Handbook of Biomass Valorization for Industrial Applications
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Handbook of Biomass Valorization for Industrial Applications» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Handbook of Biomass Valorization for Industrial Applications
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:4 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 80
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Handbook of Biomass Valorization for Industrial Applications: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Handbook of Biomass Valorization for Industrial Applications»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
BIOMASS VALORIZATION
INDUSTRIAL APPLICATIONS
The handbook provides a comprehensive view of cutting-edge research on biomass valorization, from advanced fabrication methodologies through useful derived materials, to current and potential application sectors.
Audience Handbook of Biomass Valorization for Industrial Applications
Handbook of Biomass Valorization for Industrial Applications — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «Handbook of Biomass Valorization for Industrial Applications», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
Maris et al . [24] have used Ru or Pt supported commercial carbon (Ru/C, Pt/C) as catalysts for glycerol hydrogenolysis in an aqueous phase at 473 K and a hydrogen pressure of 40 bar. At neutral pH, Ru/C shows the higher activity and promotes the formation of ethylene glycol over propylene glycol. Whereas, Pt/C shows less reactivity and catalyzes the formation of propylene glycol with good selectivity. The existence of a base enhances the catalytic performance of Pt/C to a bigger extend as compared to Ru/C [24].
Arcoya and coworkers have investigated the glycerol hydrogenolysis into 1,2-PD over ruthenium supported activated carbons (AC), originals AC, and HNO 3modifies AC (ACOx). The hydrogenolysis reaction was conducted in the liquid phase at T = 453 K and 8 MPa. Characterization techniques revealed that oxygenated groups were available on the surface of carbon, which increases the acidity of the catalyst. The high density of the acidic group makes it highly selective towards 1,2-PD. Ruthenium supported on activated carbon (Ru(Cl)/AC-Ox and Ru(n)/AC-Ox) shows higher selectivity towards the production of 1,2-PD. The overall catalytic activity has increased with an increase in the concentration of surface acidic groups. The Ru/AC in combination with acid catalysts is efficient for simultaneous hydrogenation and dehydration [25]. The glycerol hydrogenolysis over Ru and Pt-based catalysts are given in Table 4.2.
Table 4.2 Glycerol hydrogenolysis over Ru and Pt-based catalysts.
| Catalyst | Process | Main product | Medium | Conversion (%) | Selectivity (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ru/C | Hydrogenolysis | Lactic acid | NaOH | 100 | 34 | [24] |
| Pt/C | Hydrogenolysis | Lactic acid | CaO | 100 | 58 | [24] |
| (Ru(Cl)/AC-Ox | Hydrogenolysis | Ethylene glycol | – | 17 | 43 | [25] |
| Ru(n)/AC-Ox) | Hydrogenolysis | Ethylene glycol | – | 42 | 30 | [25] |
4.4.2.2 Esterification and Acetylation of Glycerol
One of the potential technologies for the valorization of glycerol from the biodiesel industry is its esterification with acetic acid using a suitable homogeneous or heterogeneous acidic catalyst. The esterification reaction of glycerol mainly produces mono-, di-, and triacetate, also recognized as monoacetin (MA), diacetin (DA), and triacetin (TA) respectively). These acetins have a broad range of applications such as raw materials for the fabrication of tanning agents, polyesters, explosives, and use as solvents, food additives, plasticizers, softening, or emulsifying agents, in cryogenics, or pharmaceutical industry. Furthermore, acetins can be used as environmentally friendly fuel bio-additives. The mixture of DA and TA are useful for improving the viscosity and cold properties of fuel [26].
Various homogeneous catalysts, for example, hydrofluoric acid, sulfuric acid, and para-toluene sulfonic acid manifest high activity and selectivity. However, these homogeneous catalysts are corrosive, lethal, and hard to separate from the products. Heterogeneous catalysts can conquer the limitations of the homogeneous catalyst due to their high recoverability and recyclability. Additionally, these catalysts show improved selectivity towards the products as compare to homogeneous catalysts. Some heterogeneous catalysts such as acid exchange resins, K-10 montmorillonite, HZSM-5, HUSY, PMo-NaUSY, niobium–zirconium mixed oxide catalysts, heteropolyacids loaded AC, and mesoporous silica has been proposed in pieces of literature [9, 12, 13]. Among various catalysts, cation-exchange resins have shown high activity and outstanding selectivity for higher esters.
Sanchez et al . have prepared a very active and stable porous carbon catalyst having acidic sites by sulfonation of carbonized sucrose using fuming sulfuric acid. The catalyst is selective towards the esterification of glycerol to acetylglycerols. Glycerol reacts with the acetic acid and leads to the formation of monoacetylglycerol (MAG) or monoacetin, di-acetylglycerol (DAG) or diacetin, tri-acetylglycerol (TAG), or triacetin with the removal of water as depicted in Scheme 4.2. The catalyst exhibits conversion above 99% and selectivity of approximately 50% towards the formation of triacetin through glycerol esterification with acetic acid [27].
The hydrothermally prepared sulfonated carbon (SHTC) from glucose shows good activity for glycerol esterification with various carboxylic acids, i.e., acetic, caprylic, and butyric acids. The selectivity of the catalyst has been varied by changing the reaction condition. The SHTC shows one of the best selectivity for the formation of monoacetins without using excess glycerol. It was found that the catalyst gets deactivated after recycling due to the generation of sulfonated ester on the catalyst surface. The recycled catalyst was again activated by acid treatment with subsequent hydrolysis of sulfonated esters. The catalyst has excellent potential for various bio-refinery processes [28].
Alemany and coworkers have prepared carbonaceous material by pyrolysis of cellulose at 600 and 800 °C. The carbonaceous support was chemically activated with HNO 3(3N) and impregnated with sulfonic groups through the impregnation method. The resulted catalyst named SO 3H-C is highly active and stable for acetalization reaction of glycerol with acetone in a batch and continuous flow reactor. The resulted catalyst leads to the formation of a five-member ring solketal as shown in Scheme 4.3which is used as a fuel additive component. The catalyst shows the absolute transformation of glycerol with 100% selectivity in a continuous flow reactor. The activity of the catalyst was retained even after 300 min of continuous flow [29]. Table 4.3summarizes the performance of different catalysts for esterification.
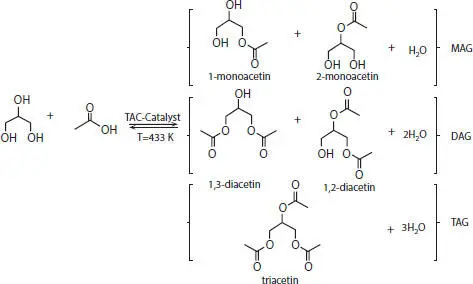
Scheme 4.2 Reaction scheme for the formation of actylglycerols [27].
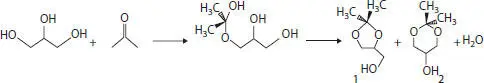
Scheme 4.3 Reaction scheme for glycerol acetalization with acetone [29].
Similarly, Chandrakala et al . have used sulfonic acid-modified heterogeneous carbon for the conversion of glycerol into TAG, a biofuel additive in two-step processes. The catalyst was synthesized by controlled carbonization and sulfonation of glycerol at 220 °C. The complete reaction scheme is shown in Scheme 4.4. The first step involves the esterification of glycerol in the presence of acetic acid and sulfonic acid functionalized heterogeneous carbon catalyst which was followed by acetylation of glycerol ester mixture with acetic anhydride using the same catalyst. The catalyst is reusable for up to five cycles without appreciable loss in its activity. The complete process is economically effective because of a highly stable and reusable carbon catalyst [30]. Higher esters (di- and tri-esters) of glycerol have a high boiling point, good miscibility with traditional fuel, and high octane and cetane numbers, so they are chosen as fuel components [31].
Sun et al . have explored the potential of rod-like carbon-based sulfonic acid-modified ionic liquids for selective glycerol esterification with the help of acetic acid or lauric acid into valuable products. The formation of catalyst takes place in two steps. The first step involves the hydrothermal treatment of glucose and cyanamide at 160 °C. In the second step, the hydrothermally synthesized nitrogen-enriched carbon nanorods undergo quaternary ammonization in the presence of 1,3-propanesultone and anion substitution with HSO 3CF 3. The final catalyst is labeled as [PrSO 3HN][SO 3CF 3]/C nanorods. The performance of the catalyst was evaluated for selective glycerol esterification using acetic acid and lauric acid. Glycerol in the presence of acetic acid leads to the formation of TAG and with lauric acid, MAG, and DAG was formed as shown in Figure 4.7. The catalyst [PrSO 3HN] [SO 3CF 3]/C nanorods show superior catalytic performance as compared to propylsulfonic acid-modified SBA-15, Amberlyst-15, p-toluenesulfonic acid, and [PrSO 3HN][SO 3CF 3] functionalized carbonaceous framework [32].
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «Handbook of Biomass Valorization for Industrial Applications»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «Handbook of Biomass Valorization for Industrial Applications» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «Handbook of Biomass Valorization for Industrial Applications» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.












