278 259
279 260
280 261
281 262
282 263
283 264
284 265
285 266
286 267
287 268
288 269
289 270
290 271
291 272
292 273
293 274
294 275
295 276
296 277
297 278
298 279
299 280
300 281
301 282
302 283
303 284
304 285
305 286
306 287
307 288
308 289
309 290
310 291
311 292
312 293
313 294
314 295
315 296
316 297
317 298
318 299
319 300
320 301
321 302
322 303
323 304
324 305
325 306
326 307
327 308
328 309
329 310
330 311
331 312
332 313
333 314
334 315
335 316
336 317
337 318
338 319
339 320
340 321
341 322
342 323
343 324
344 325
345 326
346 327
347 329
348 330
349 331
350 332
351 333
352 334
353 335
354 336
355 337
356 338
357 339
358 340
359 341
360 342
361 343
362 344
363 345
364 347
365 348
366 349
367 350
368 351
369 352
370 353
371 354
372 355
373 356
374 357
Matrices and Tensors with Signal Processing Set
coordinated by
Gérard Favier
Volume 2
Matrix and Tensor Decompositions in Signal Processing
Gérard Favier

First published 2021 in Great Britain and the United States by ISTE Ltd and John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Apart from any fair dealing for the purposes of research or private study, or criticism or review, as permitted under the Copyright, Designs and Patents Act 1988, this publication may only be reproduced, stored or transmitted, in any form or by any means, with the prior permission in writing of the publishers, or in the case of reprographic reproduction in accordance with the terms and licenses issued by the CLA. Enquiries concerning reproduction outside these terms should be sent to the publishers at the undermentioned address:
ISTE Ltd
27-37 St George’s Road
London SW19 4EU
UK
www.iste.co.uk
John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
111 River Street
Hoboken, NJ 07030
USA
www.wiley.com
© ISTE Ltd 2021
The rights of Gérard Favier to be identified as the author of this work have been asserted by him in accordance with the Copyright, Designs and Patents Act 1988.
Library of Congress Control Number: 2021938218
British Library Cataloguing-in-Publication Data
A CIP record for this book is available from the British Library
ISBN 978-1-78630-155-0
The first book of this series was dedicated to introducing matrices and tensors (of order greater than two) from the perspective of their algebraic structure, presenting their similarities, differences and connections with representations of linear, bilinear and multilinear mappings. This second volume will now study tensor operations and decompositions in greater depth.
In this introduction, we will motivate the use of tensors by answering five questions that prospective users might and should ask:
– What are the advantages of tensor approaches?
– For what uses?
– In what fields of application?
– With what tensor decompositions?
– With what cost functions and optimization algorithms?
Although our answers are necessarily incomplete, our aim is to:
– present the advantages of tensor approaches over matrix approaches;
– show a few examples of how tensor tools can be used;
– give an overview of the extensive diversity of problems that can be solved using tensors, including a few example applications;
– introduce the three most widely used tensor decompositions, presenting some of their properties and comparing their parametric complexity;
– state a few problems based on tensor models in terms of the cost functions to be optimized;
– describe various types of tensor-based processing, with a brief glimpse of the optimization methods that can be used.
I.1. What are the advantages of tensor approaches?
In most applications, a tensor χ of order N is viewed as an array of real or complex numbers. The current element of the tensor is denoted x i1,… ,iN, where each index 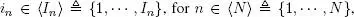 is associated with the n th mode, and I n is its dimension, i.e. the number of elements for the n th mode. The order of the tensor is the number N of indices, i.e. the number of modes. Tensors are written with calligraphic letters 1. An N th-order tensor with entries
is associated with the n th mode, and I n is its dimension, i.e. the number of elements for the n th mode. The order of the tensor is the number N of indices, i.e. the number of modes. Tensors are written with calligraphic letters 1. An N th-order tensor with entries 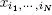 is written
is written 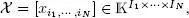 where
where 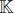 = ℝ or ℂ, depending on whether the tensor is real-valued or complex-valued, and I 1× · · · × I N represents the size of χ .
= ℝ or ℂ, depending on whether the tensor is real-valued or complex-valued, and I 1× · · · × I N represents the size of χ .
In general, a mode (also called a way) can have one of the following interpretations: (i) as a source of information (user, patient, client, trial, etc.); (ii) as a type of entity attached to the data (items/products, types of music, types of film, etc.); (iii) as a tag that characterizes an item, a piece of music, a film, etc.; (iv) as a recording modality that captures diversity in various domains (space, time, frequency, wavelength, polarization, color, etc.). Thus, a digital image in color can be represented as a three-dimensional tensor (of pixels) with two spatial modes, one for the rows (width) and one for the columns (height), and one channel mode (RGB colors). For example, a color image can be represented as a tensor of size 1024 × 768 × 3, where the third mode corresponds to the intensity of the three RGB colors (red, green, blue). For a volumetric image, there are three spatial modes ( width × height × depth ), and the points of the image are called voxels. In the context of hyperspectral imagery, in addition to the two spatial dimensions, there is a third dimension corresponding to the emission wavelength within a spectral band.
Tensor approaches benefit from the following advantages over matrix approaches:
– the essential uniqueness property 2, satisfied by some tensor decompositions, such as PARAFAC (parallel factors) (Harshman 1970) under certain mild conditions; for matrix decompositions, this property requires certain restrictive conditions on the factor matrices, such as orthogonality, non-negativity, or a specific structure (triangular, Vandermonde, Toeplitz, etc.);
– the ability to solve certain problems, such as the identification of communication channels, directly from measured signals, without requiring the calculation of high-order statistics of these signals or the use of long pilot sequences. The resulting deterministic and semi-blind processings can be performed with signal recordings that are shorter than those required by statistical methods, based on the estimation of high-order moments or cumulants. For the blind source separation problem, tensor approaches can be used to tackle the case of underdetermined systems, i.e. systems with more sources than sensors;
Читать дальше


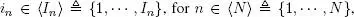 is associated with the n th mode, and I n is its dimension, i.e. the number of elements for the n th mode. The order of the tensor is the number N of indices, i.e. the number of modes. Tensors are written with calligraphic letters 1. An N th-order tensor with entries
is associated with the n th mode, and I n is its dimension, i.e. the number of elements for the n th mode. The order of the tensor is the number N of indices, i.e. the number of modes. Tensors are written with calligraphic letters 1. An N th-order tensor with entries 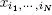 is written
is written 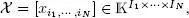 where
where 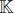 = ℝ or ℂ, depending on whether the tensor is real-valued or complex-valued, and I 1× · · · × I N represents the size of χ .
= ℝ or ℂ, depending on whether the tensor is real-valued or complex-valued, and I 1× · · · × I N represents the size of χ .










