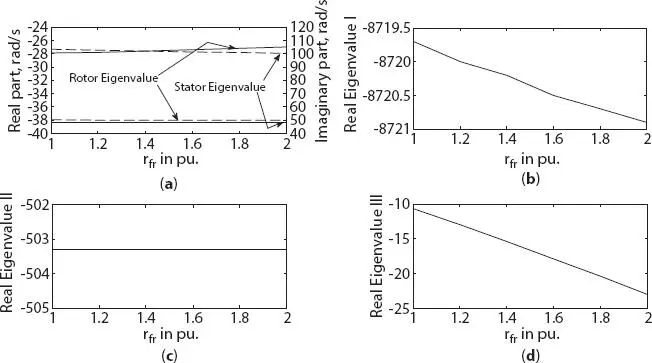
Figure 1.9 Variation in eigenvalue of three-phase synchronous machine with field circuit resistance change (a) stator and rotor eigenvalue, (b) real eigenvalue I, (c) real eigenvalue II, (d) real eigenvalue III.
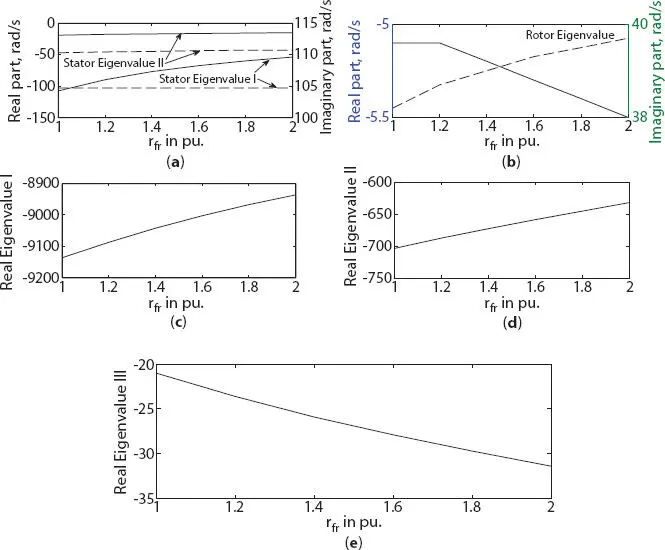
Figure 1.10 Variation in eigenvalue of six-phase synchronous machine with field circuit resistance change (a) stator eigenvalue I and II, (b) rotor eigenvalue, (c) real eigenvalue I (d) real eigenvalue II, (e) real eigenvalue III.
With the increase in field leakage reactance xlfr , magnitude of real component of stator eigenvalue was decreased for both three- and six-phase generator, as shown in Figures 1.11aand 1.12a, respectively. But, a small variation in real component of rotor eigenvalue was noted for both three- and six-phase generator, as shown in Figures 1.11aand 1.12b, respectively. A small linear or no change was noted in eigenvalue I and II for both three- and six-phase generator, as shown in Figures 1.11band cand Figures 1.12cand d, respectively. But, a larger variation in real eigenvalue III was noted for both three- and six-phase generator, as shown in Figures 1.11dand 1.12e, respectively.
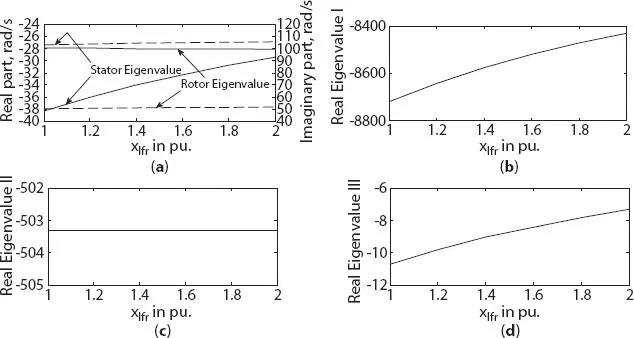
Figure 1.11 Variation in eigenvalue of three-phase synchronous machine with field circuit leakage reactance change (a) stator and rotor eigenvalue, (b) real eigenvalue I, (c) real eigenvalue II, (d) real eigenvalue III.
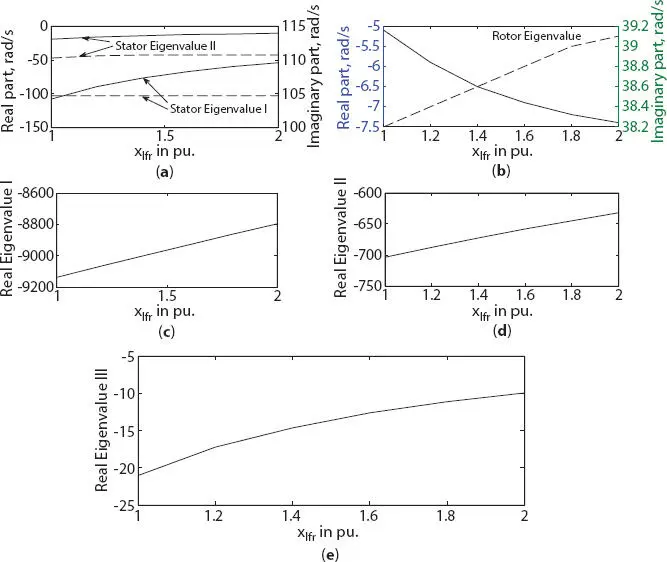
Figure 1.12 Variation in eigenvalue of six-phase synchronous machine with field circuit leakage reactance change (a) stator eigenvalue I and II, (b) rotor eigenvalue, (c) real eigenvalue I, (d) real eigenvalue II, (e) real eigenvalue III.
1.5.3 Parametric Variation of Damper Winding, Kd
In this section, parameter variation of damper winding along d -axis Kd (i.e., resistance rKd and leakage reactance xlKd ) is considered in the evaluation of generator eigenvalues. With the increase in resistance rKd , both the stator and rotor eigenvalues were found to be unchanged for three-phase generator, as shown in Figure 1.13a. However, some change was found in stator eigenvalue I and rotor eigenvalue for six-phase generator, as shown in Figures 1.14aand b, respectively. A pronounced increase in the magnitude of real eigenvalue I was found for both three- and six-phase generator, as shown in Figures 1.13band 1.14c, respectively. But no change in eigenvalue II and III was found for three-phase generator with small variation for six-phase generator, as shown in Figures 1.13cand dand Figures 1.14dand e, respectively.
With the increased value of leakage reactance xlKd , a major variation was only noted on real eigenvalue I for both three- and six-phase generator as shown in Figures 1.15band 1.16c, respectively. A slight variation in real eigenvalue III was noted for both three- and six-phase generator as shown in Figures 1.15dand 1.16e, respectively. On stator side, a small variation in real component of eigenvalue was noted (with decrease in real component of stator eigenvalue I for six-phase generator) both three- and six-phase generator as shown in Figures 1.15aand 1.16a, respectively. Real component of rotor eigenvalue was noted to have no/small variation for both three- and six-phase generator as shown in Figures 1.15aand 1.16b, respectively.
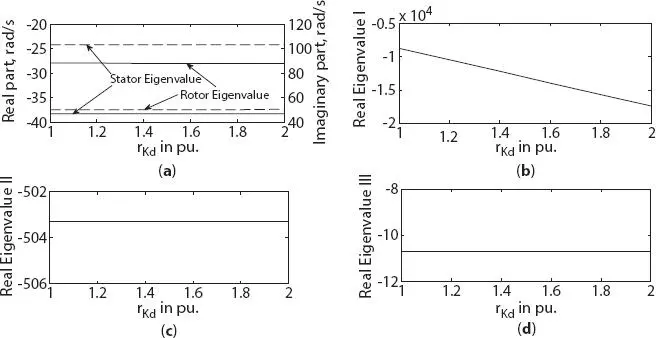
Figure 1.13 Variation in eigenvalue of three-phase synchronous machine with damper resistance change along d -axis (a) stator and rotor eigenvalue, (b) real eigenvalue I, (c) real eigenvalue II, (d) real eigenvalue III.

Figure 1.14 Variation in eigenvalue of six-phase synchronous machine with damper resistance change along d -axis (a) stator eigenvalue I and II, (b) rotor eigenvalue, (c) real eigenvalue I, (d) real eigenvalue II (e) real eigenvalue III.
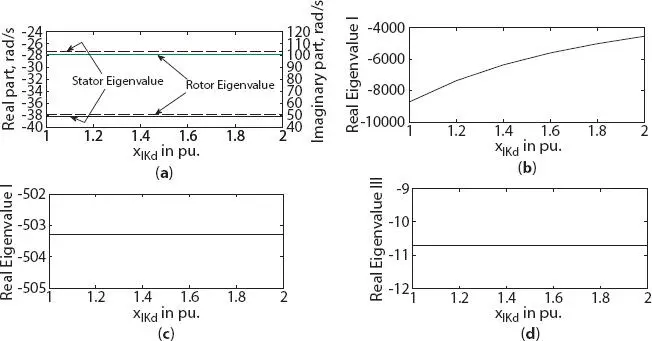
Figure 1.15 Variation in eigenvalue of three-phase synchronous machine with damper leakage reactance change along d -axis (a) stator and rotor eigenvalue, (b) real eigenvalue I, (c) real eigenvalue II, (d) real eigenvalue III.
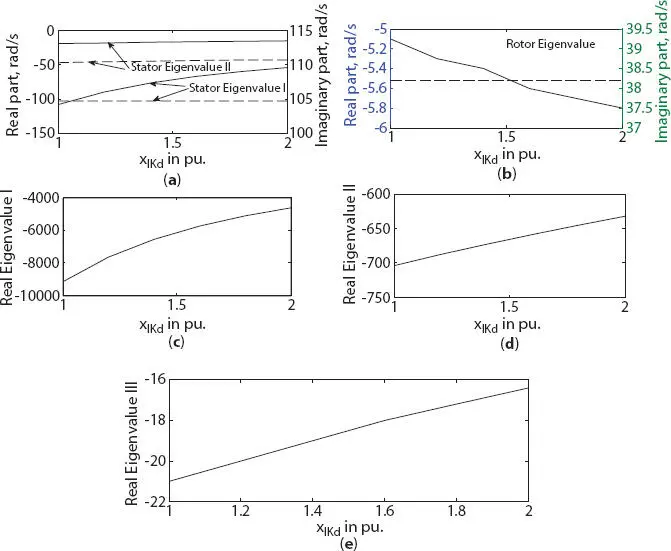
Figure 1.16 Variation in eigenvalue of six-phase synchronous machine with damper leakage reactance change along d -axis (a) stator eigenvalue I and II, (b) rotor eigenvalue (c) real eigenvalue I, (d) real eigenvalue II, (e) real eigenvalue III.
1.5.4 Parametric Variation of Damper Winding, Kq
With the increase in damper winding resistance rKq , small variation was noted on real component of stator eigenvalue in three-phase generator. But in six-phase generator, it was increased by 50% in stator eigenvalue I (and slight increase in stator eigenvalue II), as shown in Figures 1.17aand 1.18a, respectively. On rotor side, real part of eigenvalue was increased by 46.2% and 49% for both three- and six-phase generator, as shown in Figures 1.17aand 1.18b, respectively. A major effect was found on real eigenvalue II which was decreased by 112% and 82.2% for three-phase and six-phase generator as shown in Figures 1.17cand 1.18d, respectively. In three-phase generator, no change was noted in eigenvalue I and III as shown in Figures 1.17band d, respectively. But in case of six-phase generator, slight variation was found in real eigenvalue I and III, as shown in Figures 1.18cand e, respectively. During the analysis, it was noted that the effect of variation in the value of reactance xlKq was only found in real eigenvalue II, with no variation on other eigenvalues, hence not shown. Value of real eigenvalue II was increased by 45.7% and 48.2% for three- and six-phase generator as shown in Figures 1.19aand b, respectively.
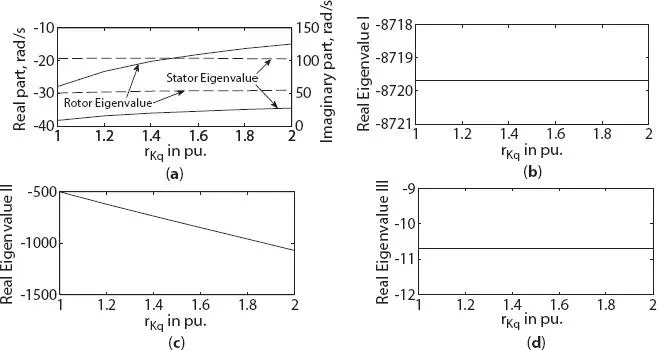
Figure 1.17 Variation in eigenvalue of three-phase synchronous machine with damper resistance change along q -axis (a) stator and rotor eigenvalue, (b) real eigenvalue I, (c) real eigenvalue II, (d) real eigenvalue III.
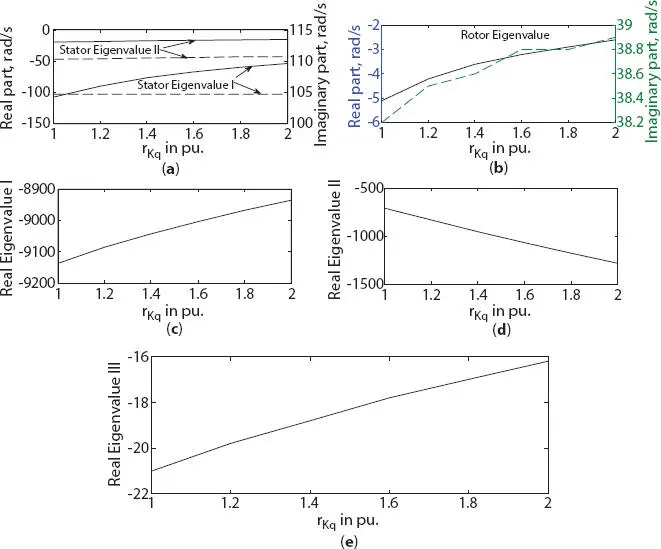
Figure 1.18 Variation in eigenvalue of six-phase synchronous machine with damper resistance change along q -axis (a) stator eigenvalue I and II, (b) rotor eigenvalue, (c) real eigenvalue I, (d) real eigenvalue II, (e) real eigenvalue III.
Читать дальше






















