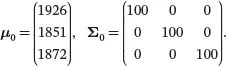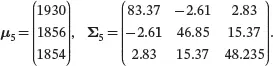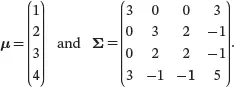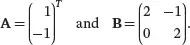Yong Chen - Industrial Data Analytics for Diagnosis and Prognosis
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Yong Chen - Industrial Data Analytics for Diagnosis and Prognosis» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Industrial Data Analytics for Diagnosis and Prognosis
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:5 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
Industrial Data Analytics for Diagnosis and Prognosis: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Industrial Data Analytics for Diagnosis and Prognosis»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
In
, distinguished engineers Shiyu Zhou and Yong Chen deliver a rigorous and practical introduction to the random effects modeling approach for industrial system diagnosis and prognosis. In the book’s two parts, general statistical concepts and useful theory are described and explained, as are industrial diagnosis and prognosis methods. The accomplished authors describe and model fixed effects, random effects, and variation in univariate and multivariate datasets and cover the application of the random effects approach to diagnosis of variation sources in industrial processes. They offer a detailed performance comparison of different diagnosis methods before moving on to the application of the random effects approach to failure prognosis in industrial processes and systems.
In addition to presenting the joint prognosis model, which integrates the survival regression model with the mixed effects regression model, the book also offers readers:
A thorough introduction to describing variation of industrial data, including univariate and multivariate random variables and probability distributions Rigorous treatments of the diagnosis of variation sources using PCA pattern matching and the random effects model An exploration of extended mixed effects model, including mixture prior and Kalman filtering approach, for real time prognosis A detailed presentation of Gaussian process model as a flexible approach for the prediction of temporal degradation signals Ideal for senior year undergraduate students and postgraduate students in industrial, manufacturing, mechanical, and electrical engineering,
is also an indispensable guide for researchers and engineers interested in data analytics methods for system diagnosis and prognosis.

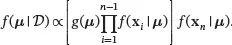 (3.32)
(3.32)