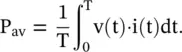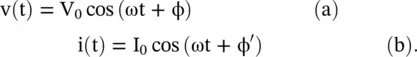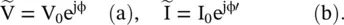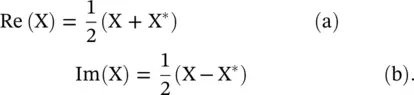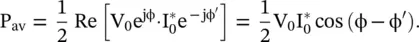Anand K. Verma - Introduction To Modern Planar Transmission Lines
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Anand K. Verma - Introduction To Modern Planar Transmission Lines» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Introduction To Modern Planar Transmission Lines
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:4 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
Introduction To Modern Planar Transmission Lines: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Introduction To Modern Planar Transmission Lines»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
rovides a comprehensive discussion of planar transmission lines and their applications, focusing on physical understanding, analytical approach, and circuit models
Planar transmission lines form the core of the modern high-frequency communication, computer, and other related technology. This advanced text gives a complete overview of the technology and acts as a comprehensive tool for radio frequency (RF) engineers that reflects a linear discussion of the subject from fundamentals to more complex arguments.
Introduction to Modern Planar Transmission Lines: Physical, Analytical, and Circuit Models Approach Emphasizes modeling using physical concepts, circuit-models, closed-form expressions, and full derivation of a large number of expressions Explains advanced mathematical treatment, such as the variation method, conformal mapping method, and SDA Connects each section of the text with forward and backward cross-referencing to aid in personalized self-study
is an ideal book for senior undergraduate and graduate students of the subject. It will also appeal to new researchers with the inter-disciplinary background, as well as to engineers and professionals in industries utilizing RF/microwave technologies.

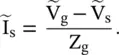
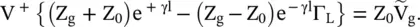
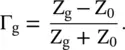
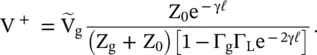
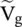 and the line section are replaced by the equivalent Thevenin's voltage,
and the line section are replaced by the equivalent Thevenin's voltage, 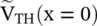 with internal impedance, i.e. the Thevenin's impedance Z TH[B.12]. Figure (2.8d)shows it. The distance is measured from the load end. Thevenin's voltage is an open‐circuit voltage at the load end. In the case of the open‐circuited load, Z L→ ∞, equation (2.1.86)provides a reflection coefficient Γ L= 1. Thevenin's voltage is obtained from equations (2.1.88a)and (2.1.97):
with internal impedance, i.e. the Thevenin's impedance Z TH[B.12]. Figure (2.8d)shows it. The distance is measured from the load end. Thevenin's voltage is an open‐circuit voltage at the load end. In the case of the open‐circuited load, Z L→ ∞, equation (2.1.86)provides a reflection coefficient Γ L= 1. Thevenin's voltage is obtained from equations (2.1.88a)and (2.1.97):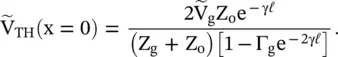
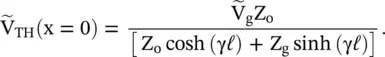
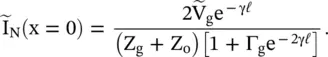
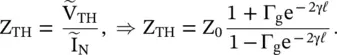
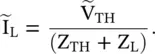
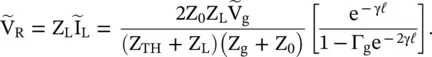
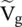 is
is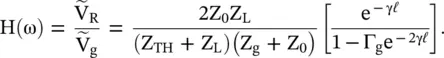
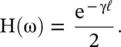
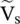 at the port – aa to the output voltage
at the port – aa to the output voltage 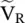 , H(ω) = e −γℓ. It is obtained from equation (2.1.104)for Z g= 0.
, H(ω) = e −γℓ. It is obtained from equation (2.1.104)for Z g= 0.