Glen E. Clarke - CompTIA Pentest+ Certification For Dummies
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Glen E. Clarke - CompTIA Pentest+ Certification For Dummies» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:CompTIA Pentest+ Certification For Dummies
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:5 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 100
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
CompTIA Pentest+ Certification For Dummies: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «CompTIA Pentest+ Certification For Dummies»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
CompTIA PenTest+ Certification For Dummies, 2nd Edition
CompTIA PenTest+ Certification For Dummies, 2nd Edition
CompTIA Pentest+ Certification For Dummies — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «CompTIA Pentest+ Certification For Dummies», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
Information gathering
The information gathering part of the penetration test is a time-consuming part of the penetration test. It involves both passive and active information gathering.
With passive information gathering , you use public Internet resources to collect information about the target such as public IP addresses used, names and email addresses of persons that could be targets to a social engineer attack, DNS records, and information about products being used. This is called passive information gathering because you are not actually communicating with the company’s live systems (unless you surf its website); instead, you are collecting public information that anyone can access and it will not look suspicious. Note that passive information gathering is also known as passive reconnaissance .
Active information gathering involves using tools to communicate with the company’s network and systems to discover information about its systems. For example, doing a port scan to find out what ports are open on the company’s systems is considered active because in order to know what ports are open on each system, you have to communicate with those systems. Once you start communicating with the company’s network, you risk detection, which is why these techniques are categorized differently than passive information gathering techniques. Note that active information gathering is also known as active reconnaissance .
Vulnerability identification
Once the information gathering subphase is complete, you should now have a listing of the ports open on the system and potentially a list of the software being used to open those ports. In the vulnerability identification subphase, you research the vulnerabilities that exist with each piece of software being used by the target. Vulnerability identification also involves using a vulnerability scanner to automate the discovery of vulnerabilities that exist on the target networks and systems.
Chapters 3and 4cover information gathering and vulnerability identification.
Attacks and exploits
The third phase of the penetration testing process is to perform the attacks and exploit systems. In this phase, with knowledge of the vulnerabilities that exist on the targets, you can then break out the penetration tools to attack and exploit the systems. This involves social engineering attacks, network attacks, software attacks such as SQL injection, and wireless attacks against wireless networks.
Once a system is compromised, you can then perform post-exploitation tasks, which involve collecting more information about the system or planting a backdoor to ensure you can gain access at a later time.
Chapters 5through 10cover attacks and exploits.
Reporting and communication
The fourth and final phase of the penetration testing process is reporting and communication. These tasks are the reason the penetration test was performed in the first place: to report on the findings and specify remediation steps the customer can take to reduce or eliminate the threats discovered.
During this phase, you will write a report of the actions you performed during the penetration test and the results of the testing. You will also include recommendations on how to better secure the systems in the report. The report will be delivered to the customer in the sign-off meeting, and the customer will sign-off on the completion of the penetration test.
Chapter 11covers reporting and communication.
 Knowing the phases to the CompTIA penetration testing process is critical on the job and for the exam. Refer to Figure 1-2 for a summary of what occurs at each phase.
Knowing the phases to the CompTIA penetration testing process is critical on the job and for the exam. Refer to Figure 1-2 for a summary of what occurs at each phase.
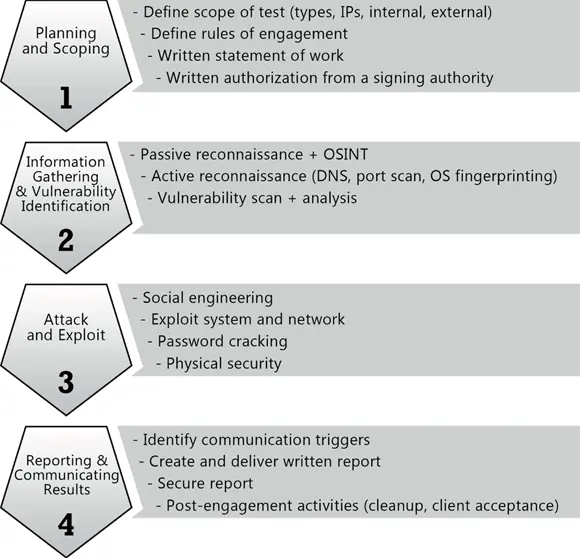
Graphic designed and created by Brendon Clarke.
FIGURE 1-2:The CompTIA penetration testing process.
Identifying Testing Standards and Methodologies
Over the years a number of security assessment and penetration testing methodologies have been developed. In this section, you learn about some of the common security assessment methodologies. Keep in mind that you should be familiar with these for the exam, but you do not need to know the detailed steps performed by each methodology.
MITRE ATT&CK
MITRE ATT&CK is a recognized knowledge base of tactics and techniques used by attackers to compromise systems. The goal of MITRE ATT&CK is to use the information collected and presented in the standard as a basis for threat modeling and analysis. At the MITRE ATT&CK website you can choose a threat and read the details about the threat, including how the threat can be detected and mitigated.
To learn more about MITRE ATT&CK, visit https://attack.mitre.org .
Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP)
The OWASP Foundation is a nonprofit foundation focused on improving the security of software. OWASP released the very popular OWASP Top 10 document that lists the ten most common security flaws in web applications that may put your organization at risk. The OWASP Foundation has other projects as well, including its OWASP Mobile Security Testing Guide. Following are the URLs for each of these projects:
OWASP Top 10: https://owasp.org/www-project-top-ten
OWASP Mobile Security Testing Guide: https://owasp.org/projects,/mstg/2021/07/29/MSTG-Release.html
OWASP Top 10 (2017)
Following is a summary of the 2017 version of the OWASP Top 10 Web Application Security Risks that you should be familiar with for the PenTest+ exam:
A1:2017-Injection: The number one flaw found in web applications is injection flaws. Injection flaws occur when data is input into an application but the input is not sanitized or validated by the developer of the application.
A2:2017-Broken Authentication: The second most common flaw in web application is flaws in authentication or session management. This may allow attackers to access passwords, keys, or session tokens.
A3:2017-Sensitive Data Exposure: The third most common flaw in web applications is sensitive data exposure flaws that involve web applications or APIs not protecting sensitive data within the application. This could be financial data, healthcare data, or Personally Identifiable Information (PII) data. This could be due to a lack of encryption at rest and in transit, or other missing access control methods.
A4:2017-XML External Entities (XXE): Poorly configured XML processors can use external entities to disclose internal files or internal file shares, and possibly perform remote code execution or denial of service (DoS) attacks.
A5:2017-Broken Access Control: Many web applications do not enforce restrictions on what an authenticated user can do within the application. An attacker that exploits this flaw can gain access to sensitive information or perform undesired actions.
A6:2017-Security Misconfiguration: Applications should have their default settings altered and security configuration settings reviewed as security misconfigurations is a common flaw in web applications.
A7:2017-Cross-Site Scripting (XSS): XSS flaws occur when an application processes and displays untrusted data in a web application without validating the information. XSS flaws enable attackers to execute malicious code in a victim’s browser and possibly hijack the session.
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «CompTIA Pentest+ Certification For Dummies»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «CompTIA Pentest+ Certification For Dummies» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «CompTIA Pentest+ Certification For Dummies» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.












