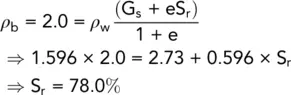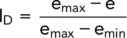The sample was then broken open and water content and particle specific gravity tests gave respectively 17% and 2.73.
The specific gravity of the wax was 0.89. Determine the bulk density, unit weight, void ratio and degree of saturation of the soil.
Solution:

Now,

Now,
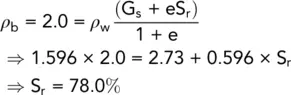
A granular soil generally has a large range into which the value of its void ratio may be fitted. If the soil is vibrated and compacted the particles are pressed close together and a minimum value of void ratio is obtained, but if the soil is loosely poured a maximum value of void ratio will result.
These maximum and minimum values can be obtained from laboratory tests and it is often convenient to relate them to the naturally occurring void ratio of the soil. This relationship is expressed as the density index, I Dor relative density , of the soil:
(1.27) 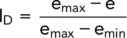
The theoretical maximum possible density of a granular soil must occur when e = e min, i.e. when I D= 1.0. Similarly, the minimum possible density occurs when e = e maxand I D= 0. In practical terms this means that a loose granular soil will have an I Dvalue close to zero whilst a dense granular soil will have an I Dvalue close to 1.0.
1.7.6 Summary of soil physical relations
A summary of the relationships established in Section 1.7is given below:

The results of a sieve analysis on a soil were:
| Sieve size (mm) |
Mass retained (g) |
| 50 |
0 |
| 37.5 |
15.5 |
| 20 |
17.0 |
| 14 |
10.0 |
| 10 |
11.0 |
| 6.3 |
33.0 |
| 3.35 |
114.5 |
| 1.18 |
63.3 |
| 0.6 |
18.2 |
| 0.15 |
17.0 |
| 0.063 |
10.5 |
The total mass of the sample was 311 g. Plot the particle size distribution curve and, from the inspection of this curve, determine the effective size and uniformity coefficient. Classify the soil.
Answer D 10= 0.7 mm; D 60= 5.2 mm. C u= 7.4. 70% gravel, 30% sand. Well graded sandy GRAVEL.
Plot the particle size distribution curve for the following sieve analysis, given the sieve sizes and the mass retained on each. Classify the soil.
Sample mass = 642 g.
Retained on 425 μm sieve – 11 g, 300 μm sieve – 28 g, 212 μm sieve – 77 g, 150 μm sieve − 173 g, 63 μm sieve – 321 g.
Answer By inspection of grading curve soil is a uniform SAND. This is confirmed from the value of C u= 2.3.
A BS cone penetrometer test carried out on a sample of boulder clay gave the following results:
| Cone penetration (mm) |
15.9 |
17.1 |
19.4 |
20.9 |
22.8 |
| Water content (%) |
32.0 |
32.8 |
34.5 |
35.7 |
37.0 |
Determine the liquid limit of the soil.
Answer w L= 35%
A liquid and plastic limit test gave the following results:
| Test no. |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
PL |
PL |
| Wet mass (g) |
33.20 |
32.10 |
28.20 |
31.00 |
11.83 |
15.04 |
| Dry mass (g) |
28.20 |
26.50 |
22.40 |
23.90 |
11.25 |
14.07 |
| Tin (g) |
7.02 |
7.04 |
7.10 |
7.02 |
7.04 |
7.25 |
| Penetration (mm) |
14.5 |
17.0 |
20.9 |
22.7 |
– |
– |
Determine the plasticity index of the soil and classify the soil.
Answer 22, CI
If the natural water content was 28%, determine the liquidity index in the field.
Answer 0.64
A sand sample has a porosity of 35% and the specific gravity of the particles is 2.73. What is its dry density and void ratio?
Answer e = 0.54, ρ d= 1.77 Mg/m 3
A sample of silty clay was found to have a volume of 14.88 ml, whilst its mass at natural water content was 28.81 g and the particle specific gravity was 2.7. Calculate the void ratio and degree of saturation if, after oven drying, the sample had a mass of 24.83 g.
Answer e = 0.618, S r= 70%
A sample of moist sand was cut from a natural deposit by means of a sampling cylinder. The volume of the cylinder was 478 ml and the mass of the soil was 884 g before drying, and 830 g after drying. The volume of the dried sample, when rammed tight into a graduated cylinder, was 418 ml and its volume, when poured loosely into the same cylinder, was 616 ml. If the particle specific gravity was 2.67, determine the density index and the degree of saturation of the deposit.
Answer I D= 69%, S r= 32%
In order to determine the density of a clay soil, an undisturbed sample was taken in a sampling tube of volume 0.001 664 m 3.
The following data were obtained:
Mass of tube (empty) = 1.864 kg
Mass of tube and clay sample = 5.018 kg
Mass of tube and clay sample after drying = 4.323 kg
Calculate the water content, the bulk, and the dry densities.
If the particle specific gravity was 2.69, determine the void ratio and the degree of saturation of the clay.
Answer w = 28%, ρ b= 1.90 Mg/m 3, ρ d= 1.49 Mg/m 3, e = 0.82, S r= 93%
Chapter 2 Permeability and Flow of Water in Soils
Learning objectives:
By the end of this chapter, you will have been introduced to:
water in soils and the differences between aeration and saturation zones;
the groundwater table and groundwater flow;
hydraulic head, the hydraulic gradient, Darcy's Law, and saturated flow;
the laboratory and field determination of the coefficient of permeability;
the use and construction of flow nets to determine flow quantities;
measurement of suction pressures in unsaturated soils;
flow of water through earth dams and deposits of different permeabilities.
This is the term used to define all water found beneath the Earth's surface. The main source of subsurface water is rainfall, which percolates downwards to fill up the voids and interstices. Water can penetrate to a considerable depth, estimated to be as much as 12 000 m, but at depths greater than this, due to the large pressures involved, the interstices have been closed by plastic flow of the rocks. Below this level, water cannot exist in a free state, although it is often found in chemical combination with the rock minerals, so that the upper limit of plastic flow within the rock determines the lower limit of subsurface water.
Читать дальше