1 ...6 7 8 10 11 12 ...17 In response, selective fermentation (SF) has been implemented as a new approach for enhancing lipid extraction for microalgae biofuel generation (i.e., biodiesel) (Lai et al ., 2016b). SF utilizes the fact that lipids are generally biodegraded more slowly than carbohydrates and proteins under an anaerobic environment (Lai et al ., 2016b; Rittmann and McCarty, 2001; Siegert and Banks, 2005), in which, the lipid fermenters, known as the slow-growing microbes (Christ et al ., 2000; Rittmann and McCarty, 2001), can be washed out of the system with a relatively short solids retention time (SRT) (Lai et al ., 2016b). Hence, the SF solely allows the removal of carbohydrates and proteins in microalgae cells, leaving the lipids intact, providing a state much easier to extract lipids (Lai et al ., 2016b). More importantly, the SF process can significantly promote the lipid extraction process (e.g., >5000-fold increase vs. untreated biomass) when using the hexane-isopropanol solvents (Lai et al ., 2016a). Moreover, the lipid extraction is also benefitted by SF due to biohydrogenation, where the dominant lipid groups on long-chain fatty acids (LCFAs) are converted to saturated forms (e.g., C18:1 to C18:0) (Liu et al ., 2019); the SF process can increase the saturation ratio of extracted lipids by up to 80% (Liu et al ., 2020c). This saturating process via SF for the LCFAs is highly desirable as they can aid the transportation fuel generation due to more energy value, higher octane number (e.g., better combustion efficiency), and greater resistance to oxidation (Knothe, 2011). Also, SF biohydrogenation is superior to the catalytic hydrogenation (e.g., requires high temperature and metal catalysts to operate) due to significantly less or no energy/ catalyst demand (McArdle et al ., 2011; Plourde et al ., 2004; Wang et al ., 2017). Figure 1.5shows a conceptual schematic of lipid extraction from microalgae using electro-selective fermentation.
However, the SF itself can suffer from the fact that the protein fermentation is slower than the carbohydrate fermentation (Lu et al ., 2010). Furthermore, accumulation of short-chain carboxylates (e.g., high COD in the system) is another challenge (Lai et al ., 2016b), resulting in the following two cases: (1) wasting the electrons from the feed biomass (e.g., not all the electrons are used up or recovered as value-added products); and (2) lowering pH, which inhibits the fermentation process (Siegert and Banks, 2005). Hence, stimulating the protein and SCFAs biodegradation is of great interest to assist lipid extractions. Previous studies have reported that MECs have the potential to accelerate the fermentation of protein along with other complex organics, such as SCFAs (Lu et al ., 2012; Velasquez-Orta et al ., 2009). Furthermore, with the increased removal of protein, hydrogen bonds between membrane proteins and lipids can be disrupted, rupturing the cell membrane and exposing intracellular lipids for much simpler extraction (Cooney et al ., 2009; Sheng et al ., 2011). Hence, this was the main motivation behind coupling MEC with SF, also known as the electro-selective fermentation (ESF), to significantly enhance lipid wet-extractions (Liu et al ., 2019; Liu et al ., 2020b; Liu et al ., 2020c).
Recently, several studies have successfully demonstrated superior lipid extraction from microalgae using the ESF (Liu et al ., 2019; Liu et al ., 2020b; Liu et al ., 2020c). Liu et al . (2019) first investigated the relative performance of ESF compared to SF, in terms of protein and COD removal. When the ESF and SF (Control) reactors were fed with microalgae biomass ( Scenedesmus acutus ), significant differences were found in TCOD removal (12% vs. 2%), TCOD-to-SCOD conversion (17% vs. 11%), and protein biodegradation (42% vs. 10%) for ESF and SF, respectively. Interestingly, although the anodic respiration only contributed to < 1% of the total electron input, the ESF system yielded much higher protein and COD degradations. More importantly, even with the greater loss of total lipids due to β-oxidation-linked-to-biohydrogenation (e.g., shifting LCFAs from C18:1 to C16:0 or C14:0) in the ESF system, it still demonstrated significantly higher lipid yields (37%) compared with the SF (12%) and the lipid extractions with hexane-isopropanol solvents (~4%). In summary, despite currently being a small component of overall COD balance, ESF exhibited superior hydrolysis of protein of microalgae biomass ( Scenedesmus acutus ), a higher saturation ratio of LCFA, and higher lipid yields (~3 folds) over SF (Liu et al ., 2019). On the other hand, Liu et al . (2020c) have introduced a flat-plate MEC based ESF to observe the performance in lipid extraction by having a large anode surface area for electroactive bacteria biofilm. The benefit was in the enhanced electron consumptions, where the electrons in the microalgae biomass were greatly scavenged by electroactive bacteria in the anode biofilm. Furthermore, the SCFAs were also efficiently converted to current (e.g., preventing the accumulation of SCFAs), maintaining the optimal working environment (e.g., preventing pH drop) for the fermentation process. Compared with Liu et al . (2019), the ESF significantly improved in microalgae lipid extraction, achieving 56% (vs. 37%) extraction from the total lipids.
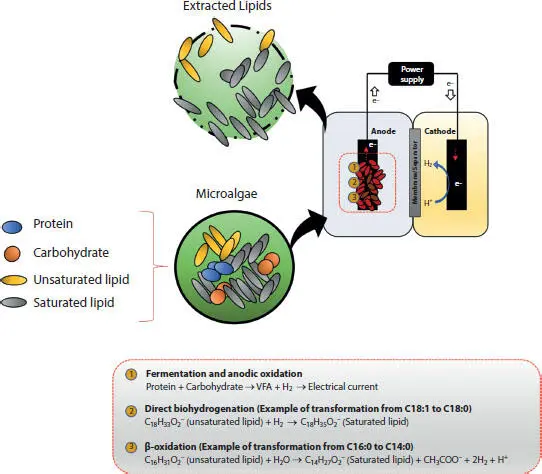
Figure 1.5 A conceptual schematic showing lipid extraction from microalgae using electro-selective fermentation. The figure is drawn with modification after Liu et al . (2019).
Finally, Liu et al . (2020b) have compared various SRTs on the ESF performance. In their study, ESF systems with different SRTs were compared (System A: start with a 6 d SRT, then switch to 2 d SRT vs. System B: start with a 2 d SRT, then switch to 6 d SRT). The ESF system A exhibited the highest lipid extractability (25%) when operated with a 6 d SRT, and gave the highest lipid productivity (450 mg/L/d) when switched to a 2 d SRT. This was attributed to establishing the microbial community containing protein fermenters at a 6 d SRT and washing out of lipid fermenters when the system A was switched to the 2 d SRT. Opposingly, the system B failed to enhance the lipid extractability. It initially (e.g., at a 2 d SRT) washed out the lipid fermenters, but it was unable to recover them when the system switched to a 6 d SRT. Ultimately, demonstrated by multiple studies, the further studies are warranted to bring this technology forward towards further development, scaling-up and potential commercialization.
Acetoin is known to be a volatile compound, which is widely utilized in chemical synthesis, cigarettes, cleaning products, food, personal care products, plant growth, pest controls, wine, etc. (Cheynier et al ., 2010; Förster et al ., 2017; Xiao and Lu, 2014). Especially, acetoin has been largely applied as food flavoring (e.g., has an intense butter flavor) and fragrance manufacturing (Xiao and Lu, 2014). Moreover, acetoin is also highly promising, ranking in the top 30 for its potential applications as the bio-based building block precursors (Werpy and Petersen, 2004), which can embrace a green environment (e.g., petro-free economy). Due to these several industrial applications, in recent years, the production of acetoin became highly desirable due to a significantly large annual consumption across the globe (e.g., 2-4 mg per day per person, equal to several thousand tons per year worldwide) (Xiao and Lu, 2014).
Читать дальше













