3 National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (2015). (NG10) Violence and Aggression: Short‐Term Management in Mental Health, Health and Community Settings. London: National Institute for Health and Care Excellence.
4 Nelson‐Jones, R. (2014). Nelson‐Jones' Theory and Practice of Counselling and Psychotherapy, 6e. London: Sage Publications.
5 Nursing & Midwifery Council (2018). Professional Standards and Practice of Behaviour for Nurse, Midwives and Nursing Associates. London: Nursing & Midwifery Council.
6 Sookoo, S. (2018). Identifying and managing risk of aggression and violence. In: The Art and Science of Mental Health Nursing: Principles and Practice, 4te (eds. I. Norman and I. Ryrie), 222–238. London: Open University Press.
1 1It may be that you feel it is outside of your skillset to reach a resolution. In this instance you may want to hand over care to a more experienced colleague. You may also find yourself in a situation where you feel risk is imminent. In this instance, extract yourself and call for help. This may involve using a silent panic button.
6 Communication – difficult conversations
Background
Working effectively in healthcare requires handling a wide range of conversations daily. Most people accessing the health services are experiencing stress and anxiety that come from uncertainty and loss. It is not always clear what will become a difficult conversation and, conversely, what will turn out to be easier to talk about than we would have expected.
Fear of the unknown regarding how a conversation might go is often the key factor that results in healthcare professionals avoiding initiating conversations they feel might be difficult. Preparing yourself and attentively listening can help you to approach and navigate these conversations.
Professional Approach: Preparing Your Self
Preparing for having these conversations is of fundamental importance. Ensure you are prepared for them to happen as a normal part of daily practice, observe others, and, as with any difficult skills, take the opportunity to practise whenever you can.
Engaging in healthcare communication is hard emotional work. Recognising this and understanding the need to develop ways of managing the emotion this causes are important. Suggestions include self‐care, developing relational skills, maintaining an empathic presence, taking a team approach, and retaining a professional identity (Luff et al. 2016).
Influencing Factors: What Conversations Might Be Considered Difficult?
Cancelled treatments.
Communicating with relatives.
Complex health promotion discussions.
Conversations around costs.
Life‐changing diagnosis.
Lost belongings.
Managing cultural differences.
Unexpected deterioration.
End‐of‐life conversations.
Influencing Factors: Requisite Qualities and Skills
1 The ability to listen.
2 A compassionate approach.
3 The courage to start or engage with conversation that maybe difficult.
4 The skills to manage a conversation that may involve a range of emotions.
5 An ability to be comfortable with silence.
Procedure: Breaking Bad News

In healthcare education we often talk about the need for “breaking bad news training”. It is important to be cautious with regard to making assumptions about what is bad news for another person. Sometimes a diagnosis can be a relief after months of uncertainty and symptoms. Sometimes the person has known for a while and it is a relief to be able to talk about it with someone else. Approaching these conversations can still create anxiety, however, hence the term “difficult conversations”.
Hence a valuable rule is: Before you tell, ask (Bryan 2007).
All conversations we have in healthcare are about communicating between two or more people, one of them being you. Thinking carefully about who those people are and what their experiences have been on that day before you have that conversation is an important starting point. Clayton et al. (2007) offer this useful model as we learn how to approach situations that we feel may be difficult.
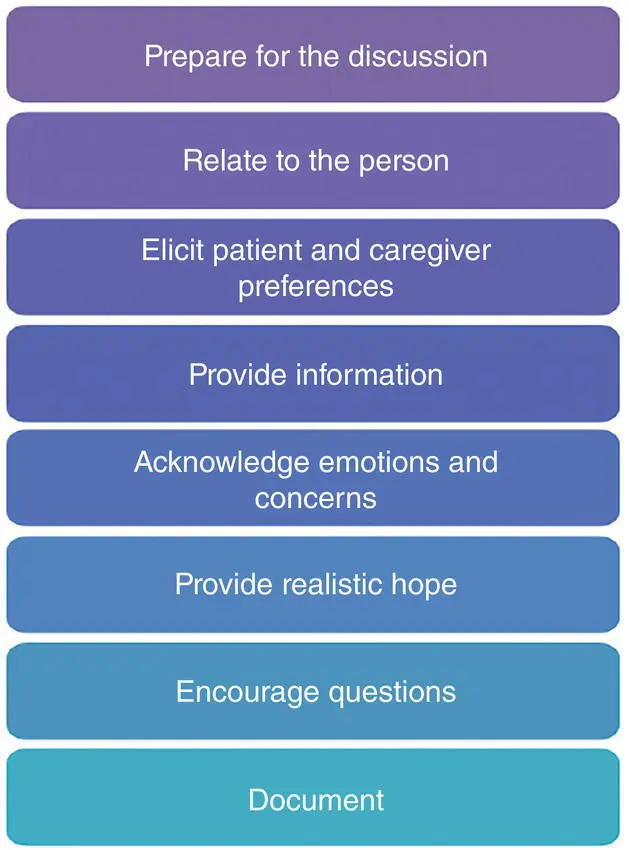
Procedure: Balancing Hope and Realism
Discussing difficult things can and will cause an emotional response to all who are involved. Emotional release can be cathartic; it is okay if someone cries. Learn to use tissues and empathetic silence.
People need time to process emotions. If you can give them time, they can develop new hope by refocusing on what is important to them. This happens better in an environment where people feel they can trust their healthcare professionals to take an individual‐centred approach to communication (Campbell et al. 2010).
1 Bryan, L. (2007). Should ward nurses hide death from other patients. End of Life Care 1 (1): 79–86.
2 Campbell, T.C., Carey, E.C., Jackson, V.A. et al. (2010). Discussing prognosis: balancing hope and realism. The Cancer Journal 16 (5): 461–466.
3 Clayton, J.M., Hancock, K.M., Butow, P.N. et al. (2007). Clinical practice guidelines for communicating prognosis and end‐of‐life issues with adults in the advanced stages of a life‐limiting illness, and their caregivers. The Medical Journal of Australia 186 (12): S77–S108.
4 Luff, D., Martin, E.B. Jr., Mills, K. et al. (2016). Clinicians' strategies for managing their emotions during difficult healthcare conversations. Patient Education and Counseling 99 (9): 1461–1466.
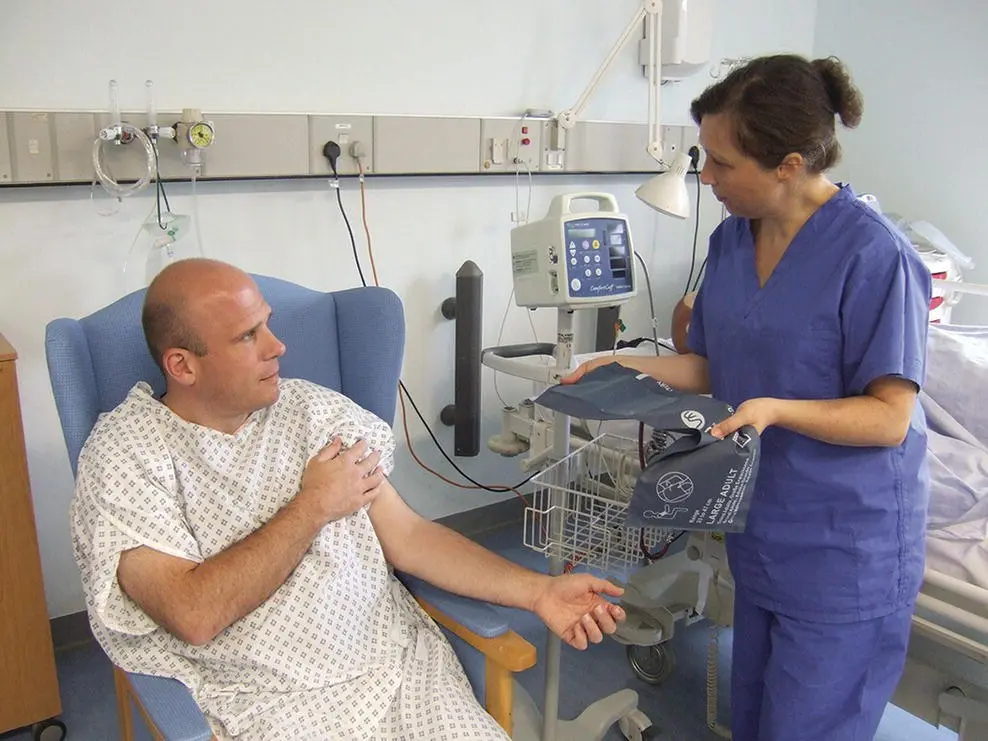
Figure 7.1 Implied consent.

Figure 7.2 Translation material.
Figure 7.3 Materials in Braille.

Figure 7.4 Written consent with signature.
Part 4of the Nursing & Midwifery Council (NMC) code highlights the need for informed consent to be obtained – 4.1 specifically states that we must “act in the best interests of all people at all times”, recognising “that we need to respect a person's right to accept or refuse treatment” (NMC 2018, p. 7).
For a person's rights to be respected we must ensure that they have all key information in order to be able to make an informed decision about accepting or refusing treatment.
This informed consent can then be given in written or oral form, but it can also be implied, such as when providing the arm for blood pressure measurement ( Figure 7.1).
Читать дальше