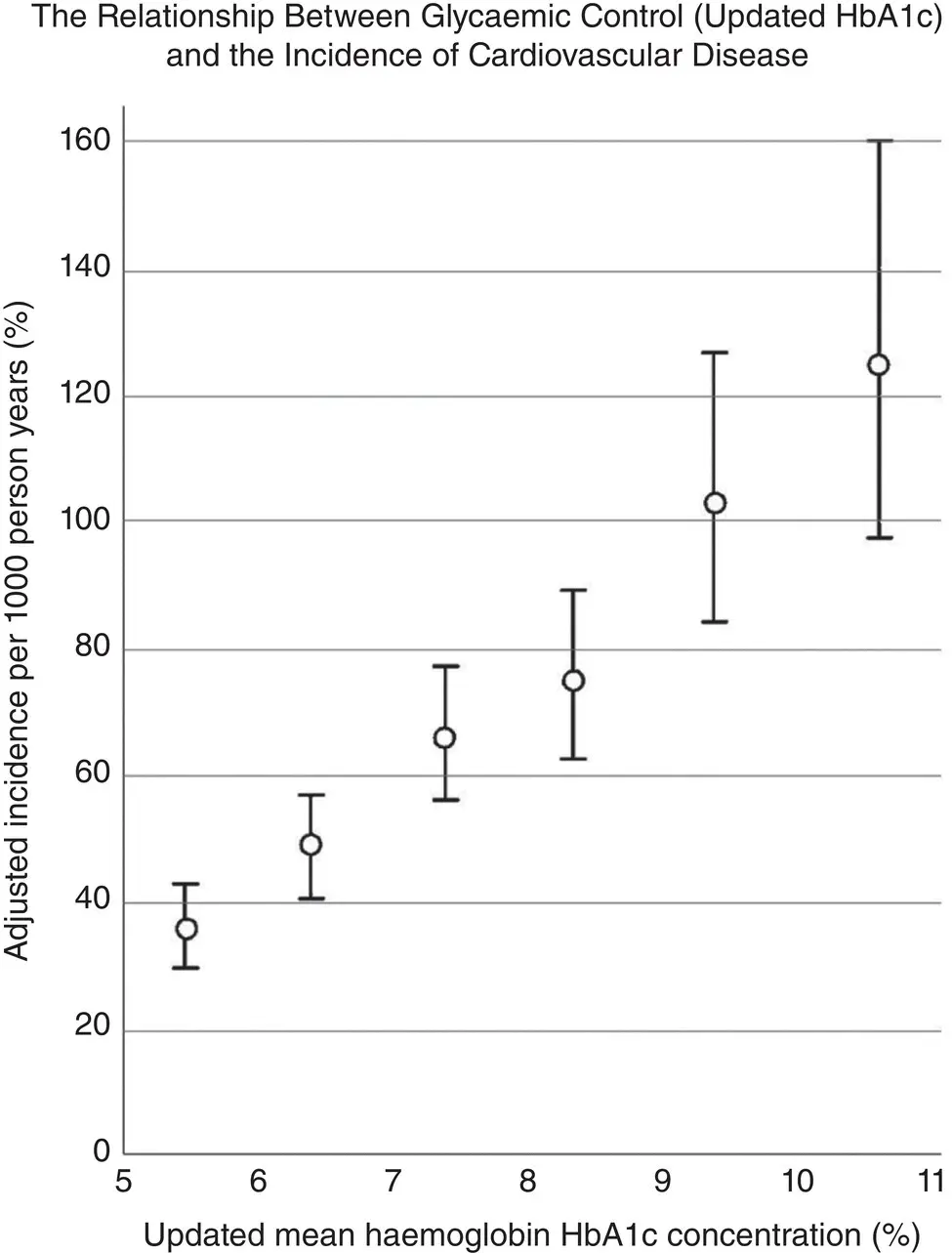
Figure 7.8 The relationship between HbA1c and the incidence of cardiovascular disease. This is a linear relationship which extends down into the prediabetic range (i.e HbA1c<6.5%). Bain et al. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism, 2016; 18(12): 1157–1166.
Insulin resistance (or, more correctly, diminished insulin sensitivity) precedes the onset of diabetes and can worsen with increasing duration ( Figure 7.13). Insulin resistance is a major factor in the aetiology of type 2 diabetes, and affects the muscle, liver, and adipose tissues ( Figure 7.14).
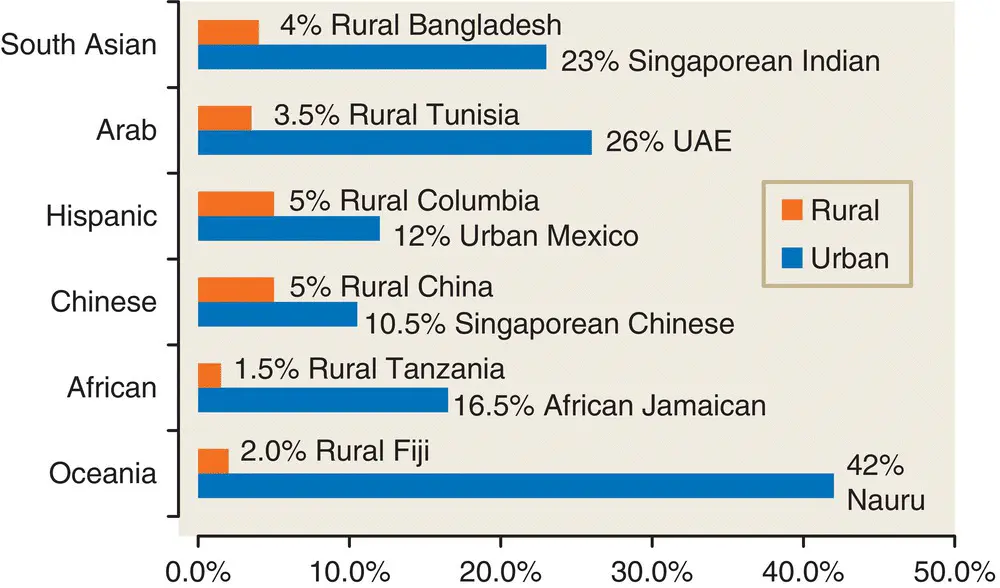
Figure 7.9 Varying prevalence rates of type 2 diabetes by ethnicity/region and location (red, rural; blue, urban) for 2007. UAE, United Arab Emirates.
Data from Diabetes Atlas .
Visceral fat liberates large amounts of non‐esterified fatty acids (NEFAs) through lipolysis, which increases gluoconeogenesis in the liver and impairs glucose uptake and utilisation in muscle. NEFAs may also inhibit insulin secretion, possibly by enhancing the accumulation of triglycerides within the β cells. In addition, adipose tissue produces cytokines, such as TNF‐α, resistin and IL‐6, all of which have been shown experimentally to interfere with insulin action. TNF‐α has been shown to inhibit tyrosine kinase activity at the insulin receptor and decrease expression of the glucose transporter GLUT‐4.
Adiponectin is a hormone with anti‐inflammatory and insulin‐sensitising properties that is secreted solely by fat cells. It suppresses hepatic gluconeogenesis and stimulates fatty acid oxidation in the liver and skeletal muscles, as well as increasing muscle glucose uptake and insulin release from the β cells. Circulating adiponectin is reduced in obesity and a recent meta‐analysis showed that the relative risk for diabetes was 0.72 for every 1‐log μg/mL increment in adiponectin level.
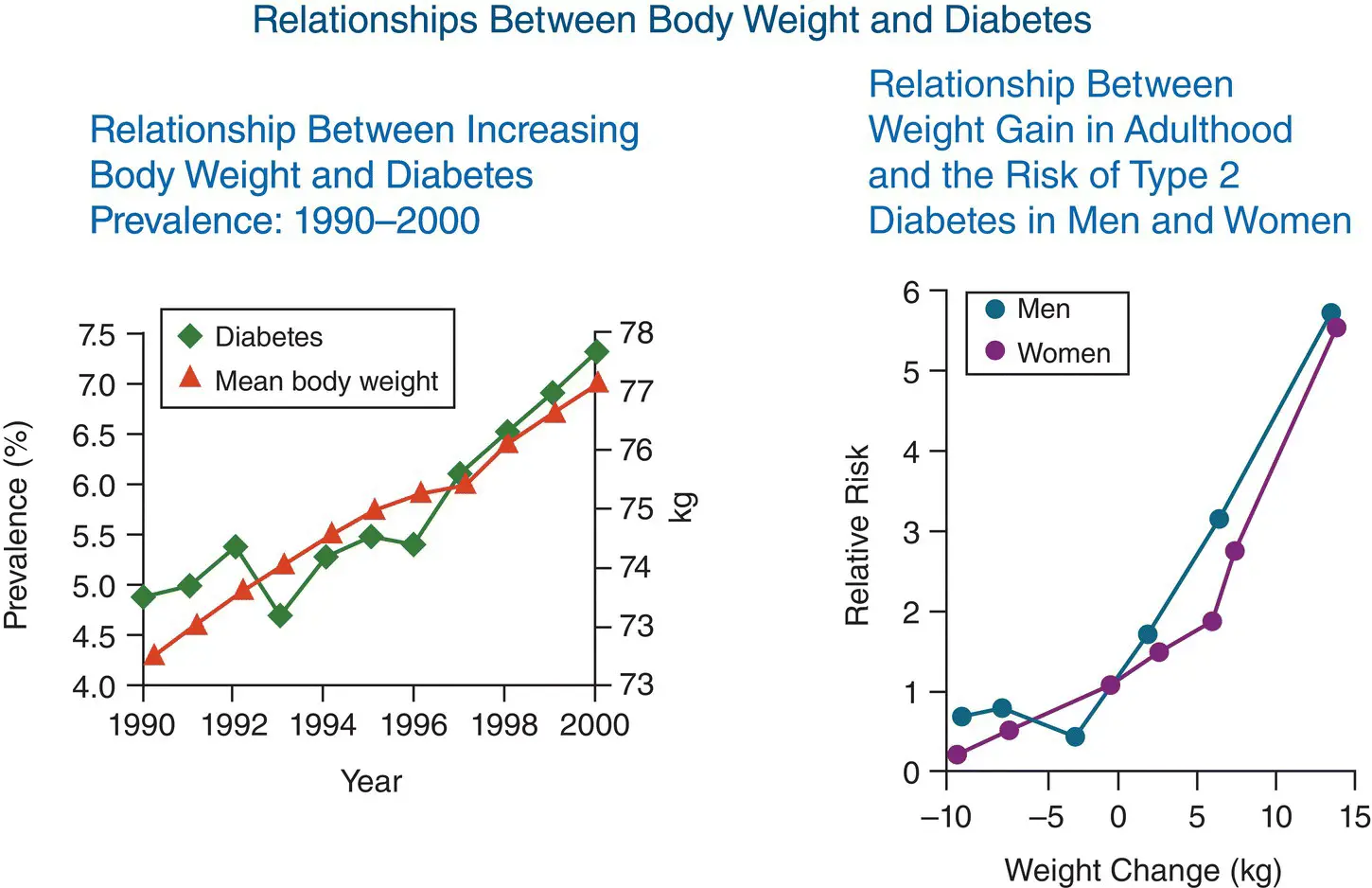
Figure 7.10 Weight gain is a particularly strong driver of type 2 diabetes risk (right panel). Small increments in body weight translate into large increases in relative risk. Haffner SM. Obesity, 2006; 14(6s): 121S–127S.
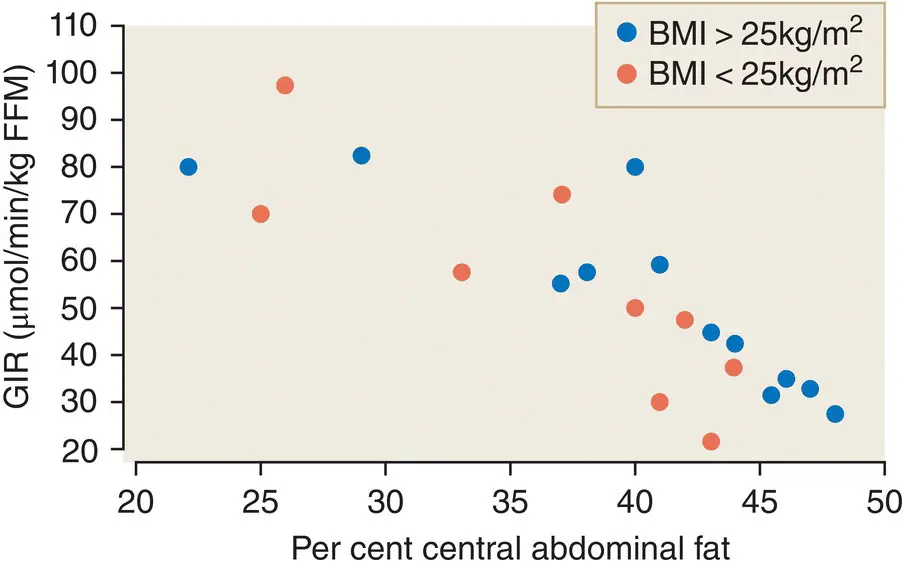
Figure 7.11 Insulin resistance (as assessed by glucose infusion rate (GIR) to maintain constant blood glucose during simultaneous insulin infusion) is proportional to visceral fat mass, independent of BMI. FFM, fat‐free mass.
Data from Pan et al. Diabetes 1997; 46: 983–988.
Resistin is an adipocyte‐secreted hormone that increases insulin resistance and was first described in rodents, being found in increased levels in experimental obesity and diabetes. In humans, it appears to be derived largely from macrophages, however, and its precise role in human diabetes is uncertain, although higher circulating levels have been found in some people with type 2 diabetes.
Leptin is an adipokine that was found to be absent in the ob/ob mouse model of obesity and diabetes. Its normal function is to suppress appetite, thus providing a candidate mechanism linking weight gain and appetite control. Although abnormal leptin function has been described in humans, these defects are very rare and paradoxically high levels have been found in type 2 diabetes.
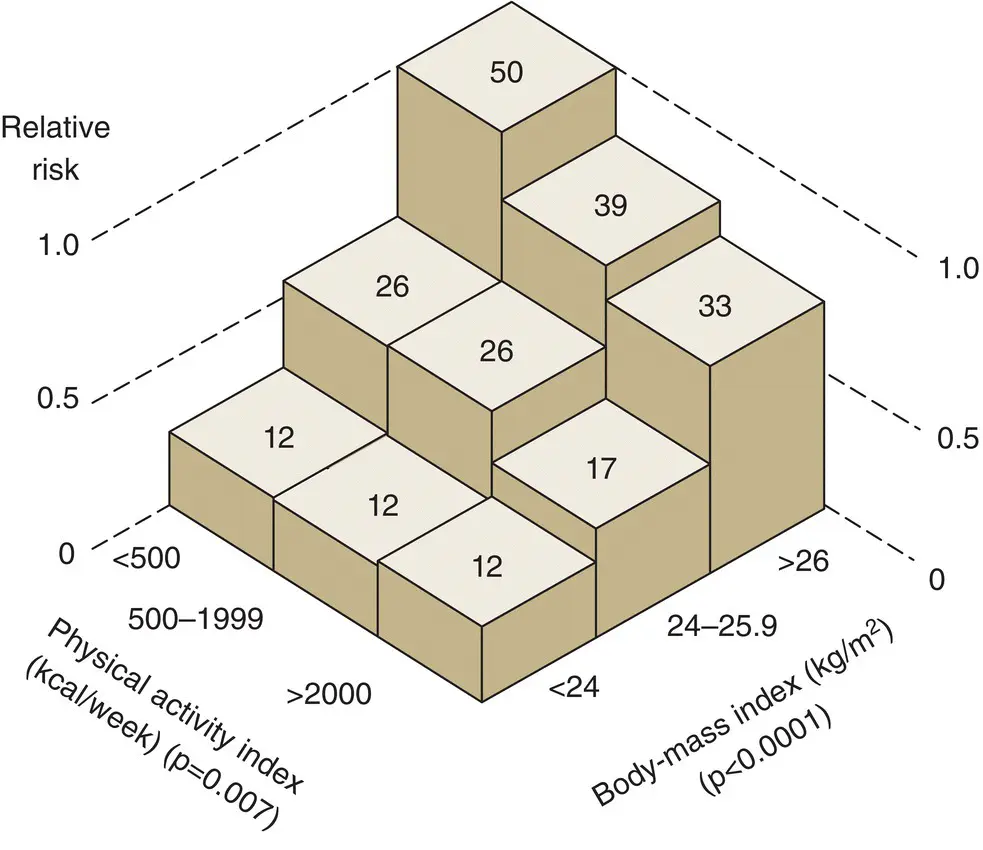
Figure 7.12 Age‐adjusted risk of type 2 diabetes among 5990 men. The figure shows data for the physical activity index in relation to BMI. Each block represents the relative risk of type 2 diabetes per 10,000 man‐years of follow‐up, with the risk for the tallest block set at 1.0. The numbers on the blocks are incidence rates of type 2 diabetes per 10,000 man‐years.
From Helmrich et al. N Engl J Med 1991; 325: 147–152.
Ghrelin is a recently described peptide secreted from the stomach and may act as a hunger signal. Circulating levels are negatively correlated with BMI and are suppressed by food intake. It has no known role in human diabetes, but antagonism may provide a therapeutic target.
Finally, there is often increased sympathetic nervous system activity in obesity, which might also increase lipolysis, reduce muscle blood flow and thus glucose delivery and uptake, and therefore directly affect insulin action.
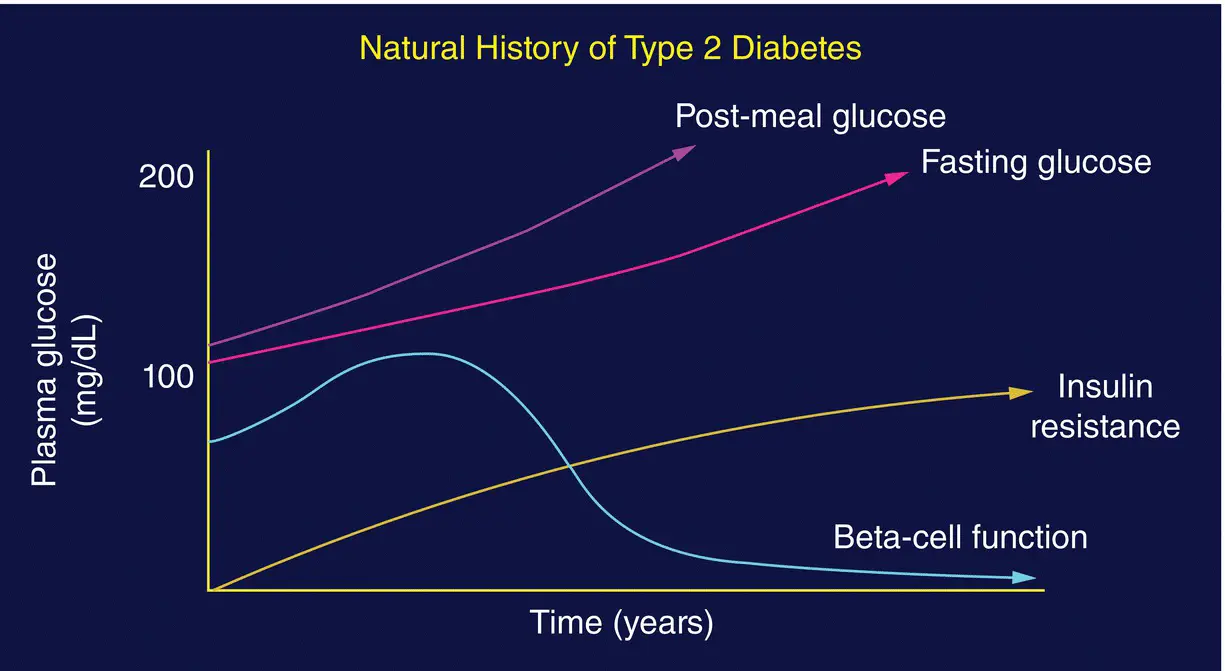
Figure 7.13 The natural history of type 2 diabetes development often begins with rising insulin resistance due to obesity, diet and low levels of exercise. This insulin resistance results in a compensatory rise in circulating insulin concentrations which, initially, maintains normal or near‐normal glycaemia. But over time the pancreas becomes exhausted and the compensatory increase in insulin secretion falls. When beta cell secretion of insulin decreases blood glucose levels rise to meet the diagnostic cut‐off for type 2 diabetes. DeFronzo R.Diabetes Care, 1992, 15: 318–368; Haffner S, et al. Diabetes Care, 1999, 22: 562–568.
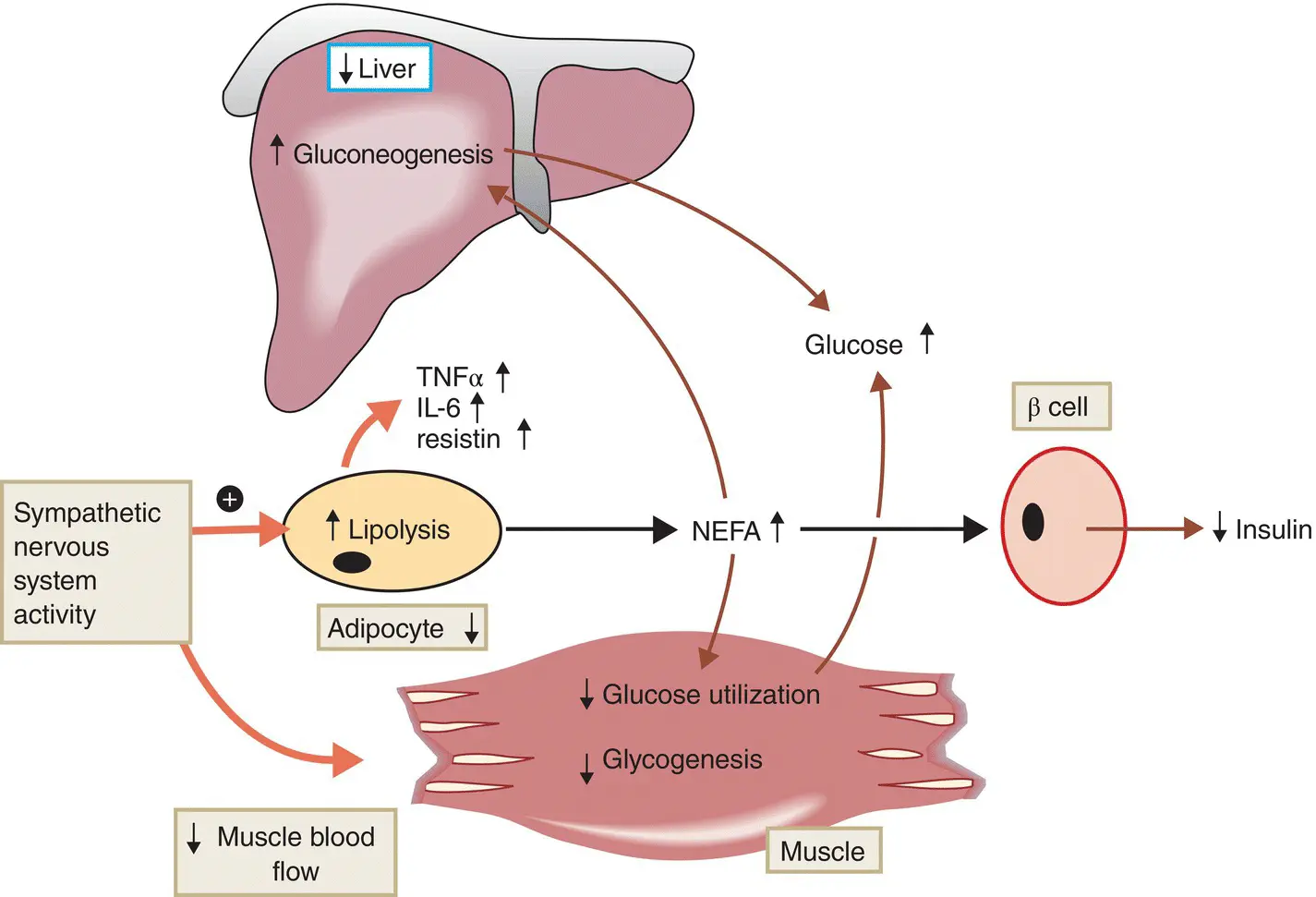
Figure 7.14 Mechanisms of insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes.
Many of these cytokines are involved in the acute‐phase response and it is therefore not surprising that circulating markers such as C‐reactive protein and sialic acid are increased in type 2 diabetes patients, as well as in those who later go on to develop the condition. Because these markers have also been found to be elevated in patients with atherosclerosis, a unifying hypothesis has evolved proposing that inflammation may be a common precursor and link between diabetes and coronary artery disease.
Evidence for a genetic basis for type 2 diabetes comes from a clear familial aggregation, but it does not segregate in a classic Mendelian fashion. About 10% of patients with type 2 diabetes have a similarly affected sibling. The concordance rate for identical twins is variously estimated to be 33–90% (17–37% in non‐identical twins), but the interpretation of this is difficult because siblings may have similar lifestyles and diets. Thus, the explanation for the high concordance may be environmental rather than genetic.
Unlike type 1, type 2 diabetes is not associated with genes in the HLA region. So far, 19 gene variants have been described and validated as being associated with type 2 diabetes. Of these, the strongest is TCF7L2; 15% of European adults carry two copies of the abnormal gene and they have double the lifetime risk of developing type 2 diabetes compared to the 40% who carry no copies. Carriers of the T risk allele have impaired insulin secretion and enhanced hepatic glucose output. Nearly all of the other described genes affect either β cell mass or function; few appear to have potential effects on insulin resistance.
Читать дальше



















