In modern theoretical cosmology, distance is absolute and the universe expands. For reasons that are not yet understood, it simultaneously becomes more richly structured. In a cosmology without both time and scale, this would correspond, in a realistic scale-free Platonia, to going from the bland centre to the more interestingly structured ‘instants of time’ situated between it and the frontiers. That is where the mist I introduced in Chapter 3 must collect most thickly – have the highest intensity – at time capsules structured so that they seem to record evolution from the symmetric centre. This would be a cosmology of pure structure, an appealing thought. The scalene and obtuse triangles that inhabit the ‘favoured belt’ in Shape Space remind me of the line in Gerard Manley Hopkins’s poem ‘Pied Beauty’, in which he praises ‘All things counter, original, spare, strange’. In such a scheme, the bland centre and degenerate frontiers still have a vital role to play in the scheme of things. This is because a kind of resonance between all the instants of time determines where the mist settles. Any acoustician will recognize the importance of the walls and centre of a building in determining its harmonies. Platonia, shown here as Shape Space, is a ‘heavenly vault’ in which the music of the spheres is played. However, I should emphasize that the more realistic Shape Spaces corresponding to universes with more than three particles are most definitely ‘open ended’ and should not be thought of as enclosed spaces, as might appear from the simple example of Triangle Shape Space. Platonia is not a claustrophobic vault but an ‘echoing canyon’ open to the sky. What is more, there is a sense in which its echo, heard at any point within it, is what we call the past.
In completing this box, I note it has a nice unplanned symbolism. Box 3 considers Shape Space, which is represented by the perfect (equilateral) triangle, which itself, through each of its points, represents all triangles, all of which are unities in the sense mentioned on p.18. Shape Space illustrates Giordano Bruno’s monas monadum , the unity of the unities.
If Laplace’s divinity contemplates a three-particle universe, its history will be a curve in Triangle Land, which, omitting the triangle size, we can show as a curve in Shape Space. The example of real Newtonian three-body gravitational interaction shown in Figure 9 brings out very clearly the main fact that we associate with time, that its instants come in a unique succession. This translates beautifully into the winding path. (You can see why I am so indebted to Dierck Liebscher, who crafted this diagram.) However, the other two important attributes of time, duration and direction, are not yet reflected in Figure 9. There are no marks along the curve to indicate how much time elapses between any two points on it. It is also impossible to say in which direction along the curve time increases.
What information must we give to determine a history of the kind encoded in the path in Figure 9? According to Laplace, simply the positions and velocities of the bodies at one instant (together with their masses). Poincaré remarked, however, that the positions and motions of the bodies are defined in absolute space, and the speeds of the bodies are defined using absolute time. This is a subtle and important qualification.
If only relative quantities count, then Newton assumed too much structure. In a universe of just three particles, only the three distances between them (the triangle they form) should count. The triangle universe cannot have an overall position and orientation in some invisible containing space. Similarly, since the idea of an external ‘grandstand clock’ is absurd, we cannot say ‘how fast’ the universe travels along the curve in Figure 9. It simply occupies all the points along it.
If Mach is right, so that time is nothing but change and all that really counts in the world is relative distances, there should be a perfect analogue of Laplace’s scenario with a divine intelligence that contemplates Platonia. Machian dynamics in Platonia must be about the determination of paths in that timeless landscape. It should be possible to specify an initial point in Platonia and a direction at that point, and that should be sufficient to determine the entire path. Nothing less can satisfy a rational mind. The history in Figure 10 starts at the centre of Shape Space, so that there the particles form an equilateral triangle, and set off in a certain direction. In Machian dynamics, the initial position and initial direction (strictly in Triangle Land, not Shape Space) should determine the complete curve uniquely. Now we can test this idea in the real world. The heavens provide plenty of triple-star systems, and astronomers have been observing their behaviour for a long time. They certainly meet the Laplace-type condition when described in Newtonian terms. But are their motions comprehensible from a Machian point of view? This is the question Poincaré posed.
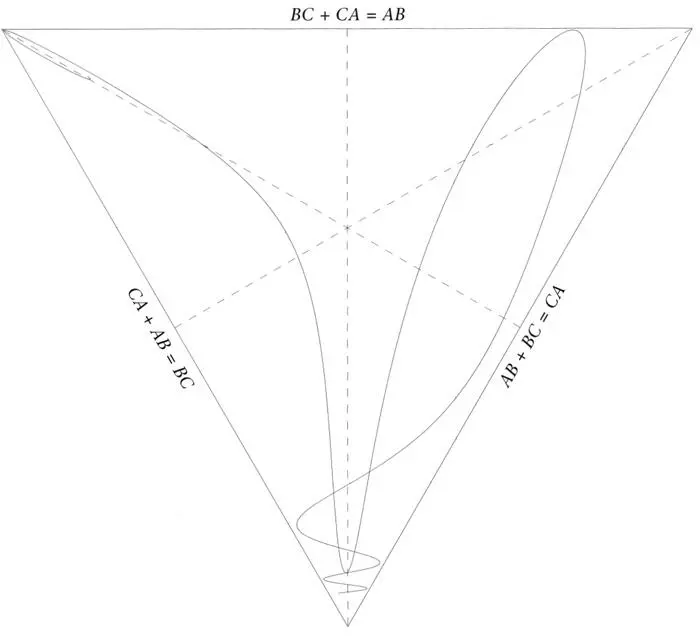
Figure 9.The (computer-generated) path traced in Shape Space by the triangles formed by three mutually gravitating particles. It is important to realize that the winding path shown is not traced by a single particle moving over the page, but that each point on the path represents the shape of a complete triangle. The curve shows the succession of triangle shapes. As explained in the text, it is impossible to say that time increases as you go in a particular direction along this curve. However, suppose we imagine it starts in the top left corner. This corresponds to particles A and C nearly colliding, while particle B is far away. Then they move to a configuration that is quite close to an equilateral triangle, after which A and B get very close together near the bottom of the diagram. Then the triangle shape evolves along the curve up to the top right. Where the curve nearly touches the top line, all three particles are almost on a line, with C between A and B. Finally the curve returns to the bottom of the figure, where the wiggles indicate that particles A and B are orbiting around each other, while C is far away. You see how history is all coded in one curve, but you just cannot tell in which direction it unfolds!
APPARENT FAILURE
The answer is very curious. The motions are nearly but not quite comprehensible. This can be highlighted by showing how different possible Newtonian motions look when represented as curves in Triangle Land, our model Platonia – or rather Shape Space, since this is much easier to represent. To create a vivid picture, let us imagine that we are holding two cardboard triangles that are slightly different. These can represent the relative configurations of three mutually gravitating bodies at two slightly different instants of Newton’s absolute time.
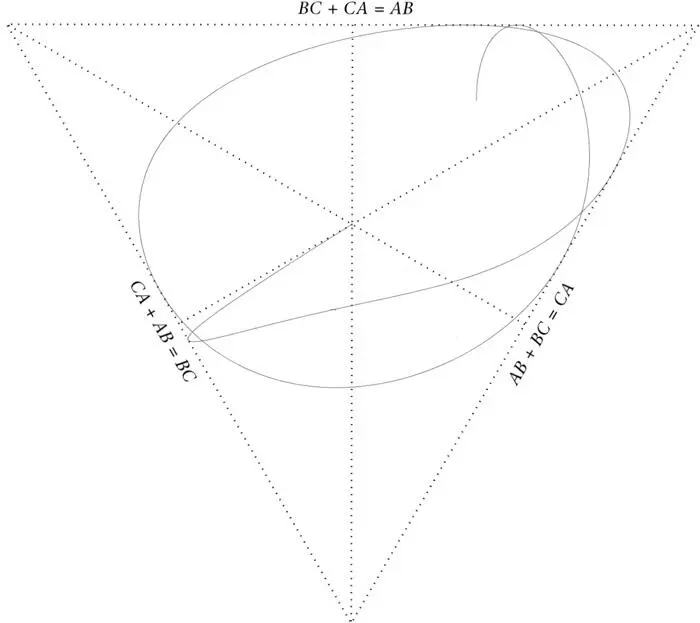
Figure 10.Another possible path traced by the same three particles as in Figure 9 (I refer to them now as bodies). This history starts (or ends if time is assumed to run the other way) at the configuration in which the three bodies form an equilateral triangle. The shape of the triangle changes in a definite way at all points along the curve. If it left the initial equilateral triangle along one of the dotted lines, that would mean two sides of the triangle remaining equal in length while the third changes – the equilateral triangle would become an isosceles triangle. In fact, for the example shown, the ratios of all three sides change. For readers used to thinking of motions in ordinary space, this example corresponds to particles that constantly orbit each other in a fixed plane. The positions at which the curve touches the dotted line that bound Shape Space correspond to eclipses, when one particle is between the other two and on the line joining them. Such a configuration is called a syzygy (that’s a nice word to show off with). In ordinary space, the one particle passes through the line joining the other two and comes out the other side. But the points on the curve in Figures 9 and 10 stand for the complete triangle, not one of the three particles. This is why the curve approaches the syzygy frontier and then returns into the interior of Shape Space. There are no triangles outside the syzygies!
Читать дальше














