Anthony R. West - Solid State Chemistry and its Applications
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Anthony R. West - Solid State Chemistry and its Applications» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Solid State Chemistry and its Applications
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:4 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
Solid State Chemistry and its Applications: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Solid State Chemistry and its Applications»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
A comprehensive treatment of solid state chemistry complete with supplementary material and full colour illustrations from a leading expert in the field. Solid State Chemistry and its Applications, Second Edition
Student Edition
Significant updates and new content in this second edition include:
A more extensive overview of important families of inorganic solids including spinels, perovskites, pyrochlores, garnets, Ruddlesden-Popper phases and many more New methods to synthesise inorganic solids, including sol-gel methods, combustion synthesis, atomic layer deposition, spray pyrolysis and microwave techniques Advances in electron microscopy, X-ray and electron spectroscopies New developments in electrical properties of materials, including high Tc superconductivity, lithium batteries, solid oxide fuel cells and smart windows Recent developments in optical properties, including fibre optics, solar cells and transparent conducting oxides Advances in magnetic properties including magnetoresistance and multiferroic materials Homogeneous and heterogeneous ceramics, characterization using impedance spectroscopy Thermoelectric materials, MXenes, low dimensional structures, memristors and many other functional materials Expanded coverage of glass, including metallic and fluoride glasses, cement and concrete, geopolymers, refractories and structural ceramics Overview of binary oxides of all the elements, their structures, properties and applications Featuring full color illustrations throughout, readers will also benefit from online supplementary materials including access to CrystalMaker® software and over 100 interactive crystal structure models.
Perfect for advanced students seeking a detailed treatment of solid state chemistry, this new edition of
will also earn a place as a desk reference in the libraries of experienced researchers in chemistry, crystallography, physics, and materials science.

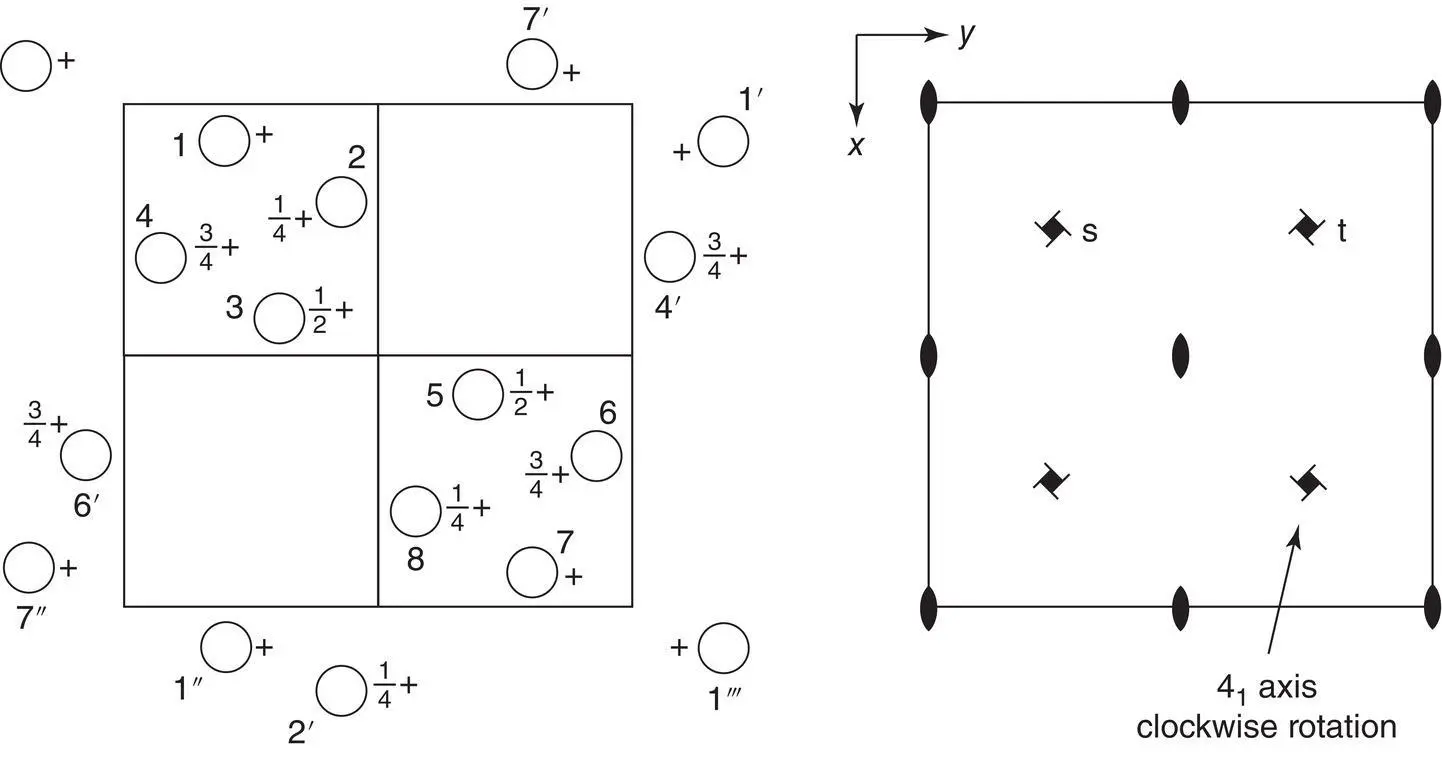
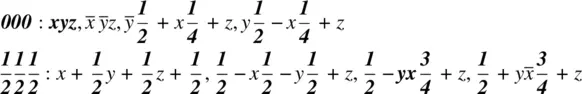
 + z; ½, ½, ½ + z; ½, 0,
+ z; ½, ½, ½ + z; ½, 0,  + z.
+ z.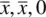 ); (½ + x , ½ – x , ½); (½ – x , ½ + x , ½)
); (½ + x , ½ – x , ½); (½ – x , ½ + x , ½)