Video 1.10 Female rectum‐related cross‐sectional anatomy: linear orientation.
Video 1.11 Arterial models.
Video 1.12 Venous models.
Video 1.13 Bronchial anatomy in a linear orientation.
2 Esophagus: Radial and Linear
James L. Wise and John C. Deutsch
Essentia Health Care Systems, Duluth, MN, USA
Layers of the esophageal wall
Staging the depth of involvement of tumors and the layer of origin of subepithelial masses is an important component of competency in endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS). An intimate knowledge of the normal layers of the esophageal wall is critical for this to be done accurately. The wall of the esophagus has four readily appreciable layers by EUS using standard operating frequencies (5–12 MHz). The layers are seen in concentric, alternating rings of hyperechoic and hypoechoic structures emanating out distally from the tip of the endoscope. Starting with the layers closest to the scope tip, they are as follows:
Interface echo between the superficial mucosa and water (hyperechoic).
Deep mucosa (hypoechoic).
Submucosa plus the acoustic interface between the submucosa and muscularis propria (hyperechoic).
Muscularis propria minus the acoustic interface between the submucosa and muscularis propria (hypoechoic).
If a higher resolution frequency probe is used, greater number of layers could be visualized as detailed in Chapter 4. The esophagus lacks an obvious fifth layer as there is no serosa.
In our opinion, visualization and discernment of the layers of the esophageal wall is usually best accomplished using radial compared to linear instruments.
Figure 2.1shows the esophageal walls using radial and linear instruments. To help separate the layers, these images include a muscularis mucosae leiomyoma that was subsequently resected. Images show subepithelial hypoechoic lesion in echolayer II as well as in the other defined layers of the esophageal wall.
Normal radial extraesophageal anatomy ( Video 2.1)
Standard examination of the esophagus and mediastinum begins with advancing the radial instrument to the gastroesophageal (GE) junction at or near the squamocolumnar junction. At this level the aorta is seen as an anechoic circular structure in the 5 o’clock position. The descending aorta is kept in this position as all radial mediastinal imaging will then correlate quite nicely with cross‐sectional imaging. Other structures visible at the level of the GE junction are the inferior vena cava (IVC) seen between 7 and 9 o’clock and the liver between 6 o’clock and 12 o’clock surrounding the IVC ( Figure 2.2).
As the scope is withdrawn, the vena cava moves clockwise and superiorly into the right atrium. The spine soon comes into view adjacent to the descending aorta at 6 o’clock.
Further withdrawal upward to usually around 30–35 cm reveals the anechoic chamber of the left atrium in the 12 o’clock position ( Figure 2.3). With this field, relatively slight movement of the scope will reveal the mitral valve ( Figure 2.4), aortic root, and the aortic valve ( Figure 2.5). In the inferior portion of the field the descending aorta, the spine, the thoracic duct, and a relatively prominent azygos vein can be seen.
As the scope is withdrawn the bronchi come together at the carina. At or just proximal to this level the azygos arch ( Figure 2.6) can be identified traveling superiorly and laterally into the superior vena cava. This is also the area of the aortopulmonary (AP) window at approximately 2 o’clock.
The endoscope can be pushed down from here or pulled up slightly from the position of the left atrium to reach the subcarinal space. Of interest in the subcarinal space are the right and left mainstem bronchi seen emanating out as ribbed‐like air‐filled structures. As many have suggested, these can be imagined to have the appearance of two headlights.
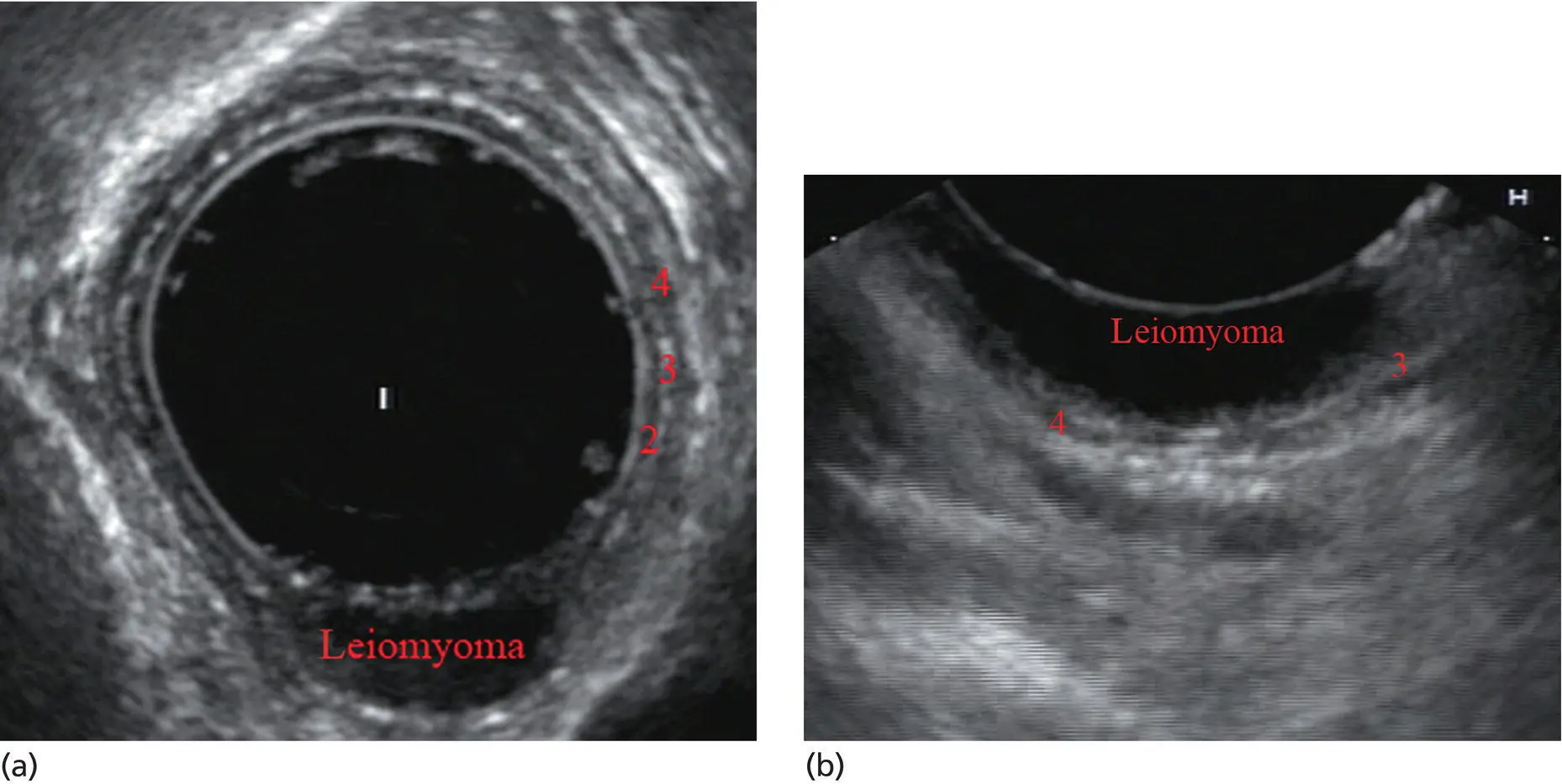
Figure 2.1 (a) Radial array image of esophageal wall with small echolayer II leiomyoma. (b) Linear array image of esophageal wall with small echolayer II leiomyoma.
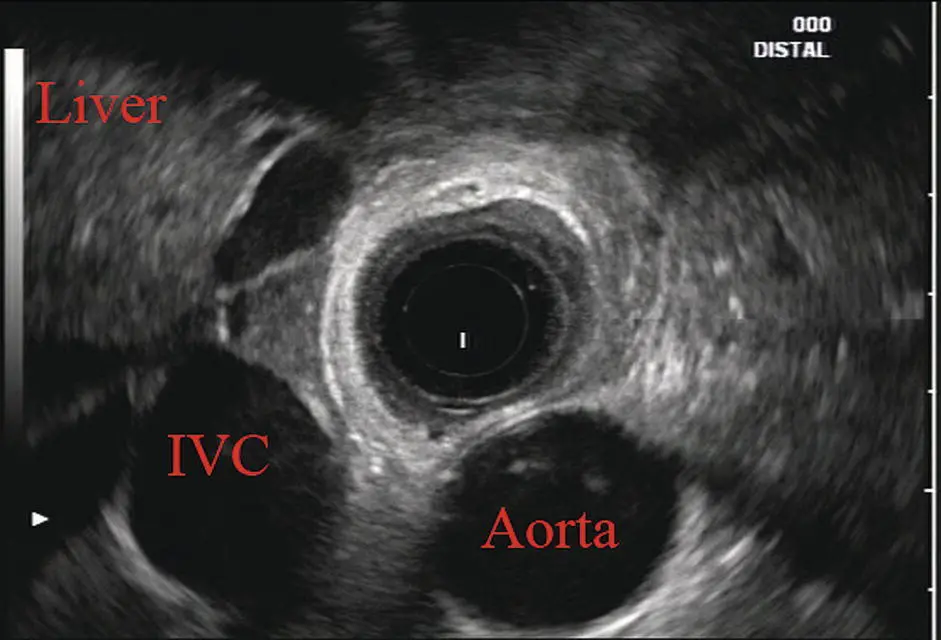
Figure 2.2 Radial array image at gastroesophageal (GE) junction. IVC, inferior vena cava.
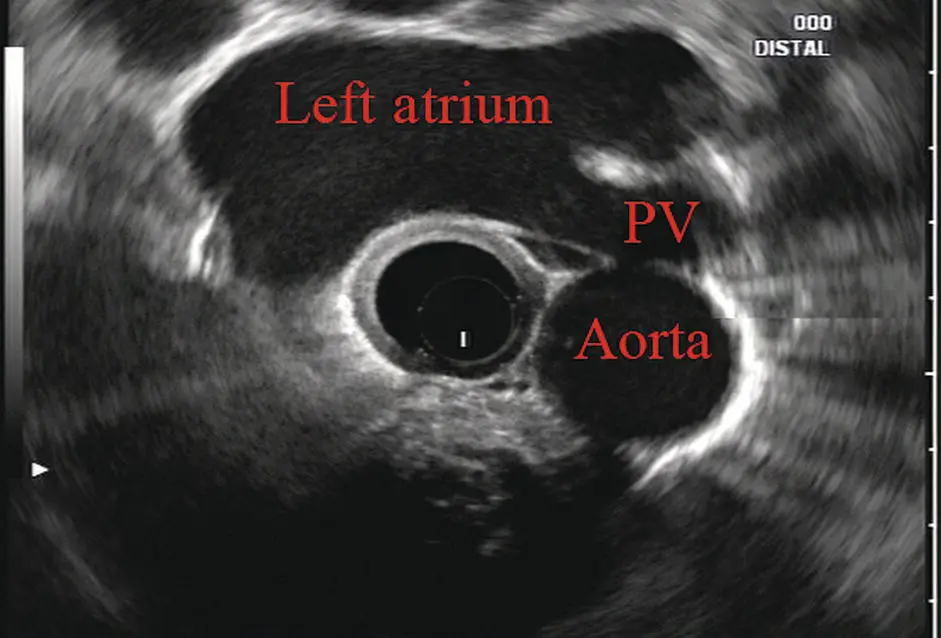
Figure 2.3 Radial array image at the level of the left atrium. PV, pulmonary vein.

Figure 2.4 Radial array image at the level of the mitral valve.
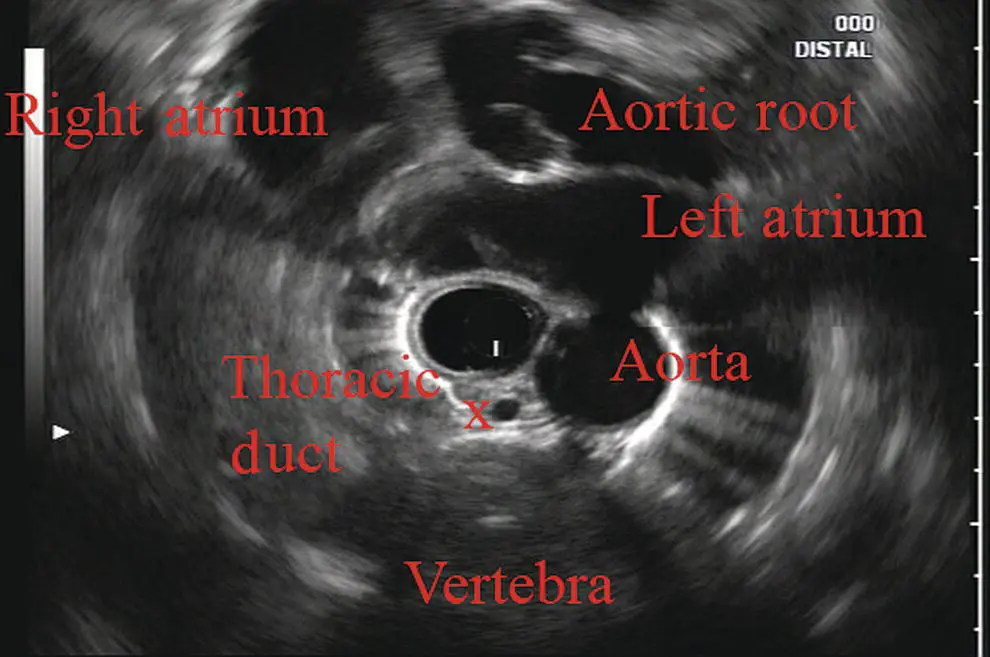
Figure 2.5 Radial array image at the level of the aortic root.
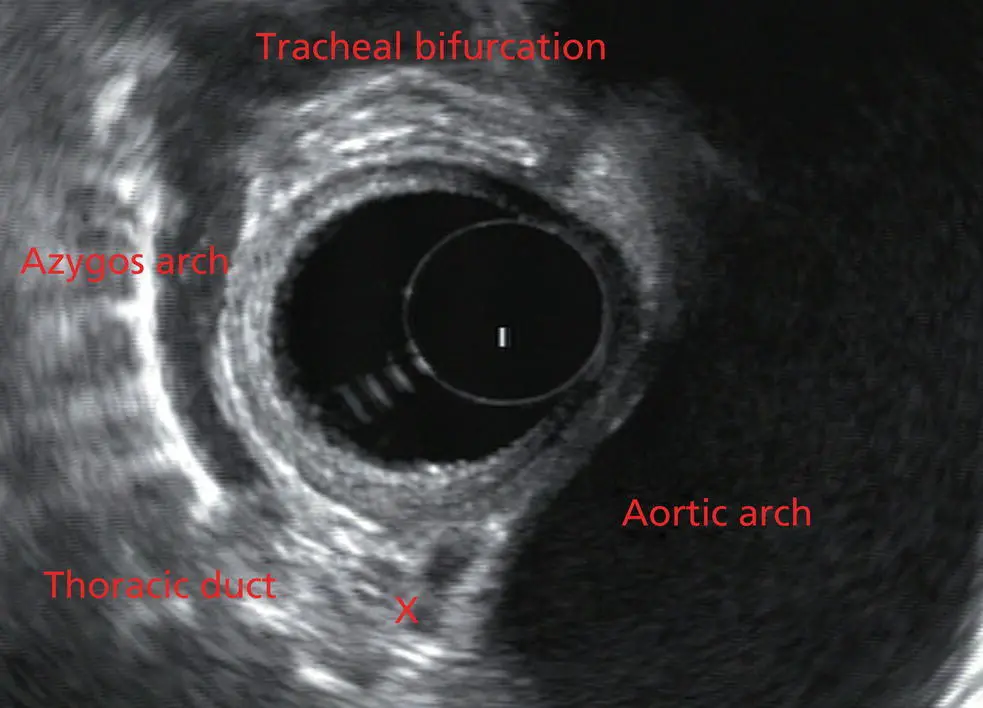
Figure 2.6 Radial array image at the level of the azygos arch.
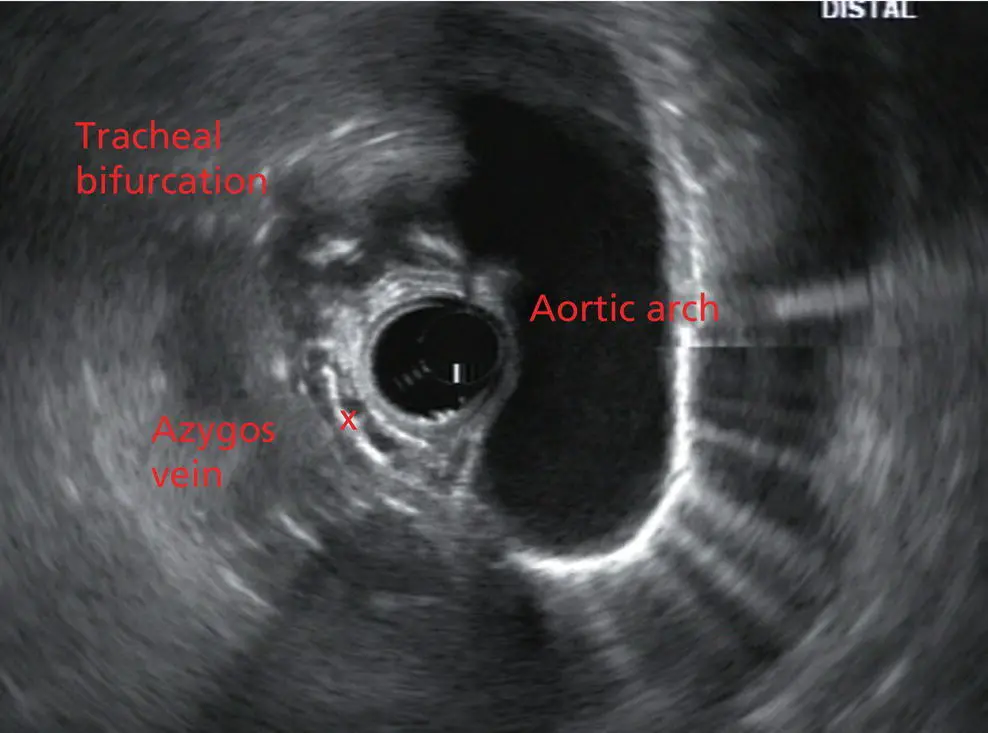
Figure 2.7 Radial array image at the mid aortic arch.
More proximally from the area at the AP window the aorta elongates and forms the aortic arch ( Figure 2.7). This usually creates a semicircle on the entire right side of the image correlating to the left‐sided arch. However, with usual orientation the aorta should not cross the midline. The left carotid and left subclavian artery can easily be seen to leave the aortic arch as small round structures on the right side of the image ( Figure 2.8). The brachiocephalic artery can sometimes be seen as well superior to the carotid on the right. As the scope is withdrawn the thyroid comes into view. For example, on the right of Figure 2.9a prominent thyroid can be seen with a cystic structure within it.
Normal linear thoracic anatomy
The linear scope is advanced to the GE junction by following the descending aorta from the level of the arch downward ( Figure 2.10). In order to follow this path, the scope is usually torqued clockwise 90–180 degrees and, as the aorta is followed down, the scope is gently rotated counterclockwise to stay on the aorta. As seen in Video 2.2, the thyroid is visualized briefly and the scope is then advanced to the level of the GE junction.
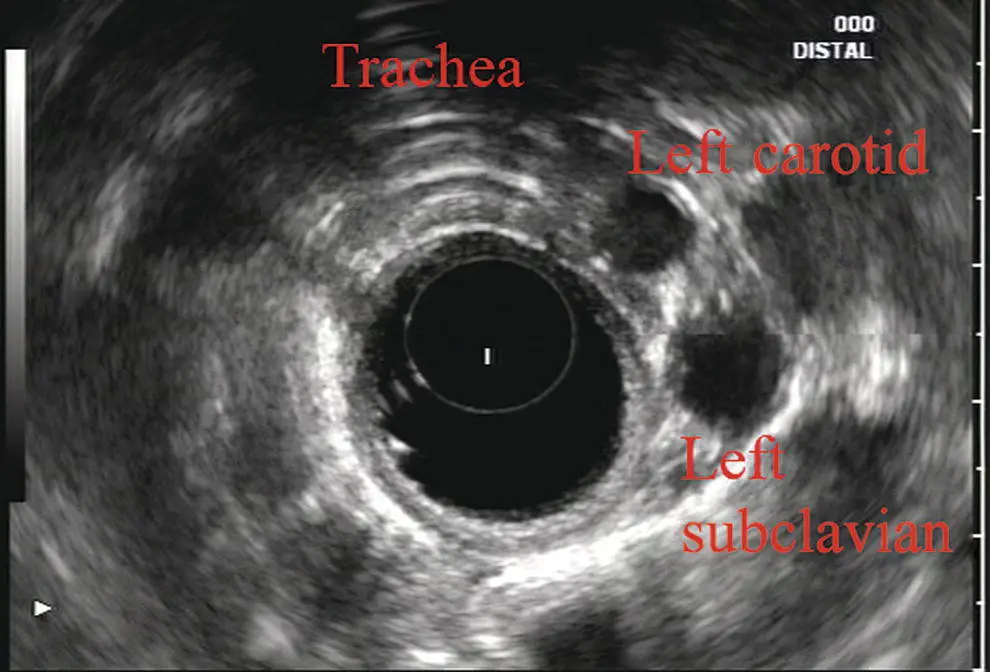
Figure 2.8 Radial array image at the level of the left carotid and subclavian arteries.
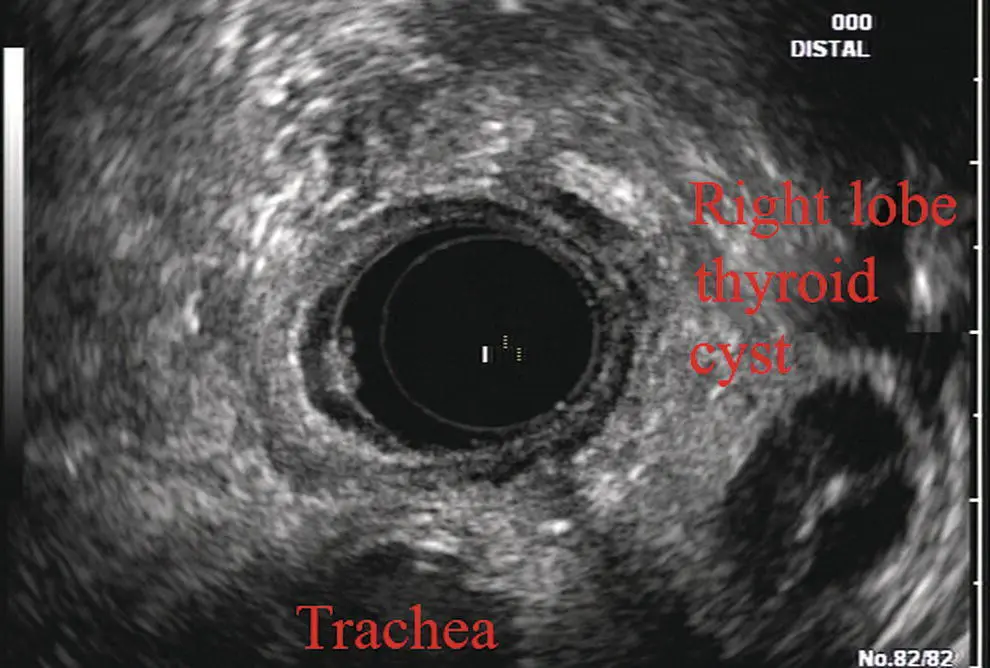
Figure 2.9 Radial array image at the level of the thyroid.
Читать дальше





















