1.2. Review: filtering of time-domain signals
We start by reviewing the filtering in discrete-time linear time-invariant (LTI) systems, which has been extensively studied in literature. Suppose that a one-dimensional discrete-time signal x nis obtained by sampling its continuous-time counterpart x ( t ) , with a fixed sampling period T , i.e. x n = x ( nT ) . A two-dimensional image signal can be similarly obtained by performing sampling in both the horizontal and vertical directions. In this case, the spatial sampling period usually corresponds to the spacing between an array of photosensors.
Suppose that an impulse response of a filter h nis given a priori . The discrete-time filtered signal y nin the LTI system is calculated from x nand h nby convolution as follows:
[1.1] 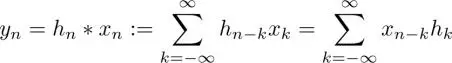
This equation is based on the shift of the signal or impulse response. In LTI systems, we (implicitly) assume that the shift of a discrete-time signal is well defined, i.e. x n−kis unique and time invariant. Therefore, equation [1.1]is equivalently represented as
[1.2] 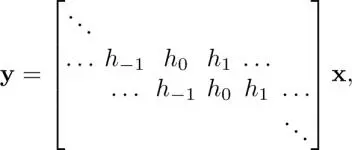
where x:= [..., x −1, x 0, x 1,... ] Tand y:= [..., y −1, y 0, y 1,... ] T. 1
In equation [1.2], the impulse response h kis invariant for n , i.e. the same filter is used for different values of n . Instead, we can use different filters for different values of n to yield y n, whose impulse response h k[ n ] is often defined in a signal-dependent manner, i.e. h k[ n ] 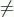 h k[ m ] for m
h k[ m ] for m 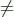 n . It is formulated as
n . It is formulated as
[1.3] 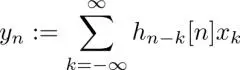
and its matrix form representation is
[1.4] 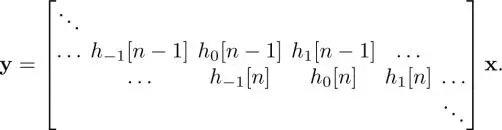
Famous image processing filters in this category include the bilateral filter (Tomasi and Manduchi 1998; Barash 2002; Durand and Dorsey 2002; Fleishman et al. 2003), anisotropic diffusion (Weickert 1998; Desbrun et al. 1999), adaptive directional wavelets (Chang and Girod 2007; Ding et al. 2007; Tanaka et al. 2010) and their variants.
It is well known that convolution in the time domain equation [1.1]has an equivalent expression in the frequency (i.e. Fourier) domain as follows:
[1.5] 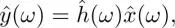
where
[1.6] 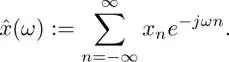
Here, 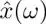 is the discrete-time Fourier transform (DTFT) of x n. We utilize the fact that convolution in the time domain is identical to multiplication in the frequency domain. Note that the fixed filter has a corresponding fixed frequency response, and thus, we can intuitively understand the filter characteristics from the frequency response. In contrast, the frequency response of a signal-dependent filter is not always clear in general. Fortunately, this drawback can be partially solved with a graph spectral domain perspective, which is described further.
is the discrete-time Fourier transform (DTFT) of x n. We utilize the fact that convolution in the time domain is identical to multiplication in the frequency domain. Note that the fixed filter has a corresponding fixed frequency response, and thus, we can intuitively understand the filter characteristics from the frequency response. In contrast, the frequency response of a signal-dependent filter is not always clear in general. Fortunately, this drawback can be partially solved with a graph spectral domain perspective, which is described further.
1.3. Filtering of graph signals
In this chapter, we consider linear graph filters. Readers can find nonlinear graph filters, like one used in deep learning, in the following chapters, specifically Chapter 10.
Let us denote a graph filter as H∈ R N×N, where its elements are typically derived from 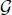 and x. As in the LTI system, the filtered signal is represented as
and x. As in the LTI system, the filtered signal is represented as
[1.7] 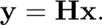
The representation of its element y nis similar to that observed in equation [1.3], i.e.
[1.8] 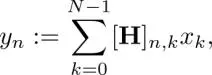
where [·] n,kis the n, k- element in the matrix. Similar to discrete-time signals, graph signal filtering may be defined in the vertex and graph frequency domains. These are described in the following.
1.3.1. Vertex domain filtering
Vertex domain filtering is an analog of filtering in the time domain. However, GSP systems are not shift-invariant: This means node indices do not have any physical meaning, in general. Therefore, the shift of graph signals based on the indices of nodes, similar to that used for discrete-time signals, would be inappropriate. Moreover, the underlying graph will exhibit a highly irregular connectivity, i.e. the degree in each node will vary significantly. For example, the star graph shown in Figure 1.1has one center node and N − 1 surrounding nodes. It is clear that N − 1 edges are connected to the center node, i.e. the center node has degree N − 1 , whereas all of the surrounding nodes have degree 1 . In an image processing perspective, such an irregularity comes from the edge and texture regions. An example is provided on the right side of Figure 1.1. Suppose that we construct a graph based on pixel intensity, i.e. pixels are nodes, and they are connected by edges with higher weights when their pixel values are closer. In this situation, pixels along edge/texture directions will be connected to each other strongly with a large degree, whereas those across edge/texture directions may have weaker edges, or may even be disconnected. Filtering based on such a graph will therefore reflect structures in the vertex (i.e. pixel) domain.
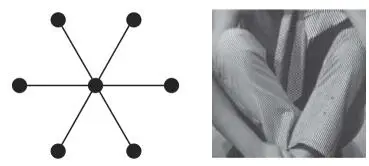
Figure 1.1. Left: Star graph with N = 7 . Right: Textured region of Barbara
Vertex domain filtering can be defined more formally as follows. Let 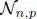 be a set of p- hop neighborhood nodes of the n th node. Clearly
be a set of p- hop neighborhood nodes of the n th node. Clearly  varies according to n .
varies according to n .
Читать дальше

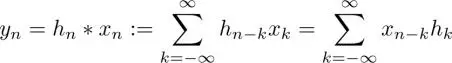
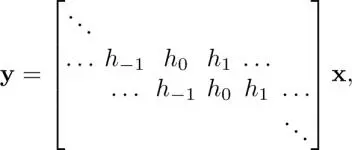
 h k[ m ] for m
h k[ m ] for m  n . It is formulated as
n . It is formulated as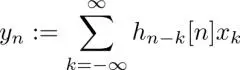
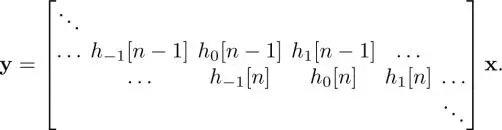
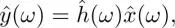
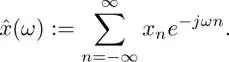
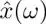 is the discrete-time Fourier transform (DTFT) of x n. We utilize the fact that convolution in the time domain is identical to multiplication in the frequency domain. Note that the fixed filter has a corresponding fixed frequency response, and thus, we can intuitively understand the filter characteristics from the frequency response. In contrast, the frequency response of a signal-dependent filter is not always clear in general. Fortunately, this drawback can be partially solved with a graph spectral domain perspective, which is described further.
is the discrete-time Fourier transform (DTFT) of x n. We utilize the fact that convolution in the time domain is identical to multiplication in the frequency domain. Note that the fixed filter has a corresponding fixed frequency response, and thus, we can intuitively understand the filter characteristics from the frequency response. In contrast, the frequency response of a signal-dependent filter is not always clear in general. Fortunately, this drawback can be partially solved with a graph spectral domain perspective, which is described further.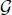 and x. As in the LTI system, the filtered signal is represented as
and x. As in the LTI system, the filtered signal is represented as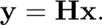
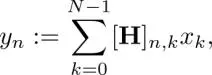

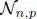 be a set of p- hop neighborhood nodes of the n th node. Clearly
be a set of p- hop neighborhood nodes of the n th node. Clearly 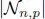 varies according to n .
varies according to n .










