|
β→ |
1 |
10 |
100 |
1000 |
10,000 |
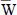 |
(0.5, 0.5, -0.5h) |
-1.55045(-1.55041) |
-0.80673(-0.80672) |
-0.47167(-0.47167) |
-0.07767(-0.07767) |
-0.00174(-0.00179) |
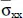 |
(0.5, 0.5, z) |
|
|
|
|
|
| z = 0.5h |
-1.30381(-1.30409) |
-3.68270(-3.68274) |
-17.8693(-17.8692) |
-63.5162(-63.5153) |
-92.9483(-92.9222) |
| z = 0.4h + |
-0.71151(-0.70956) |
0.70904(0.70917) |
15.5178(15.5175) |
62.5785(62.5774) |
92.7600(92.7827) |
| z = 0.4h- |
-0.71151(-0.70956) |
0.05412(0.05413) |
0.13952(0.13952) |
0.05564(0.05564) |
0.00816(0.00814) |
| z = -0.4h + |
0.53608(0.53463) |
-0.03570(-0.03569) |
-0.06779(-0.06780) |
-0.01411(-0.01411) |
-0.00082 |
| z = -0.4h- |
0.53608(0.53463) |
-0.34646(-0.34641) |
-6.56097(-6.56090) |
-11.5108(-11.5113) |
-2.59311(-1.9654) |
| z = -0.5h |
0.90503(0.90518) |
1.92738(1.92735) |
7.39749(7.39739) |
11.6037(11.6042) |
2.58611(2.41811) |
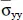 |
(0.5, 0.5, z) |
|
|
|
|
|
| z = 0.5h |
-1.12800(-1.12813) |
-3.06623(-3.06624) |
-11.9076(-11.9075) |
-39.5773(-39.5766) |
-57.5749(-57.5841) |
| z = 0.4h + |
-0.73700(-0.73607) |
-0.31380(-0.31374) |
8.78405(8.78389) |
38.4871(38.4863) |
57.3827(57.3665) |
| z = 0.4h- |
-0.73700(-0.73607) |
-0.18445(-0.18444) |
-0.05495(-0.05496) |
-0.02475(-0.02477) |
-0.00442(-0.00463) |
| z = -0.4h + |
0.58971(0.58899) |
0.06560(0.06560) |
-0.04952(-0.04952) |
-0.03041(-0.03040) |
-0.00524(-0.00247) |
| z = -0.4h- |
0.58971(0.58899) |
0.75187(0.75190) |
-2.96035(-2.96026) |
-6.72640(-6.72638) |
-1.55007(-1.46223) |
| z = -0.5h |
0.83614(0.83621) |
2.17320(2.17319) |
5.68229(5.68223) |
7.57969(7.57976) |
1.65537(1.42636) |
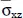 |
(X=0, Y=0.5) |
|
|
|
|
|
| z = 0.4h + |
0.22882(0.22878) |
0.36501(0.36502) |
0.30164(0.30166) |
0.11080(0.11086) |
0.01593(0.03117) |
| z = -0.4h + |
0.17656(0.17652) |
0.23854(0.23853) |
0.16531(0.16530) |
0.03726(0.03723) |
0.00302(0.00056) |
Table 1.5. Normalized results for the [0/90/0] laminated plate with C–C–SS–SS and F–F–SS–SS boundary conditions
| a/h |
Variable |
Clamped–Clamped |
Free-Free |
| Vel and Batra |
Present |
Vel and Batra |
Present |
| 5 |
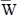 (a/2, b/2, h/2) (a/2, b/2, h/2) |
1.1800 |
1.1771 |
1.5250 |
1.4649 |
 (a/2, b/2, 0) (a/2, b/2, 0) |
-4.2350 |
-4.2757 |
-6.9870 |
-7.2402 |
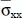 (a/2, b/2, h) (a/2, b/2, h) |
4.5040 |
4.5437 |
7.1800 |
7.4300 |
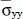 (a/2, b/2, h/3) (a/2, b/2, h/3) |
-3.7260 |
-3.7185 |
-4.784 |
-4.582 |
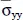 (a/2, b/2, 2h/3) (a/2, b/2, 2h/3) |
3.5760 |
3.5652 |
4.639 |
4.4364 |
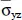 (a/2, 0, h/2) (a/2, 0, h/2) |
1.4700 |
1.4711 |
1.9110 |
1.8494 |
| 10 |
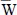 (a/2, b/2, h/2) (a/2, b/2, h/2) |
0.4460 |
0.4457 |
0.7530 |
0.72872 |
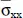 (a/2, b/2, 0) (a/2, b/2, 0) |
-3.0000 |
-2.9746 |
-5.8980 |
-5.983 |
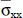 (a/2, b/2, h) (a/2, b/2, h) |
3.0320 |
3.0066 |
5.9060 |
5.9901 |
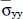 (a/2, b/2, h/3) (a/2, b/2, h/3) |
-1.7130 |
-1.7113 |
-2.882 |
-2.7854 |
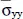 (a/2, b/2, 2h/3) (a/2, b/2, 2h/3) |
1.6740 |
1.672 |
2.845 |
2.748 |
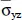 (a/2, 0, h/2) (a/2, 0, h/2) |
0.7220 |
0.7243 |
1.2280 |
1.1973 |
This work differs from the classical Ritz method in that the basis functions are not required to satisfy the essential boundary conditions. In the Ritz method, we can use a penalty parameter to enforce essential boundary conditions in a weak sense and use the present basis functions. In the traditional finite element method (FEM), we discretize each layer into disjoint domains called finite elements (FEs) and the compact support of the FE basis function for a node equals all FEs sharing that node. We could use the FEM by first taking the inner product of the nine governing equations R a= 0 with a nine-dimensional test function and integrating the result over the laminate. The matrix Kin K A= Fwill not be symmetric. We can improve on the accuracy of the numerical solution by either increasing the order of polynomials in the basis functions or reducing the element size or both. Even though we have not tried it, in general, it takes more computational resources than those needed for the present least-squares approach. Of course, only using one FE with the current basis functions is possible. Then, the difference will be in deriving matrices Kand Fand satisfying boundary conditions.
We have numerically solved three-dimensional linear elasticity equations by taking the three transverse stresses, three strain–displacement relations in the xy plane and three displacement components as independent variables and using the least-squares method to minimize the residuals in the expressions for these nine variables. For a simply supported rectangular plate, using complete polynomials of degree 4 in the z direction, and at most, 10 in each of the x and y directions provides, with very few degrees of freedom, an accurate solution relative to the exact solutions with error less than 0.3% in each of the nine variables, even for a very thick plate of aspect ratio 2. However, when edges are either clamped or free, a higher degree polynomial is needed in each direction to achieve the same accuracy. For a sandwich plate with ratio β of the axial modulus of the facesheet to that of the core up to 1000 and aspect ratios varying from 2 to 100, accurate results are obtained for each one of the nine variables. For β = 10,000, the accuracy considerably deteriorates with errors approaching 100%.
Читать дальше

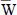
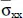
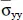
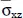
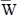 (a/2, b/2, h/2)
(a/2, b/2, h/2) (a/2, b/2, 0)
(a/2, b/2, 0)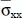 (a/2, b/2, h)
(a/2, b/2, h)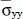 (a/2, b/2, h/3)
(a/2, b/2, h/3)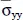 (a/2, b/2, 2h/3)
(a/2, b/2, 2h/3)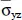 (a/2, 0, h/2)
(a/2, 0, h/2)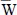 (a/2, b/2, h/2)
(a/2, b/2, h/2)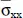 (a/2, b/2, 0)
(a/2, b/2, 0)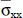 (a/2, b/2, h)
(a/2, b/2, h)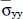 (a/2, b/2, h/3)
(a/2, b/2, h/3)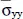 (a/2, b/2, 2h/3)
(a/2, b/2, 2h/3)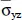 (a/2, 0, h/2)
(a/2, 0, h/2)










