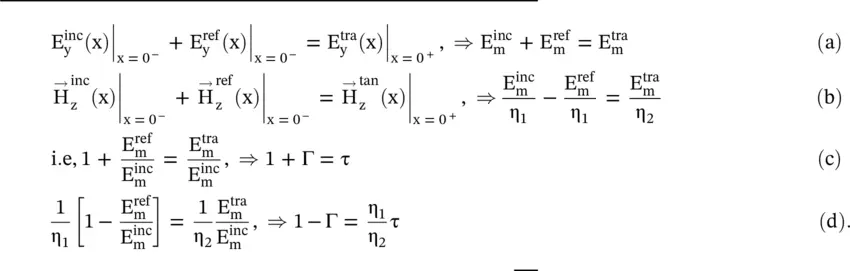20 B.20 Yariv, A.; Yeh, P.: Optical Waves in Crystals, Wiley, New York, 1984.
21 B.21 Kong, J.A.: Electromagnetic Wave Theory, Wiley, New York, 1986.
22 B.22 Mackay, T.G.; Lakhtakia, A.: Electromagnetic Anisotropy and Bianisotropy: A Field Guide, World Scientific, Singapore, 2010.
23 B.23 Lindell, I.V.; Sihvola, A.H.; Tretyakov, S.A.; Viitanen, A.J.: Electromagnetic Waves in Chiral and Bi‐anisotropic Media, Artech House, Boston, MA, 1994.
24 B.24 Hoffmann, R.: Microwave Integrated Circuit Handbook, Artech House, Boston, MA, 1985.
25 B.25 Capolino, F. (Editor): Theory and Phenomena of Metamaterials, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 2009.
26 B.26 The Heaviside Centenary Volume, The Institution of Electrical Engineers, London, 1950.
27 B.27 Whittaker, E.T.: Oliver Heaviside, In Electromagnetic Theory, Vol. 1, Oliver Heaviside, Reprint, Chelsea Pub. Co., New York, 1971.
28 B.28 Behrend, B.A.: The work of Oliver Heaviside, In Electromagnetic Theory, Vol. 1, Oliver Heaviside, Reprint, Chelsea Pub. Co., New York, 1971.
29 B.29 Kraus, J.D.: Antenna, 2nd Edition, McGraw‐Hill, 1988.
30 B.30 Collett, E.: Polarized Light: Fundamentals and Applications, Marcel Dekker, Inc., 1993.
31 B.31 Saleh, B.E.A.; Teich, M.C.: Fundamental of Photonics, Wiley, New York, 1991.
1 J.1 Jacob, Z.; Alekseyev, L.V.; Narimanov, E.: Optical hyperlens: far‐field imaging beyond the diffraction limit, Opt. Express, Vol. 14, No. 18, pp. 8247–8256, 2006.
2 J.2 Lee, H. et al.: Development of optical hyperlens for imaging below the diffraction limit, Opt. Express, Vol. 15, pp. 15886–15891, 2007.
3 J.3 Seddon, N.; Bearpark, T.: Observation of the inverse Doppler effect, Science, Vol. 302, pp. 1537–1539, Nov. 2003.
4 J.4 Mosallaei, H.; Sarabandi, K.: Magneto‐dielectrics in electromagnetics: concept and applications, IEEE Trans. Ant. Propagat., Vol. 52, No. 6, pp. 1558–1567, June 2004.
5 J.5 Alu, A.; Engheta, N.: Pairing an epsilon–negative slab with a mu‐negative slab: anomalous tunneling and transparency, IEEE Trans. Antenna Proag., Special Issue on Metamaterials, Vol. 51, No. 10, pp. 2558–2570, Oct. 2003.
6 J.6 Lee, H.; Xiong, Y.; Fang, N.; Srituravanich, N.; Durant, S.; Ambati, M.; Sun, C.; Zhang, X.: Realization of optical superlens imaging below the diffraction limit, New Journal of Physics, Vol. 7, No. 255, pp. 1–16, 2005.
7 J.7 Kim, M.; Rho, J.: Metamaterials and imaging, Nano Convergence, Vol. 2, No. 22, pp. 1–16, 2015.
5 Waves in Material Medium‐II: ( Reflection & Transmission of Waves, Introduction to Metamaterials )
Introduction
The characteristics of material media and EM‐waves propagation in unbounded media are discussed in the previous chapter 4. Continuing the topics, this chapter is about the normal and oblique incidence of EM‐waves at the interface of two media. The characteristics of both the normal and oblique incident EM‐waves are obtained using an analytical method and convenient equivalent transmission line models. Under certain conditions, the interface surface of two media could acquire the property of a perfect electric conductor (PEC), or perfect magnetic conductor (PMC), or even a reactive impedance surface (RIS). These surfaces play a significant role in the modern microwave and antenna technologies. Some electromagnetic characteristics of the engineered composite materials, with negative permittivity and permeability, are also presented in the present chapter. These artificially structured materials are known as metamaterials . The realization, circuit modeling, and some applications of the metamaterials and metasurfaces are further presented in chapters 21and 22, respectively. The properties of natural and artificial dielectrics are further examined in chapter 6.
To discuss the normal and oblique incidence of the EM‐waves at the interface of two media.
To present the transmission line model of the normal and oblique incidence of the EM‐waves.
To obtain the dispersion diagrams of refracted waves in the isotropic and anisotropic media.
To obtain characteristics of Brewster and the critical angles of incidence.
To discuss the general properties of metamaterials media and their classifications.
To obtain some characteristics of the EM‐wave propagation in the metamaterials.
To obtain the circuit models of metamaterials.
To discuss the possibility of obtaining the flat lens, superlens, and hyperlens beyond the diffraction limit.
To discuss the nature of the Doppler effect and Cerenkov radiation in the metamaterials.
To discuss metamaterials as thin microwave absorbers.
5.1 EM‐Waves at Interface of Two Different Media
The EM‐waves can strike the interface of two media with different electrical characteristics, either normally or obliquely. If the second medium is a dielectric medium, the waves undergo both reflection and transmission, whereas if the second medium is a perfect conductor, the reflection occurs. The obliquely incident plane waves follow the well‐known Snell's law (also called Snell-Descartes law) of reflection and refraction. There are important applications of obliquely incident EM‐waves.
5.1.1 Normal Incidence of Plane Waves
Figure (5.1a)shows an interface of two media #1 and #2. The media are electrically characterized by the primary parameters ε ri, μ ri, σ i; i = 1, 2 and also by the secondary parameters, such as the refractive index n i, and intrinsic or wave impedance η i. Initially, both media are considered lossless dielectric media. Next, the second medium is treated as a PEC.
The incident wave in the medium #1, propagating in the x‐direction with propagation constant k 1, is y‐polarized with an electric field component 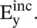 The direction‐x is normal to the interface PQ along the y ‐axis; so the incident magnetic field component
The direction‐x is normal to the interface PQ along the y ‐axis; so the incident magnetic field component 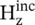 is +z directed. This is a special case of the TM‐polarized obliquely incident wave, discussed in section (5.2.2). The incident ray strikes at the location O and gets partly reflected and refracted (i.e. transmitted) at O with the field components
is +z directed. This is a special case of the TM‐polarized obliquely incident wave, discussed in section (5.2.2). The incident ray strikes at the location O and gets partly reflected and refracted (i.e. transmitted) at O with the field components  , and
, and 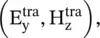 respectively. In the medium #2, the propagation constant is k 2. In general, the k is a wavevector with three components. Figure (5.1a)shows that the direction of propagation is decided by the direction of the Poynting vector. The field components are summarized in equation (5.1.1) on suppressing the time‐harmonic dependence e jωt:
respectively. In the medium #2, the propagation constant is k 2. In general, the k is a wavevector with three components. Figure (5.1a)shows that the direction of propagation is decided by the direction of the Poynting vector. The field components are summarized in equation (5.1.1) on suppressing the time‐harmonic dependence e jωt:
(5.1.1) 
where η 1and η 2are the intrinsic impedance of medium #1 and medium #2, respectively. The total tangential components of the electric and magnetic fields in both media are continuous across the interface at x = 0:
(5.1.2) 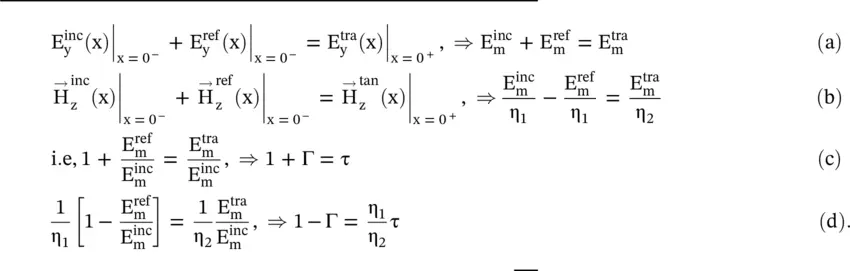
Читать дальше

 The direction‐x is normal to the interface PQ along the y ‐axis; so the incident magnetic field component
The direction‐x is normal to the interface PQ along the y ‐axis; so the incident magnetic field component 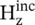 is +z directed. This is a special case of the TM‐polarized obliquely incident wave, discussed in section (5.2.2). The incident ray strikes at the location O and gets partly reflected and refracted (i.e. transmitted) at O with the field components
is +z directed. This is a special case of the TM‐polarized obliquely incident wave, discussed in section (5.2.2). The incident ray strikes at the location O and gets partly reflected and refracted (i.e. transmitted) at O with the field components 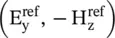 , and
, and 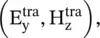 respectively. In the medium #2, the propagation constant is k 2. In general, the k is a wavevector with three components. Figure (5.1a)shows that the direction of propagation is decided by the direction of the Poynting vector. The field components are summarized in equation (5.1.1) on suppressing the time‐harmonic dependence e jωt:
respectively. In the medium #2, the propagation constant is k 2. In general, the k is a wavevector with three components. Figure (5.1a)shows that the direction of propagation is decided by the direction of the Poynting vector. The field components are summarized in equation (5.1.1) on suppressing the time‐harmonic dependence e jωt: