 1.7. Illustrations of (a) a possibility distribution function (PoDF); (b) the cumulative possibility function (CPoF) and the corresponding cumulative necessity function (CNeF)
Note that for the example shown in Figure 1.7, the most likely values are those in the interval [5,7], which have a possibility of 1. The larger intervals encompassing this latter then have progressively smaller possibility values, until they reach 0 for the interval [1,10]. Values below 1 or above 10 are thus considered impossible. All the properties of equations [1.13]– [1.17]can be verified on these curves. Note also that the stepwise nature of the cumulative functions is typical of the modeling of epistemic uncertainties using alternative approaches. Indeed, the quantification of uncertainty is, most of the time, based on experts who would assign likelihood values to the different intervals, thus allowing the construction of the PoDF. The more finely the expert can elicit the uncertainty (by assigning likelihood values to many successively larger nested intervals), the smaller the steps will be. Finally, in terms of uncertainty propagation, given that the PoDFs are, most of the time, based on fuzzy set theory membership functions, they also make use of the same propagation techniques discussed in section 1.6. Propagation is thus typically done by interval propagation for different α -cuts.
Читать дальше


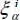 and
and 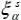 be the lower and upper bounds of the α-cut of ξ. Let f be a non-negative weighting function f : [0,1] → ℝ , monotonically decreasing and verifying the condition of normalization in the integral sense. The f-weighted possibilistic mean operator is:
be the lower and upper bounds of the α-cut of ξ. Let f be a non-negative weighting function f : [0,1] → ℝ , monotonically decreasing and verifying the condition of normalization in the integral sense. The f-weighted possibilistic mean operator is: