Motivating Example: Konica Minolta Using RPA
The Japanese tech giant Konica Minolta Inc. adopted RPA in 2018 through the RPA provider Automation Anywhere and has since seen massive returns through working hours saved. In 2018, the company saved 19 000 full‐time employee (FTE) hours through 55 automation deployments with higher aims in the coming years. Achieving these kinds of returns can be tough though. An IT director at Konica Minolta explained that “of course, like every other company, we have faced many obstacles while going through the journey of RPA before becoming successful. For example, in Konica Minolta's Asia Pacific team, we [had to] create an RPA governance structure, training framework for the region, internal RPA application process, disaster recovery plan. [Afterwards, in the local team], such as Konica Minolta Hong Kong, [had] to go through a series of learning workshops.” This sheds some light on the complexity that comes with rolling out RPA in a large multinational company without even scratching the surface of the planning and preparation that must be done.
To successfully roll out RPA, Konica Minolta had to increase its RPA training program to include nearly five times the number of employees that were in training when they decided to adopt throughout 2018. Some of those trained would become RPA champions in different branches who oversaw further training, identifying processes with potential for automation and creating an RPA culture within their offices. This was a massive shift for parts of their workforce going from knowing little about RPA to being leaders of its development within their company. In addition to the careful planning and testing that comes before RPA is rolled out, upskilling and gaining buy‐in from workers represents another huge challenge. However, navigating these complexities can be seen to have large returns when done correctly. After their successful initial RPA rollout, Konica Minolta aimed to nearly double the number of hours saved in the following year, and they show no intention of slowing down. The IT director shared, “The RPA journey in Konica Minolta has provided an invaluable insight into how automation can change a company's culture and the ways its employees work. However, we will not stop here, and we have already planned RPA 2.0, which is allowing staff to interact with the RPA bot in real‐time. This is for sure an exciting time for all of us.” With returns like Konica Minolta has seen, it certainly shows that RPA can be rolled out if the investment in training is there.
RPA is best understood when compared to a Microsoft Excel macro. In an Excel macro, you can automate cell activities by using VBA coding and Excel functions. RPA adds an advantage in that it can automate tasks across many different applications with simple programming language and function calls. As shown in the Konica Minolta case, one of the first tasks needed is to identify the RPA provider. The company ran through a series of RPA software provider comparisons and finally selected the application from Automation Anywhere, a leading provider in this space.
Konica Minolta's RPA Roadmap
Konica Minolta implemented RPA using the following roadmap:
1 Train a country RPA developer.
2 Identify the highly repetitive business processes that can make use of RPA from hundreds of processes and prioritize for which to develop a solution first.
3 Form a business technology communication unit to perform change management education.
4 Convert existing workflow (normal human can read) to become RPA workflow (RPA developer can read).
5 Create metrics to measure ROI in terms of calculated full‐time employee (FTE) labor hours.
6 Communicate results to management in global and regional offices.
7 Investigate and integrate RPA into each of the different business units.
8 Expand RPA locally by training more local RPA champions who can help to spread knowledge and increase the number of RPA processes.
9 Multiply the power of RPA by combining it with Excel macros.
10 Distribute messages and hold further training to create an RPA culture within offices.
11 Continue to invest in upskilling the team and get them certified.
Processes that Konica Minolta has built RPA bots for include updating shipping schedules and generating customer consumption reports. More examples can be found in the chart below that demonstrates how Konica Minolta deployed bots across various department functions ( Figures 5.1and 5.2).
In 2018, over 55 automatic bots were developed and deployed, with a similar number in the work pipeline. Konica Minolta could save around 19 000 hours in 2018 and expects to save 33 000 hours in the fiscal year 2019. The goal here was not to replace staff through RPA but to add more business value to their customers. The company's RPA journey gives invaluable insights to how automation can change a company's culture and the ways its employees work.
Though Konica Minolta is not a logistics company, this roadmap would look extremely similar if the implementation was happening in one. Identifying highly repetitive tasks, converting workflow to one that an RPA developer can read, forming a team to manage adoption and training, and creating metrics to quantify ROI would be standard steps in any company's RPA journey whether they provide logistics services or technology solutions. The positive results and hours saved that Konica Minolta have experienced since deploying their first bots therefore could be shared by logistics companies since many of the functions that the bots handle will be the same regardless of the industry that they serve. For example, Konica Minolta's use of bots for creating market data reports, generating quality assessment reports, and managing inventory could very easily be applied to a logistics provider as these functions will generally look quite similar across different organizations. In addition to this, Konica Minolta used RPA specifically to update their shipping schedules, a task that is done daily in many logistics companies. Later on in this section, we will look at an example of how DHL have seen equally impressive results to Konica Minolta's during their own RPA journey.
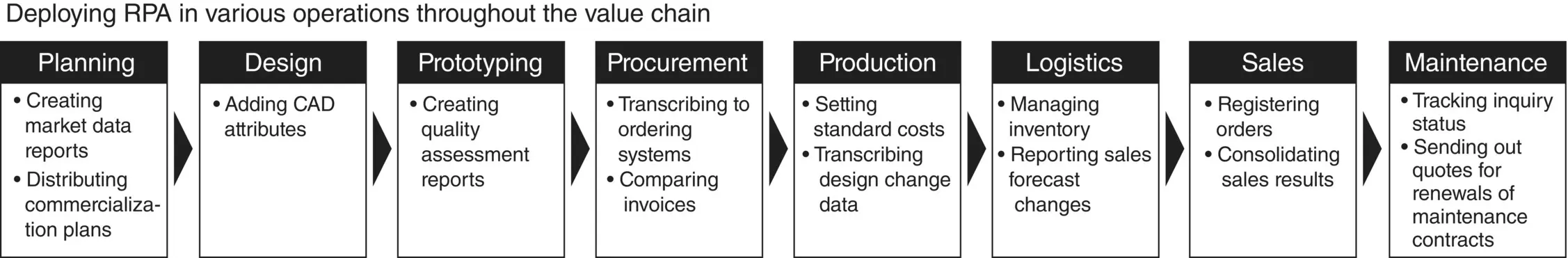
Figure 5.1 Deploying RPA in various operations throughout the value chain.
Source : Konica Minolta © (2020).
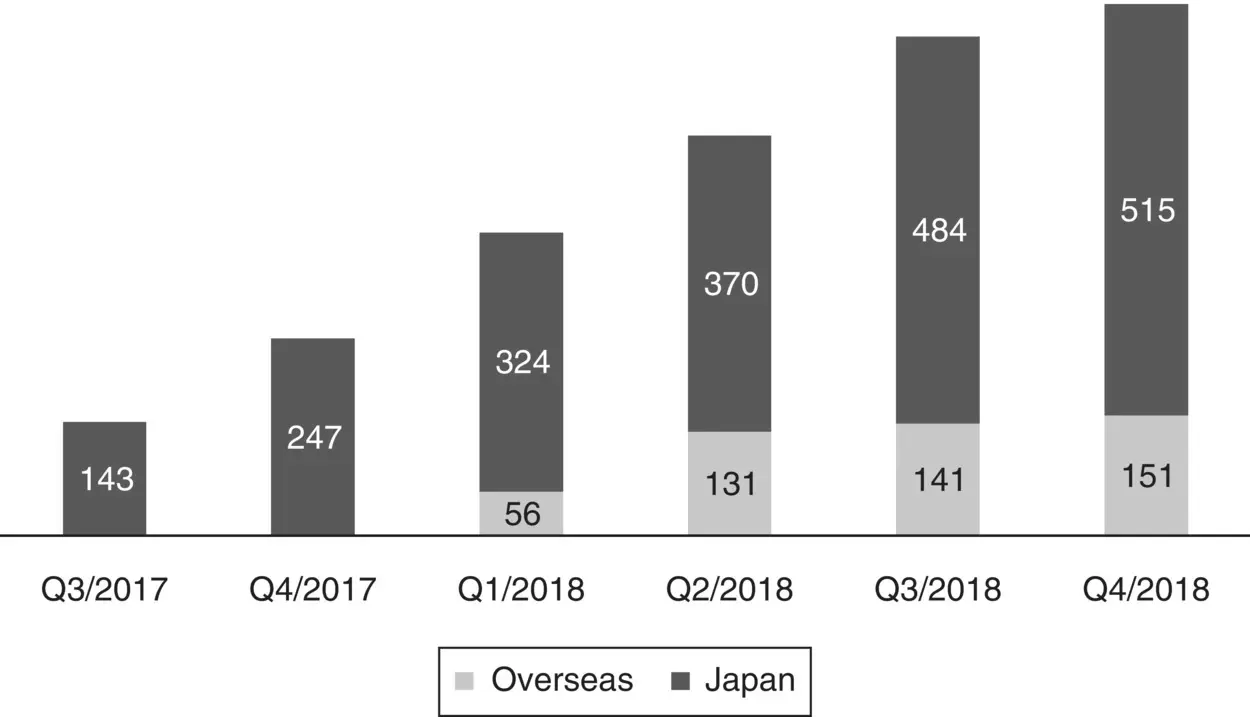
Figure 5.2 Internal RPA training course participants.
Source : Konica Minolta © (2020).
Use Cases for RPA in Logistics
Track and Trace
Logistics service providers are seeing customer expectations increasingly rise in areas where they simply do not have the margins to throw extra staff at the solution. E‐commerce and SaaS solutions are changing the visibility expectations of buyers. When you can price shop and buy a Boeing 747 online and track penny items turn by turn as they approach your house, the expectations in the business‐to‐business sector shift as well (Sheetz 2017). In international shipping, this has traditionally been a huge issue as carriers, forwarders, port authorities, rail operators, customs agencies, trucking companies, warehouses, and their customers often all have different levels of digital communication capabilities. In this scenario where a buyer of a container of goods in the United States wants to track his cargo from China to his warehouse door outside of Chicago, Illinois, they most often look to their freight forwarder as an aggregator of data and communication window. The freight forwarder typically does not directly own or control any of the carriers along the way, so they must find ways of grabbing event milestones to give updates to their customers. They have a few different options when it comes to retrieving such milestones. First, they could have direct integration with each of these carriers via EDI, although it requires a significant investment in mapping event fields from the carrier's system back to the forwarder's system. Second, they could have their staff locally go to each carrier website and retrieve the information as it is updated and key it back into their tracking database manually. Third, they could identify low‐cost labor in an offshore location to update and key in the data. Fourth, they could pay a third‐party aggregator for the milestones who often utilizes a combination of cheap labor and EDI connections. Lastly, they could train or hire someone to train an RPA bot that could go out and do the work of their local or offshore staff.
Читать дальше














