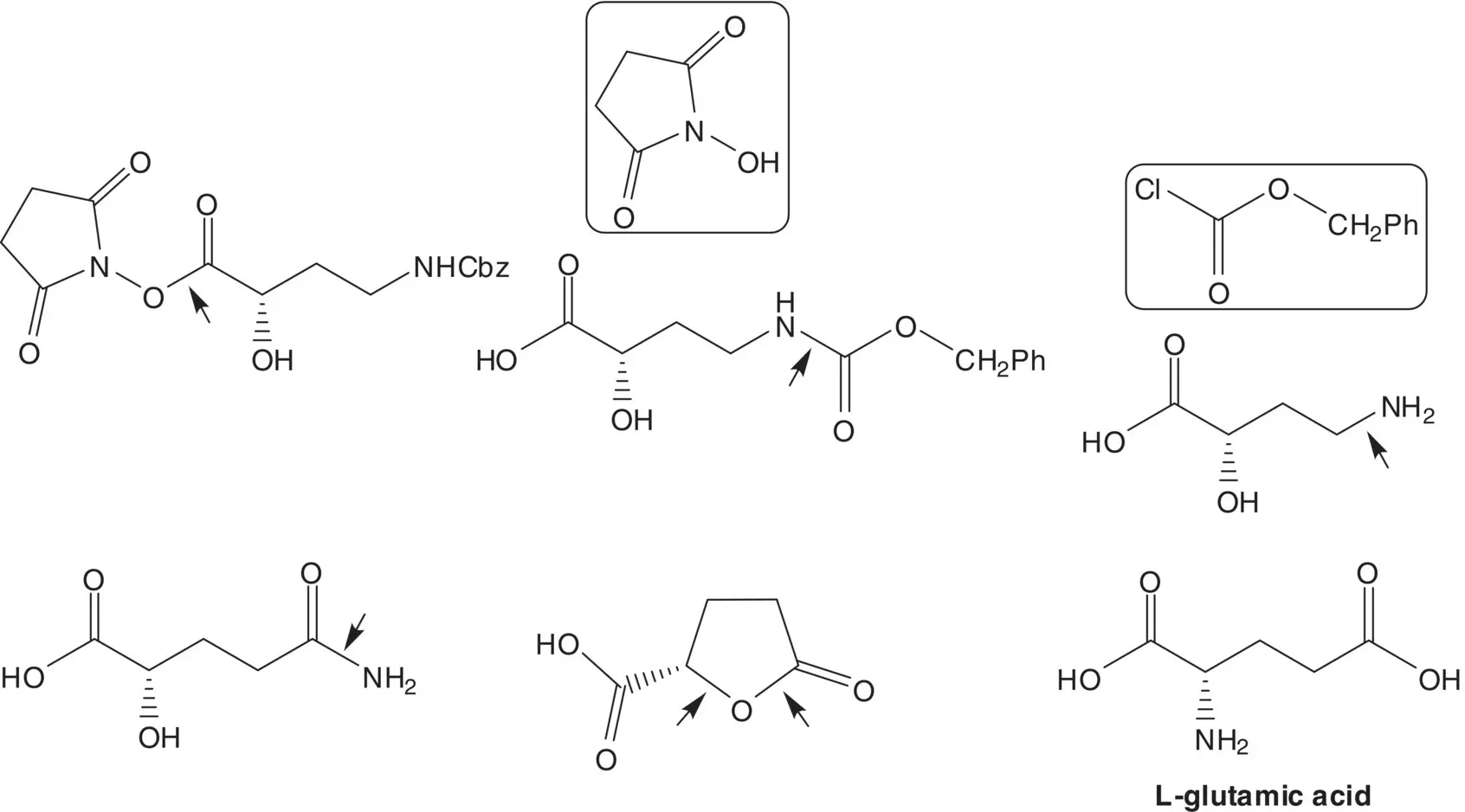
Draw the structures of three side products which are likely to be formed in the reaction of kanamycin A with two equivalents of benzyl chloroformate. Draw the structure(s) of likely impurities in amikacin as each side product is carried through the amide formation and carbamate hydrogenolysis.
or
Draw the structures of the retrosynthetic analysis of the alternative route to ( S )‐4‐amino‐2‐hydroxybutanoic acid from L‐asparagine. List the pros and cons for both routes and select one route as the preferred route.
Diuretic
A nitrogen substituent on a pyrazine ring carbon is often introduced by displacement of chloride. The substitution is facilitated by the adjacent ring nitrogen and can be further facilitated by an electron‐withdrawing group (NO 2 , SO 2 R, COOR, CN) on a para ring carbon.
Discussion.The guanidine group is introduced in the final step by reaction of guanidine with the methyl ester. Chloride at the 5‐position of the 5,6‐dichloropyrazine is displaced by ammonia. The 5,6‐dichloropyrazine is formed by chlorination of methyl 3‐aminopyrazine‐2‐carboxylate. The methyl ester is formed from the carboxylic acid ( Fischer Esterification).
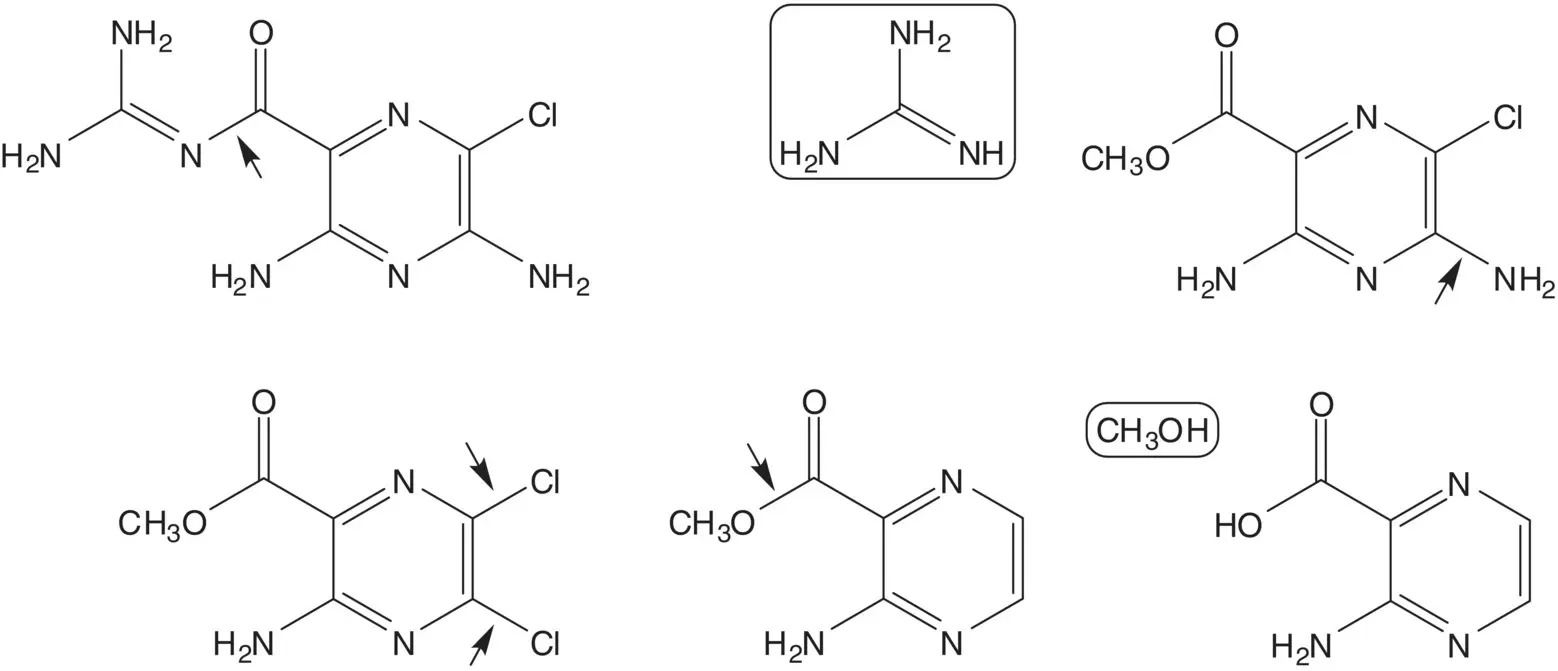
3‐Aminopyrazine‐2‐carboxylic acid is formed by hydrolysis of the pyrimidine ring of lumazine (1H‐pteridine‐2,4‐dione). The pyrazine ring of lumazine is formed by reaction of 5,6‐diaminouracil with glyoxal. The amino group at the 5‐position of 5,6‐diaminouracil is formed by reduction of a nitroso group. The nitroso group is introduced by nitrosation of 6‐aminouracil. 6‐Aminouracil is formed from ethyl cyanoacetate and urea.
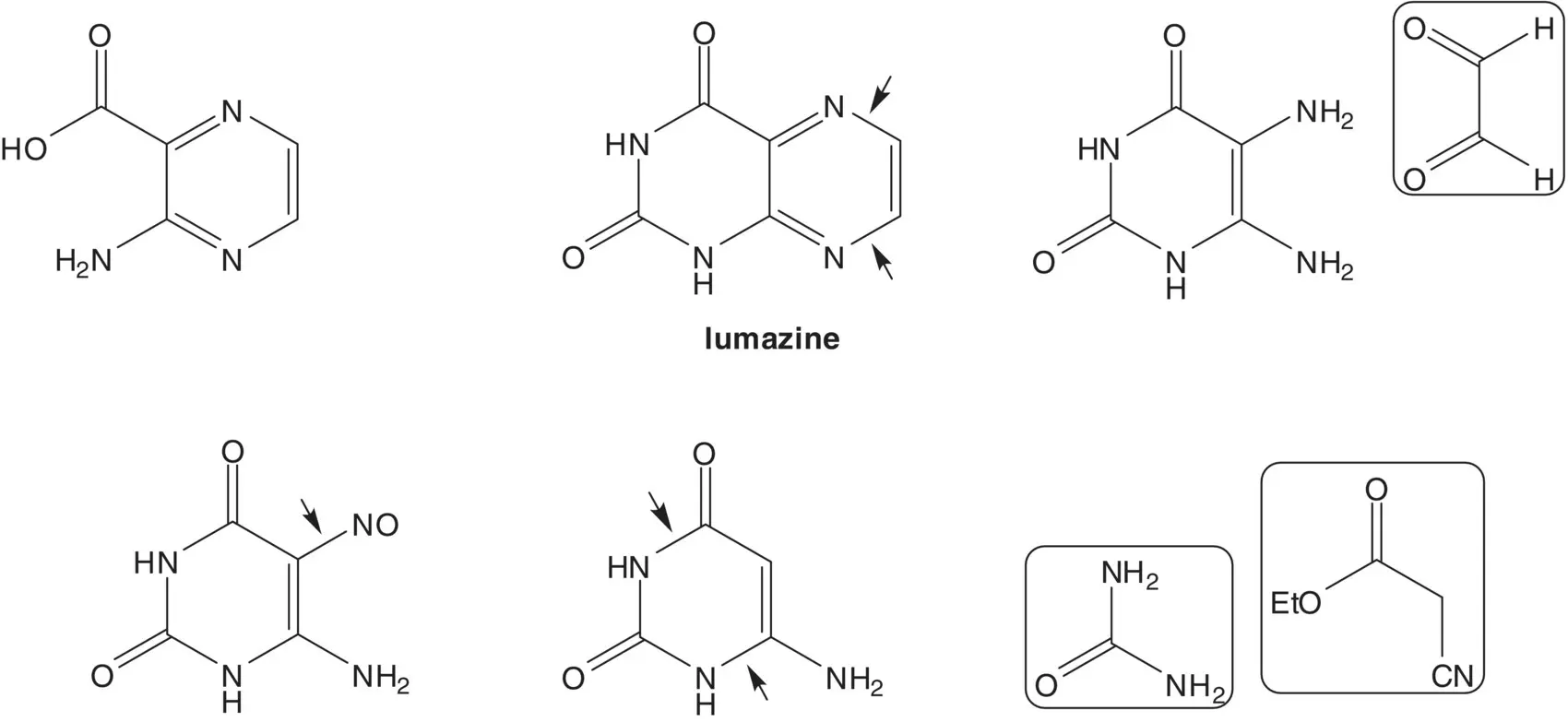
Draw the structures of the retrosynthetic analysis of one alternative route to 3‐aminopyrazine‐2‐carboxylic acid. Include the structures of the retrosynthetic analysis of any organic starting material(s) from petrochemical or biochemical raw materials. List the pros and cons for both routes and select one route as the preferred route.
Anti‐Infective Medicines/Antibacterials/Antituberculosis Medicines
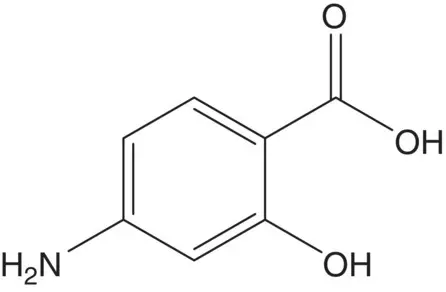
A 2‐hydroxybenzoic acid is often formed by carboxylation of the phenol (Kolbe–Schmitt Reaction).
Discussion.4‐Aminosalicylic acid is formed from 3‐aminophenol and carbon dioxide ( Kolbe–Schmitt Reaction) (Draw the structure of one side product formed in this reaction. How is pure 4‐aminosalicylic acid isolated from the product mixture?).

A preferred route to 3‐aminophenol is from benzene via resorcinol. Draw the structures of a retrosynthetic analysis of one alternative route to 3‐aminophenol. Include the structures of the retrosynthetic analysis of any organic starting material(s) from petrochemical or biochemical raw materials. List pros and cons for the two routes and select one route as the preferred route.
Cardiovascular Medicines/Antihypertensive Medicines
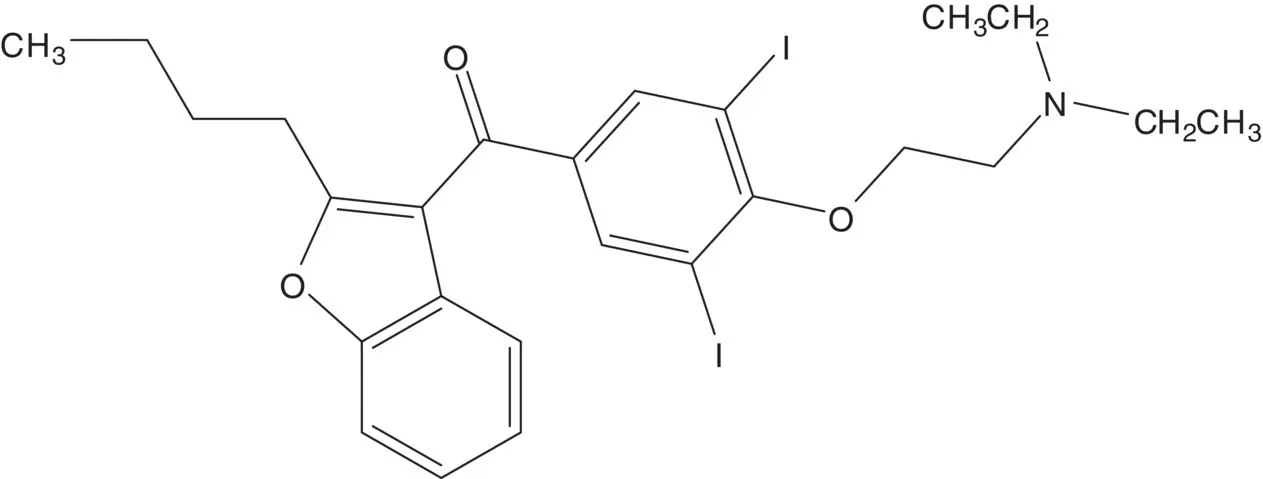
An aromatic ketone is often formed by Friedel–Crafts Acylation.
Discussion.The ether is formed in the final step by displacement of the chloride of 2‐chloro‐ N,N ‐diethylethanamine by the phenol ( Williamson Ether Synthesis).
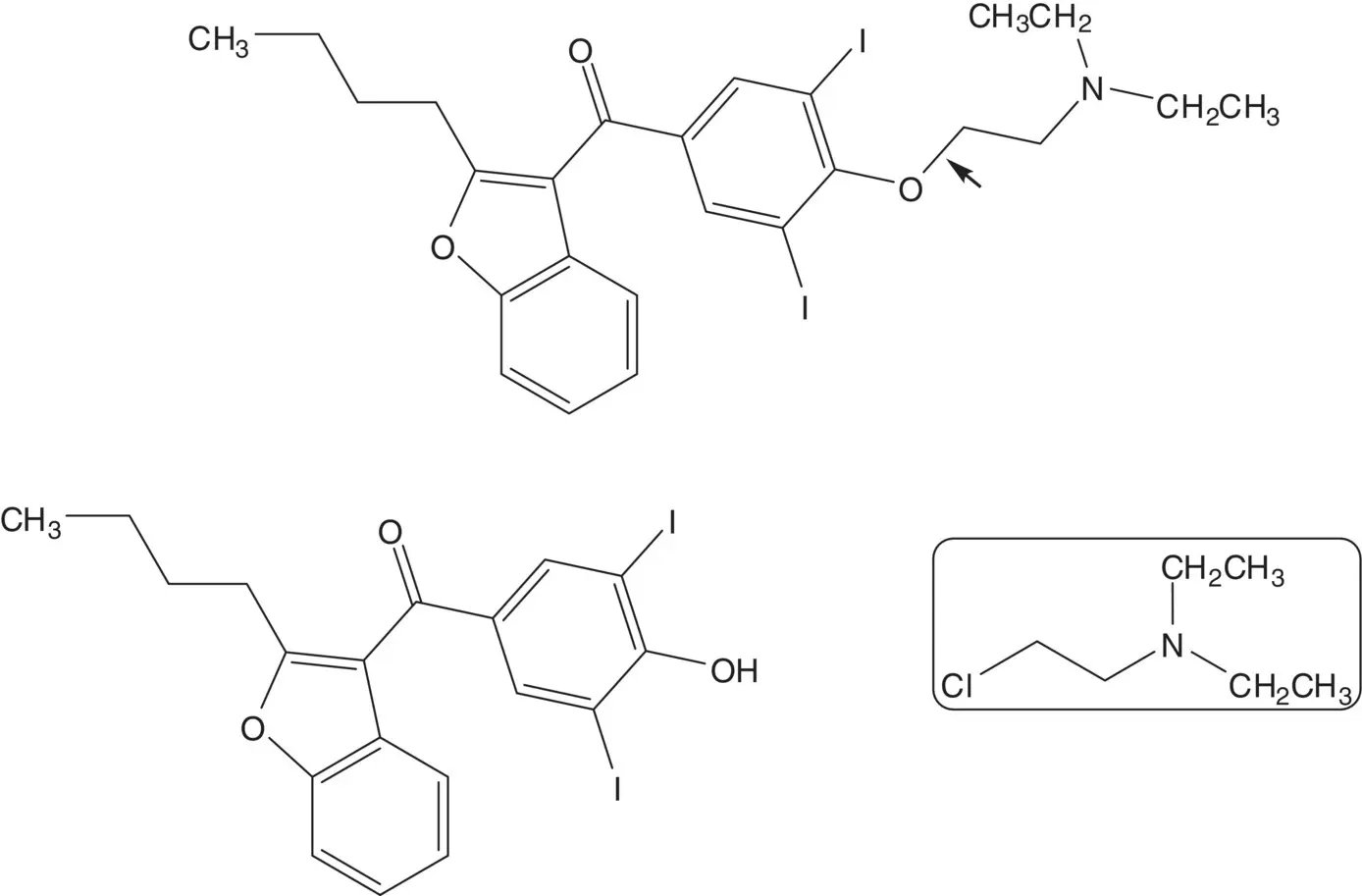
The phenol is iodinated in both ortho positions. The phenol is formed by demethylation of the ether. The ketone is formed by acylation of 2‐butyl‐2,3‐benzofuran with 4‐methoxybenzoyl chloride ( Friedel–Crafts Acylation). 4‐Methoxybenzoyl chloride is formed from para ‐anisic acid.
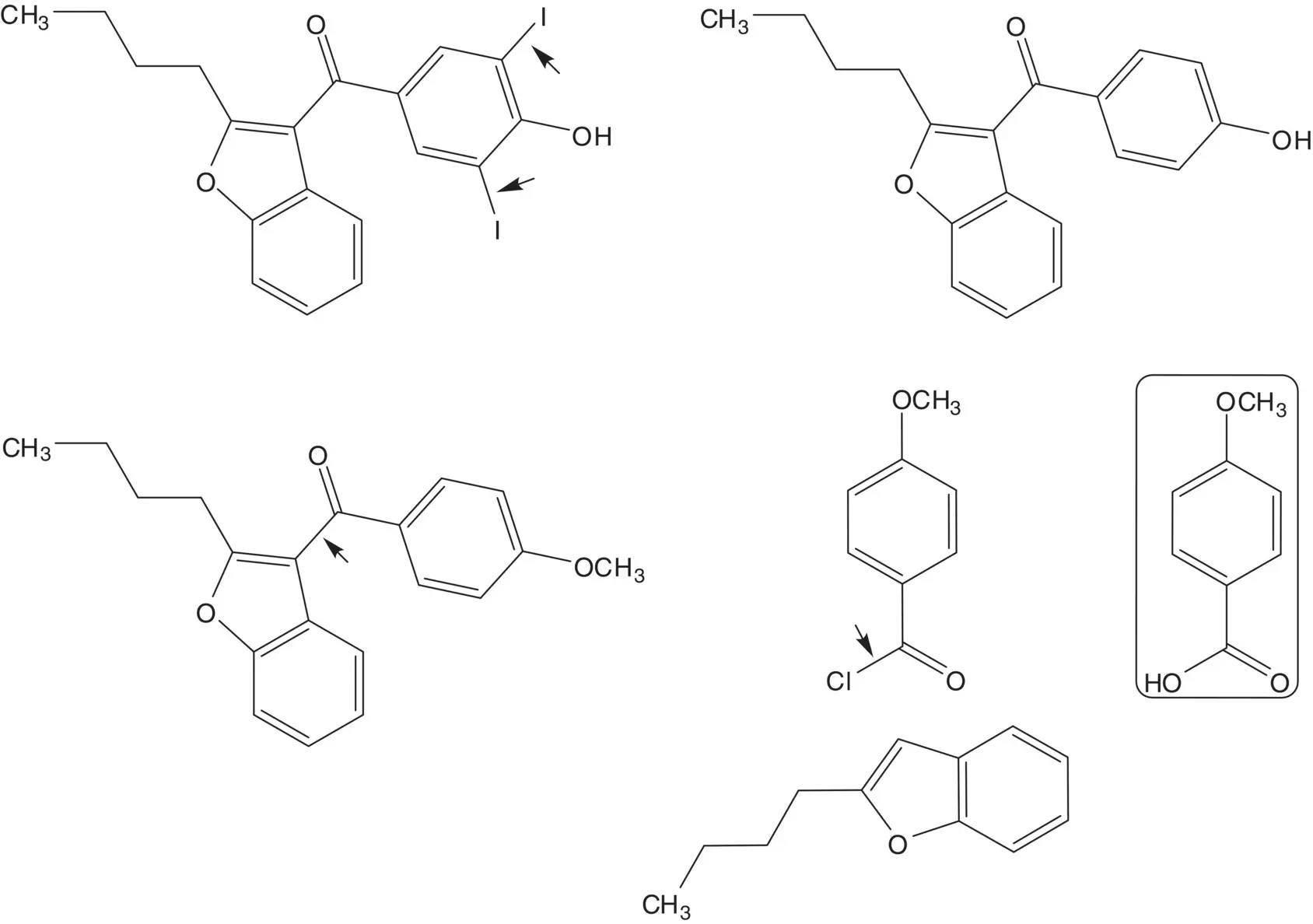
2‐Butylbenzofuran is formed by rearrangement of the chlorohydrin. The tertiary alcohol of the chlorohydrin is formed by addition of butylmagnesium chloride to the ketone ( Grignard Reaction). Butylmagnesium chloride is formed from 1‐chlorobutane. 2‐Chloro‐2′‐hydroxyacetophenone is formed from phenol and chloroacetonitrile ( Sugasawa Reaction).
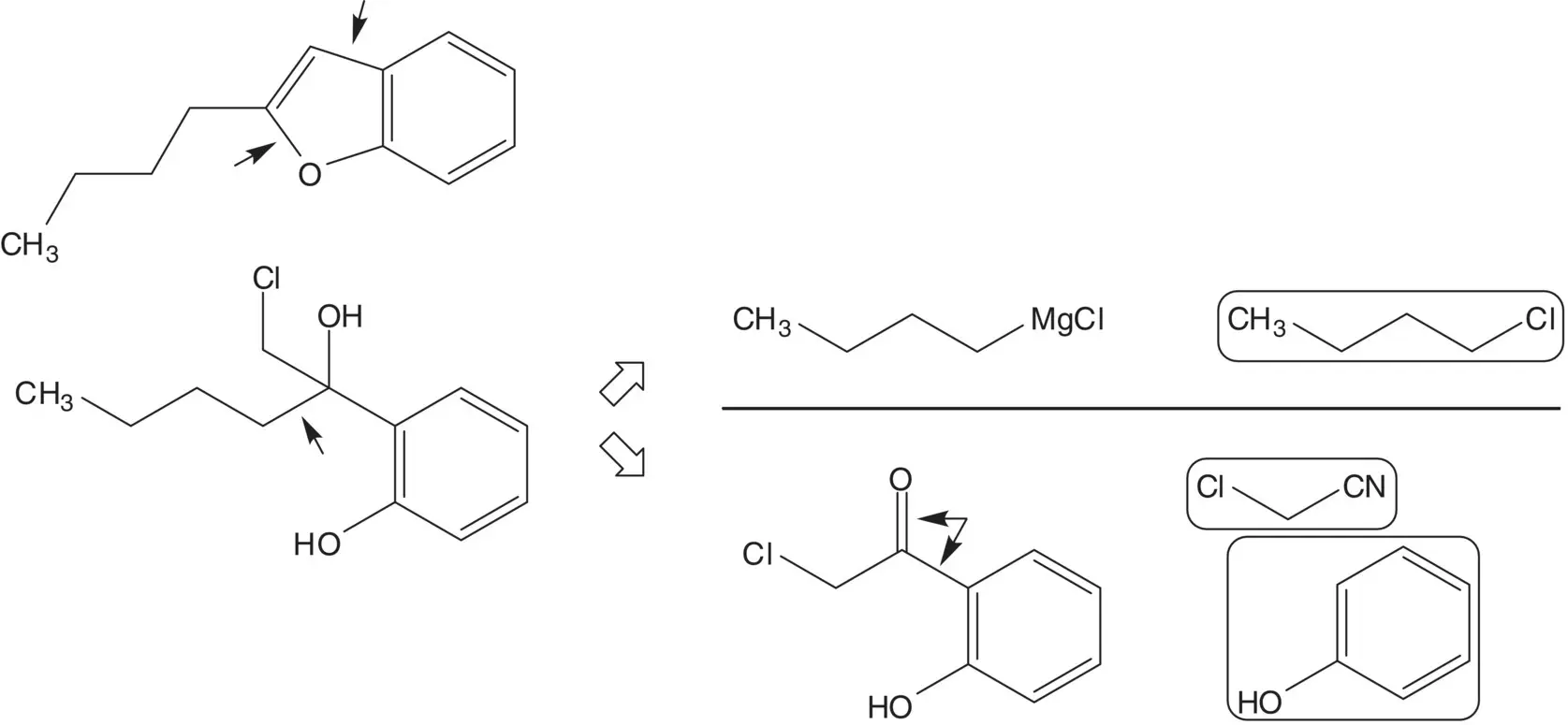
Draw the structures of the retrosynthetic analysis of one alternative route to 2‐butylbenzofuran. Include the structures of the retrosynthetic analysis of any organic starting material(s) from petrochemical or biochemical raw materials. List the pros and cons for both routes and select one route as the preferred route.
Medicines for Pain and Palliative Care/Medicines for Other Common Symptoms in Palliative Care
Medicines for Mental and Behavioral Disorders/Medicines Used in Mood Disorders/Medicines Used in Depressive Disorders
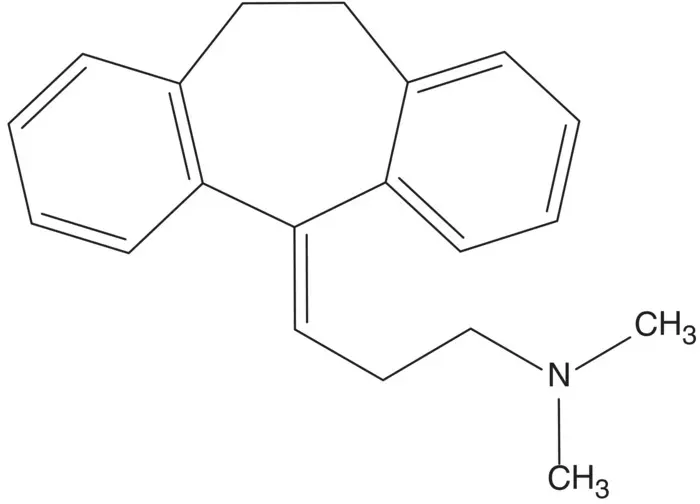
An alkene conjugated to two aromatic rings is often formed by dehydration of an alcohol.
Discussion.The alkene is formed in the final step by dehydration of the tertiary alcohol. The tertiary alcohol is formed by addition of the alkylmagnesium chloride to dibenzosuberone ( Grignard Reaction). The alkylmagnesium chloride is formed from 3‐chloro‐ N,N ‐dimethylpropan‐1‐amine. Dibenzosuberone is formed by cyclization of 2‐phenethylbenzoic acid ( Friedel–Crafts Acylation). 2‐Phenethylbenzoic acid is formed by reduction of benzalphthalide. Benzalphthalide is formed from phthalic anhydride and phenylacetic acid.
Читать дальше
























